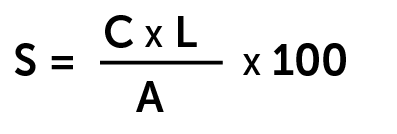Browse
Use Finder
Enter a use to see how it is organized in the Zoning Code.
Article 14. General Rules
Div. 14.1. Introduction
Sec. 14.1.1. Opening Provisions
-
General
-
This Article (General Rules) contains Div. 14.2. (General Standards & Measurements) which includes definitions, measurements, and standards related to rules in this Chapter.
-
This Article (General Rules) also contains Div. 14.3. (Glossary), which contains all defined terms, abbreviations, and symbols used throughout this Zoning Code (Chapter 1A).
-
Where a definition contains a list of examples, the examples listed are provided as illustrative examples to guide users, and not an exhaustive list.
-
The provisions of Chapter I. (General Provisions and Zoning), Sec. 11.01.(b) (Grammatical Interpretation) and Sec. 11.01.(c) (Civil Code Provisions) shall apply to the interpretation of this Article (General Rules).
-
-
Definitions & Standards
Text in italics below a heading provides a definition of that heading. A definition may be supported by development standards and/or measurement instructions specific to that defined heading.
-
Illustrations & Graphics
Illustrations and graphics are included in this Article (General Rules) only to assist users in understanding the intent and requirement of the text. In the event that a conflict occurs between the text of this Article (General Rules) and any illustrations or graphics, the text shall prevail.
Div. 14.2. General Standards & Measurement
The following definitions and standards apply to this Zoning Code (Chapter 1A).
Sec. 14.2.1. Building Footprint
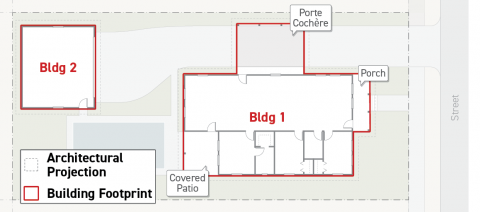
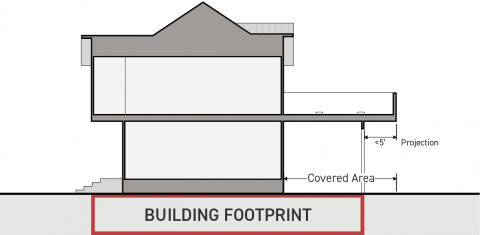
Building footprint is defined as the area of a lot occupied by a building, measured horizontally. Also referred to as "structure footprint".
-
Definitions & Standards
The following definitions and standards apply to building footprints:
-
Building footprint includes those portions of a lot covered by buildings or structures.
-
Building footprint does not include portions of a lot covered by architectural projections (including roof overhangs, and projecting balcony) that meet both of the following criteria:
-
The architectural projection does not include floor area; and
-
The architectural projection projects less than five feet from the nearest wall, column, spanning beam, or other structural element carrying gravity loads to the ground.
-
-
Sec. 14.2.2. Covered Area (%)
Covered area is defined as the measurement of how open an occupiable space is to the sky.
-
Definitions & Standards
The following definitions and standards apply to a covered area:
-
Covered
A space or structure is considered covered if less than 25 percent of its area is open to the sky.
-
Uncovered
A space or structure is considered uncovered if 25 percent of more of its area is open to the sky. Areas containing overhead, non-solid structures, such as lattice and pergolas, may be considered uncovered provided that 25 percent or more of their area is open to the sky.
-
Sheltered
A space or structure is considered sheltered if no portion of its area is open to the sky.
-
-
Measurement
Covered area is a percentage, measured as the cumulative area that is not open to the sky divided by the total area of the subject space or structure.
Sec. 14.2.3. Distance
-
Definitions & Standards
The following definitions and standards apply to distance or walking distance:
-
Distance
Distance is defined as the amount of space between two points.
-
Measurement
-
When distance is specified as being measured horizontally or vertically between two points, a line shall be projected from each of the points along the same plane until the projected lines can be connected by a perpendicular line. The distance between the two points is measured along the perpendicular line.
-
When distance is not specified as being measured horizontally or vertically, it shall be measured in the shortest straight line from one point to another.
-
-
-
Walking Distance
Walking distance is the distance measured as the most direct path of travel for a pedestrian.
-
Measurement
Walking distance is measured horizontally along the most direct route of travel on the ground in the following manner:
-
Starting at the nearest street-facing entrance accessible to the majority of tenants or residents on the subject lot;
-
In a straight line to the nearest public sidewalk, walkway, street, or road;
-
Along a public sidewalk, walkway, street, or road; and
-
In a straight line ending at the nearest pedestrian access point to the destination use.
-
-
-
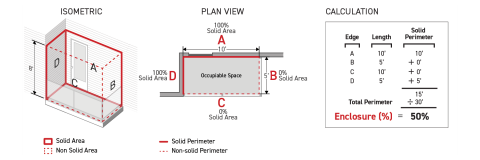
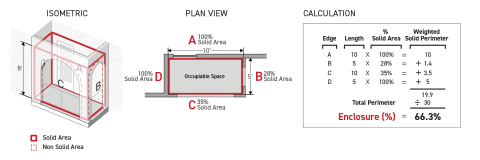
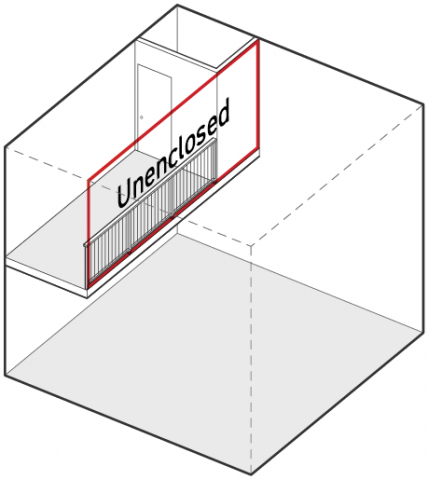
Sec. 14.2.4. Enclosure
Enclosure is defined as the measurement of how closed off an occupiable space is to its surroundings.
-
Definitions & Standards
The following definitions and standards apply to an enclosure:
-
Enclosed
A space is considered to be enclosed when the perimeter of the space has an enclosure of at least 66.7 percent.
-
Unenclosed
A space is considered to be unenclosed when the perimeter of the space has an enclosure of less than 66.7 percent.
-
Perimeter Plane
A perimeter plane is defined as an imaginary vertical plane along the perimeter of a space used to measure the enclosure of a space. A perimeter plane shall be projected for a height of eight feet measured from the floor or ground surface of the space.
-
Solid Area
A solid area is defined as the portions of the perimeter planes that have a permanent structure or component physically obstructing the space from its surroundings. For the purpose of measuring the enclosure of a space, portions of the perimeter plane are considered solid area where a permanent structure or component is located within five feet of the perimeter plane, measured perpendicular to the perimeter plane and away from the subject space.
-
Non-Solid Area
A non-solid area is defined as the portions of the perimeter planes along the perimeter of a space that have no permanent structure or component obstructing the space from its surroundings. For the purpose of measuring the enclosure of a space, portions of the perimeter plane are considered non-solid area where no permanent structure or component is located within five feet of the perimeter plane, measured perpendicular to the perimeter plane and away from the subject space.
-
Solid Perimeter
A solid perimeter is defined as the length of a perimeter of a space that consists of solid area for the entire height of the perimeter plane.
-
Weighted Solid Perimeter
Where perimeter planes consist of a mix of solid area and non-solid area, the weighted solid perimeter for each perimeter plane is the length of the perimeter plane weighted by the percent of the perimeter plane area that is composed of solid area.
-
-
Measurement
Enclosure is measured as a percentage, calculated by dividing the cumulative length of the perimeter of a space that is solid perimeter by the total perimeter of the space.
-
Solid Perimeter Method
For spaces with perimeter planes that do not contain a mixture of solid area and non-solid area for the full height of the perimeter plane, enclosure shall be calculated as the length of the solid portion of the perimeter divided by the total perimeter.
-
Weighted Solid Perimeter Method
For spaces with perimeter planes that contain a mixture of solid area and non-solid area across their height, enclosure shall be calculated as the sum of the weighted solid perimeter of all perimeter planes divided by the total perimeter of the space.
-
-
Exceptions
-
Safety barriers 45 inches in height or less, measured from finished floor elevation, having an opacity of no more than 40 percent do not count toward solid area or solid perimeter.
-
Safety barriers 45 inches in height or less, measured from finished floor elevation, that are transparent with a minimum visual light transmittance of 60 percent and maximum external reflectance of 20 percent do not count toward solid area or solid perimeter.
-
Sec. 14.2.5. Encroachments
-
Horizontal Encroachments
A horizontal encroachment is defined as a structure or assembly that extends horizontally into a space where structures are typically prohibited.
-
Definitions & Standards
The following definitions and standards apply to a horizontal encroachment:
-
Architectural Details
Architectural details are defined as building elements attached to or integrated into the structure of a building, not intended for human occupation. Types of architectural details include, but are not limited to: cornices, belt courses, sills, lintels, pilasters, pediments, or chimneys.
-
Roof Projections
Roof projections are defined as roof elements that overhang or cantilever beyond the building footprint and do not include posts or columns. Types of roof projections include, but are not limited to: eaves, roof overhangs, gutters, awnings, or canopies.
-
Unenclosed Structures: Ground Story
To be eligible as a horizontal encroachment for Unenclosed Structures: Ground Story, an unenclosed structure on the ground story shall have all finished floors and ground surfaces at or below the maximum finished floor elevation of the ground story as specified in the applied Frontage District (Part 3B.) and shall have a total structure height of 15 feet or less, measured from surrounding finished grade. Types of eligible unenclosed structures include, but are not limited to: porches, decks, stoops, landing platforms, gazebos, trellises, arbors, pergolas, basketball hoops, or volleyball nets.
-
Unenclosed Structures: Above Ground Story
To be eligible as a horizontal encroachment for Unenclosed Structures: Above Ground Story, an unenclosed structure above the ground story shall have finished floors or ground surfaces above the maximum finished floor elevation of the ground story as specified in the applied Frontage District (Part 3B.) or shall have a total structure height of 15 feet or greater, measured from surrounding finished grade. Types of eligible unenclosed structures include, but are not limited to: balconies, upper-story light shelves, or exterior stairways.
-
Enclosed Structures: Projecting
To be eligible as a horizontal encroachment for Enclosed Structures: Projecting, a structure shall; project, overhang, or cantilever beyond the building footprint; meet the definition of enclosed; and shall have a cumulative length less than 25 percent of the length of the building. Types of eligible enclosed structures include, but are not limited to: bay windows, oriel windows, sleeping porches, overhanging volumes, or enclosed balconies.
-
Mechanical/Electrical Equipment: Ground Mounted
To be eligible as a horizontal encroachment for Mechanical/Electrical Equipment: Ground Mounted, the weight of the mechanical equipment or electrical equipment including the equipment's related wires, conduits, and pipes shall be primarily supported by the ground. Examples of eligible equipment include, but are not limited to: gas meter, water softener, pool equipment, HVAC equipment, gas tank, cistern, wind turbine, or solar panel.
-
Mechanical/Electrical Equipment: Wall Mounted
To be eligible as a horizontal encroachment for Mechanical/Electrical Equipment: Wall Mounted, the mechanical equipment or electrical equipment including the equipment's related wires, conduits, and pipes shall be attached to and primarily supported by a wall. Examples of eligible equipment include, but are not limited to: gas meter, electric meter, electrical panel, water heater, HVAC equipment, or gas tank.
-
Waste Enclosure
Waste enclosure is defined as waste areas and their required screening structures. Examples of waste enclosures include, but are not limited to enclosures for: trash compactors, garbage, recycling, or food waste.
-
Utility Equipment
Utility equipment is defined as equipment related to publicly-operated or utility-operated systems, including their related wires, conduits and pipes. Examples of utility equipment include, but are not limited to: hydrants, transformers, utility cabinets, water utility devices, cable television boxes, Internet boxes, or phone boxes.
-
Underground Structures
Underground structures are defined as covered structures located entirely below finished grade. Examples of underground structures include, but are not limited to: cellars, basements, underground parking structures, stormwater storages, or cisterns.
-
Flatwork
Flatwork is defined as constructed objects 30 inches in height or less, measured from finished grade. Examples of flatwork may include, but are not limited to: pavement, sidewalk, multi-use path, patio, a low deck, or stairs or ramps 30 inches in height or less.
-
Fences, Walls, Hedges, & Screening
Fences, walls, or hedges used for the purposes of screening or any required screening may encroach into any required setback up to the lot line, provided that fences and walls in any frontage yard are allowed by the frontage yard fence & wall standards specified in the applied Frontage District (Part 3B.).
-
Vegetation
To be eligible as a horizontal encroachment for Vegetation, the vegetation shall meet the definition of vegetation. Vegetation horizontal encroachments also include planters that meet the requirements of Sec. 4C.6.4.C.2. (Planting Areas).
-
Outdoor Furniture
Outdoor furniture is defined as permanent or movable furniture not located within an enclosed space. Examples of outdoor furniture may include, but are not limited to: benches, tables, or bike or scooter parking racks.
-
Outdoor furniture may encroach into any required setback up to the lot line.
-
-
Signs
For standards on horizontal encroachment of signs see Sec. 4C.11. (Signs).
-
-
Measurement
-
Encroachment
Horizontal encroachment is measured as the horizontal distance from the edge of the area where structures are restricted.
-
Distance from Lot Line
For purposes of measuring horizontal encroachment distance from lot line is measured as the horizontal distance from a lot line and toward the interior of the lot along the full perimeter of the lot line.
-
-
-
Vertical Encroachments
A vertical encroachment is defined as a structure or assembly that extends vertically into a space where structures are typically prohibited.
-
Definitions & Standards
The following definitions and standards apply to vertical encroachments:
-
General
No vertical encroachments that contribute to floor area are allowed.
-
Mechanical/Electrical Equipment: Roof Mounted
To be eligible as a vertical encroachment for Mechanical/Electrical Equipment: Roof Mounted, mechanical equipment or electrical equipment including the equipment's related wires, conduits, pipes and visual screens shall be supported by a roof. Eligible equipment also include the required screening pursuant to Sec. 4C.12.1. (Roof-Mounted Equipment). Examples of eligible equipment include, but are not limited to: HVAC equipment, cisterns, water tanks, wind turbines, solar panels, solar water heaters, exhaust ducts, smokestacks, wireless masts, communication equipment, satellite dishes, ventilation fans, chimney, flues, vent stacks, or generators.
-
Architectural Elements
Architectural elements are defined as building elements attached to or integrated onto the roof of a building, not intended for human occupation. Examples of architectural elements may include, but are not limited to: skylights, steeples, spires, belfries, cupolas, domes, flagpoles, or lighting.
-
Vertical Circulation
Vertical circulation is defined as enclosed and covered structures used for building circulation and rooftop access. Examples of vertical circulation may include, but are not limited to: elevator rooms and associated equipment, and stair accesses to a roof.
-
Safety Barriers
Safety barriers are defined as vertical barriers that are 45 inches in height or less and required for safety and protection by Chapter IX. (Building Regulations) of this Code to protect occupants from falling from walking surfaces. Examples of safety barriers may include, but are not limited to: parapets, railings, or banisters.
-
Unenclosed Structures
To be eligible as a vertical encroachment for Unenclosed Structures, structures shall meet the definition of unenclosed, be attached to or integrated onto the roof of a building, and be intended for human shelter or activity. Examples of eligible unenclosed structures may include, but are not limited to: shade structures, cabanas, pergolas, rooftop bars, outdoor dining, permanent seating, beehives, sports courts, or cooking facilities.
-
Flatwork
Flatwork is defined as constructed objects 30 inches in height or less. Examples of flatwork may include, but are not limited to: decking, walkways, patios, or planters.
-
Vegetation
To be eligible as a vertical encroachment for Vegetation, the vegetation shall meet the definition of vegetation. Vegetation vertical encroachments also include planters that meet the requirements of Sec. 4C.6.4.C.2. (Planting Areas).
-
Signs
For standards on vertical encroachment of signs see Sec. 4C.11. (Signs).
-
-
Measurement
-
Encroachment
-
Height in Feet
For any Form District (Part 2B.) with a maximum height in feet standard, vertical encroachment is measured as the vertical distance from the maximum allowed height in feet to the topmost point of the encroaching object.
-
Height in Stories Only
For Form Districts (Part 2B.) where height is regulated only in stories, vertical encroachment is measured as the vertical distance from the top of the roof structure to the topmost point of the encroaching object.
-
-
Setback from Roof Edge
For the purposes of measuring vertical encroachment, setback from roof edge is measured as the horizontal distance from the outermost edge of the roof structure and inward along the full perimeter of the roof structure.
-
-
Sec. 14.2.6. Facing
Facing is defined as the exterior portions of a structure that are exposed to a specified object or site element.
-
Standards
-
Measurement
For the purposes of measuring facing the following standards apply:
-
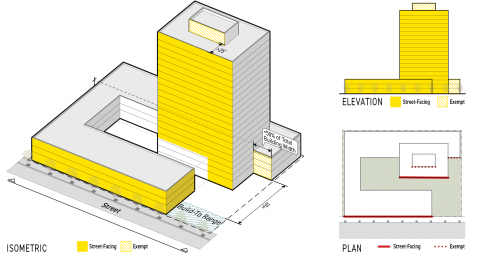
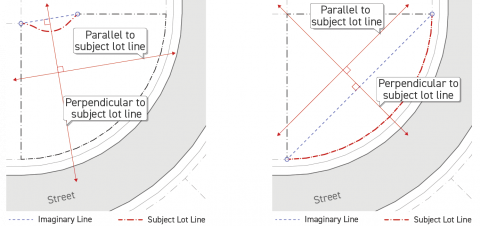
Where the exterior portions of a structure are specified as exposed to a linear (or one dimensional) site element, those exterior portions are considered to be facing where they are visible from a building elevation projected parallel to the specified object or site element, such as a lot line. For example see Subsection B. (Lot Line-Facing Facade) below. To determine facing for building elevations projected along curved or complex lot lines or other linear site elements, see Sec. 14.2.14. (Irregular Lot lines).
-
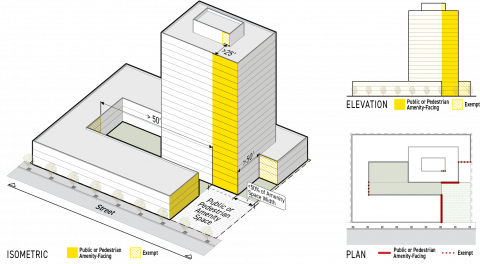
Where the exterior portions of a structure are specified as exposed to an area or an object/site element (such as a building or structure) all portions of a subject structure visible from any of the four building elevations projected parallel to each side of and oriented away from the smallest rectangle that circumscribes the footprint of the object or site element, are considered to be facing the specified object or site element. Building elevations projected that include no visible portions of the structure do not need to be included. See Subsection C. (Pedestrian Amenity & Public Amenity-Facing Facade) below, for an example.
-
-
Exceptions
Portions of a structure that would otherwise be considered to be facing a specified object or site element which are located more than 50 feet from the specified object or site element, are not included, provided they are less than 50 percent of the total width of the specified object or site element measured parallel to the building elevations required in Subsection A. (Standards) above.
-
-
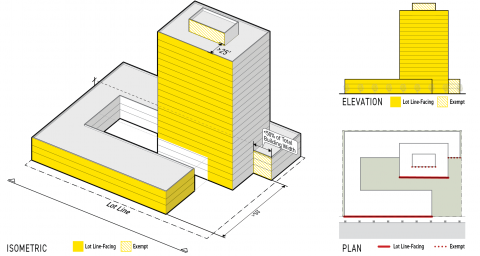
Lot Line-Facing Facade
The portions of any frontage applicable facade pursuant to Sec. 3A.2.2.B.3. (Frontage Applicable Facades) having no permanent structure (not including fences or walls) located between the building facade and a common lot line.
-
Measurement
-
All facades visible from a building elevation projected parallel to the lot line are considered lot line-facing. Fences and walls shall not be considered as affecting visibility.
-
To measure lot line-facing facade for building elevations along curved or complex lot lines, see Sec. 14.2.14. (Irregular Lot lines).
-
-
Exceptions
-
Portions of a facade that would otherwise be considered to be lot line-facing that meet the following conditions are exempt from any requirements of lot line-facing facades:
-
Portions of a frontage applicable facade, pursuant to Sec. 3A.2.2.B.2. Frontage Applicable Portions of a Lot, having an allowable fence or wall, per the applied Frontage District (Part 3B.), located between the building facade and a street lot line or special lot line are still considered lot line-facing facades. Fences and walls shall not be considered as affecting visibility for purposes of determining if a facade is lot line-facing.
-
-
-
Pedestrian Amenity & Public Amenity-Facing Facade
The portions of any frontage applicable facade pursuant to Sec. 3A.2.2.B.3. (Frontage Applicable Facade) having no permanent structure (not including fences or walls) located between the building facade and a pedestrian amenity space or public amenity space.
-
Measurement
-
All portions of a facade visible from the required building elevations below are considered pedestrian amenity facing or public amenity facing. Fences and walls shall not be considered as affecting visibility.
-
A building elevation from the pedestrian amenity space or public amenity space projected parallel to the frontage lot line; and
-
A building elevation from the pedestrian amenity space or public amenity space projected perpendicular to the frontage lot line.
-
-
For purposes of measuring pedestrian amenity & public amenity-facing facade for building elevations along curved or complex frontage lot lines, see Sec. 14.2.14. (Irregular Lot lines).
-
-
Exceptions
Portions of a facade that would otherwise be considered to be pedestrian amenity-facing facade or public amenity-facing facade that meet the following conditions are exempt from any requirements of pedestrian amenity & public amenity-facing facades:
-
Facades set back 50 feet greater than the facade nearest to the lot line, provided they are less than 50 percent of the total width of the pedestrian amenity space or public amenity space.
-
Facades that are located entirely above the sixth story and are stepped-back more than 25 feet from the exterior perimeter of the story below.
-
-
-
Street-Facing Facade
Street-facing facade is defined as the portions of any frontage applicable facade, pursuant to Sec. 3A.2.2.B.3. (Frontage Applicable Facades), having no permanent structure (not including fences or walls) located between the building facade and a street lot line or special lot line.
-
Measurement
-
All facades visible from a building elevation projected parallel to the street lot line or special lot line are considered street-facing. Fences and walls shall not be considered as affecting visibility.
-
For purposes of measuring street-facing facade, for building elevations along curved or complex frontage lot lines, see Sec. 14.2.14. (Irregular Lot lines).
-
-
Exceptions
Portions of a facade that would otherwise be considered to be street-facing that meet the following conditions are exempt from any requirements of street-facing facades:
-
Facades more than 50 feet from the build-to zone, provided they are less than 50 percent of the total building width.
-
Facades that are located entirely above the sixth story and are stepped-back more than 25 feet from the exterior perimeter of the story below.
-
-
Sec. 14.2.7. Floor Area
Floor area is defined as the cumulative amount of interior floor space on a lot, within a room, or within a covered and enclosed space.
-
Measurement
-
General
-
Floor area is calculated as the sum of all interior floor space for each story of a building.
-
The following areas are included in the calculation of floor area:
-
All areas within the exterior walls of a building; or
-
All areas within the exterior walls of any structure that is both enclosed and covered.
-
-
Exceptions
The following areas and structures shall not be considered in determining floor area:
-
Bicycle parking areas;
-
All interior floor space dedicated to automobile parking, except as specified in Paragraph 2. (House Form Districts) below and Paragraph 3. (Development Standards District 5) below;
-
Spaces with ceiling heights less than seven feet measured from finished floor, including floored attic space;
-
Basements including underground parking and cellars, with the exception of storage, indoor: self-service use areas;
-
Stairways and elevator shafts;
-
Areas dedicated to housing mechanical equipment or machinery utilized for the operation of on-site buildings, provided that the equipment does not serve any off-site buildings;
-
Waste enclosures dedicated to waste receptacles that are integral or incidental to the operation of on-site buildings, provided that the waste receptacles do not serve any off-site buildings; and
-
Outdoor dining areas that have not been subject of a wage claim under Chapter XVIII. (Employee Wages and Protections), Article 8. (Los Angeles Office of Wage Standards Ordinance) of this Code.
-
-
House Form Districts
In a lot with an applied House Form District (Div. 2B.3.), the following rules apply:
-
Any floor or portion of a floor with a ceiling height greater than 14 feet counts as twice the square footage of that area.
-
Up to 400 square feet of a detached garage is exempt from the calculation of floor area, provided the structure is:
-
Separated from the primary structure a minimum of 10 feet; and
-
Located a minimum of 40 feet from a primary street lot line.
-
-
Up to 200 square feet of an attached garage is exempt from the calculation of floor area.
-
No more than 400 square feet of garage floor area per lot shall be exempt.
-
Detached accessory buildings that do not exceed 18 feet in height and 200 square feet in floor area are exempt from the calculation of floor area, provided that the total combined area exempted of all the detached accessory buildings on a lot does not exceed 400 square feet in floor area.
-
-
Development Standards District 5
In a lot with an applied Development Standards District 5 (Div. 4B.5.), the following rules apply:
-
All covered, above-grade parking areas located on a lot zoned with Development Standards District 5 (Div. 4B.5.) are included in the calculation of floor area.
-
Active spaces with a minimum depth of 30 feet measured from the street-facing facade and located on the ground story are exempt from the calculation of floor area.
-
-
Sec. 14.2.8. Frequency
Frequency is defined as the rate at which something occurs or is repeated over a given distance
-
Measurement
-
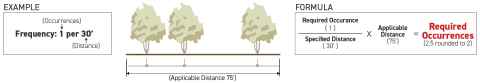
Spacing frequency is a ratio measured as the number of required occurrences of an object over a specified distance (displayed as occurrences: distance or occurrences per distance).
-
To calculate the number of required objects over a provided distance, divide the required occurrence of an object by the specified distance in the frequency ratio, then multiply this quotient by the applicable distance.
-
When calculating the number of required objects results in the requirement of a fractional occurrence, any fraction greater than 0.5 shall be rounded up to the nearest whole occurrence and any fraction of 0.5 or less may be may be rounded down to the nearest whole occurrence so long as at least one occurrence is provided.
-
Frequency standards do not preclude irregular spacing.
-
Sec. 14.2.9. Grade Plane Elevation
Grade plane elevation is defined as a reference plane, representing the average elevation of the existing ground level adjoining a building and its exterior walls, from which the height of a building or structure shall be measured.
-
General
-
Average Grade Elevation
For all buildings and structures that have no applicable building perimeter pursuant to Subsection B. (Applicable Building Perimeter) below, the grade plane elevation shall be established in accordance with Subsection E. (Average Grade Method) below.
-
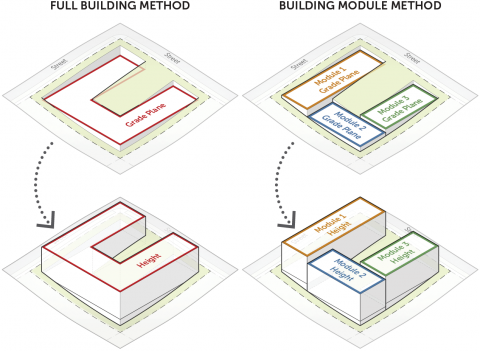
Full Building Method & Building Module Method
The grade plane elevation may be established for either an entire building in accordance with Subsection C. (Full Building Method) below or separately for different building modules in accordance with Subsection D. (Building Module Method) below.
-
-
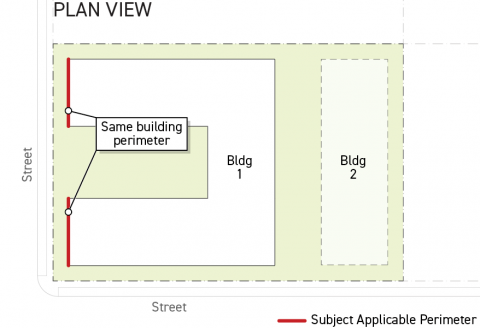
Applicable Building Perimeter
-
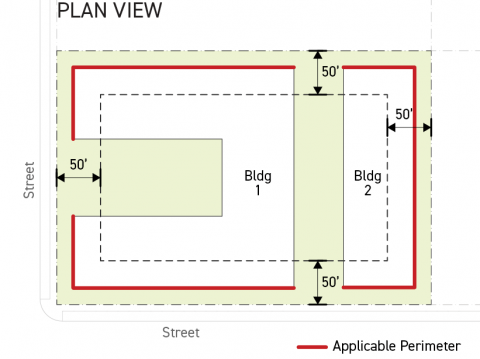
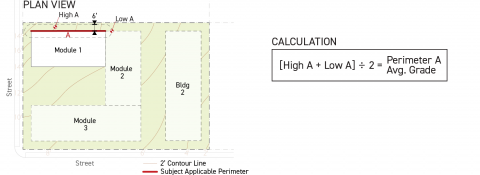
Only building perimeters located within 50 feet of the lot line that the building perimeter faces are considered applicable perimeters when calculating grade plane elevation using the Subsection C. (Full Building Method) below or Subsection D. (Building Module Method) below.
-
Applicable building perimeters associated with the same building and facing the same lot line are considered a singular or part of the same building perimeter even where they are not contiguous.
-
Where a building has no lot line-facing perimeter within 50 feet of a lot line, the grade plane elevation shall be established according to Subsection E. (Average Grade Method) below.
-
-
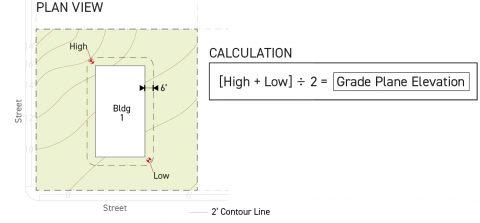
Full Building Method
-
When using the full building method, the entirety of each building perimeter shall be governed by a uniform weighted average elevation reference.
-
Where there are multiple buildings, each building shall independently establish its own weighted average elevation.
-
Establishing the weighted average elevation using the full building method is determined by following the steps below:
-
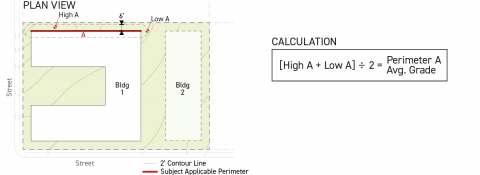
Step 1
For each applicable building perimeter pursuant to Sec. 14.2.9.B. (Applicable Building Perimeter), calculate the building perimeter average grade by averaging the highest and lowest elevation of on-site existing grade located within six feet of the subject applicable building perimeter.
-
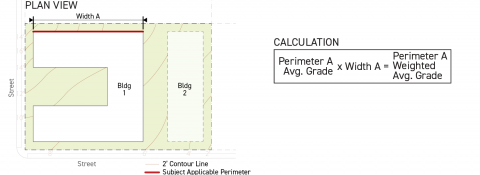
Step 2
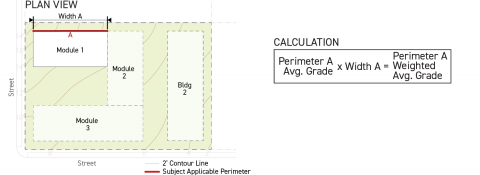
For each applicable building perimeter pursuant to Sec. 14.2.9.B. (Applicable Building Perimeter), calculate the weighted building perimeter average existing grade by multiplying the building perimeter average existing grade by the width of the applicable building perimeter, measured parallel to the lot line that it faces.
-
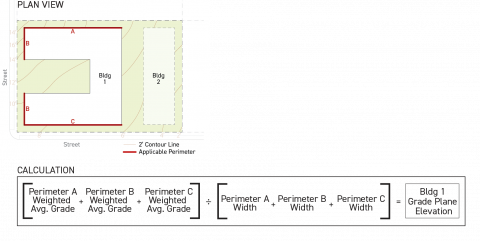
Step 3
Sum the weighted building perimeter average existing grade (for all applicable building perimeters) and divide the sum by the cumulative total length of all applicable building perimeters associated with the building.
-
-
-
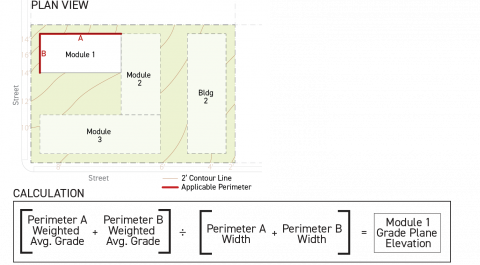
Building Module Method
-
When using the building module method, a building footprint may be broken up into multiple modules, each possessing its independently established weighted average elevation.
-
Building modules shall be delineated according to the following steps:
-
All portions of a building footprint shall be designated to a building module.
-
Each building module shall not encompass any area external to the building footprint.
-
Each building module shall have an individual building footprint and shall not overlap with another building module's building footprint.
-
All components of a building module area shall be contiguous.
-
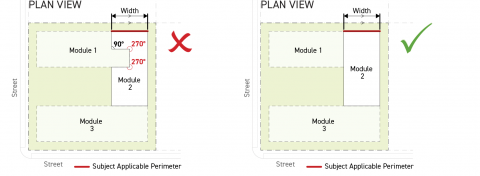
All building modules shall have at least one building perimeter qualifying as an applicable building perimeter pursuant to Subsection B. (Applicable Building Perimeter) above.
-
Building module perimeters internal to a structure shall not include any interior angles greater than 180 degrees.
-
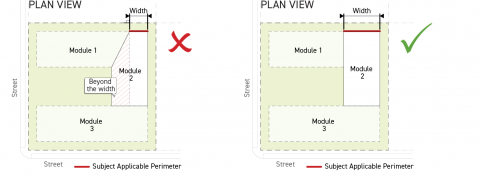
Building modules shall not include a building footprint that extends beyond the width of its applicable building perimeter, measured parallel to the lot line that the applicable building perimeter faces.
-
-
Using the building module method, grade plane elevation shall be established independently for each building module following the steps below:
-
Step 1
For each applicable building perimeter pursuant to Subsection B. (Applicable Building Perimeter) above, calculate the building perimeter average grade by averaging the highest and lowest elevations within six feet of the applicable building perimeter of the existing grade.
-
Step 2
For each applicable building perimeter pursuant to Subsection B. (Applicable Building Perimeter) above, calculate the weighted building perimeter average grade by multiplying the building perimeter average grade by the width of the applicable building perimeter, measured parallel to the lot line that it faces.
-
Step 3
Sum the weighted building perimeter average grade from all applicable building perimeters associated with the building module and divide this sum by the total cumulative length of all applicable perimeters associated with the building module.
-
-
-
Average Grade Method
When using the average grade method the grade plane elevation shall be established by averaging the building footprint elevation measured from the lowest and highest elevation points of the existing grade, within six feet of the exterior wall or lot line, whichever is less.
Sec. 14.2.10. Story
Story is defined as the portion of a building or structure included between the upper surface of a floor and the upper surface of the floor next above, except that the topmost story is that portion of a building or structure included between the upper surface of a floor and the upper surface of the ceiling structure above.
-
Ground Story
The story of a building that meets the criteria of either of the Paragraph 1. (Continuous Ground Story (Typical) or Paragraph 2. (Ground Story Modules) below:
-
Continuous Ground Story (Typical)
-
A ground story shall be designated for all portions of a building footprint.
-
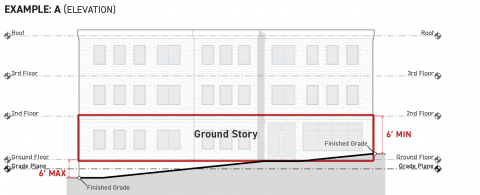
The ground story is the lowest story of a building or structure meeting the following standards:
-
The ground story facade shall be exposed a minimum of six feet above finished grade along the full width of each frontage applicable facades pursuant to Sec. 3A.2.2.B.3. (Frontage Applicable Facades).
-
The ground story structural floor shall be no more than six feet above finished grade for at least 75 percent of its applicable building perimeter pursuant to Sec. 14.2.9.B. (Applicable Building Perimeter), measured cumulatively.
-
The ground story shall comply with the ground story height and ground floor elevation standards specified by the applied Frontage District (Part 3B.).
-
-
-
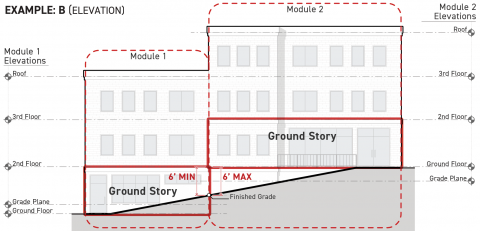
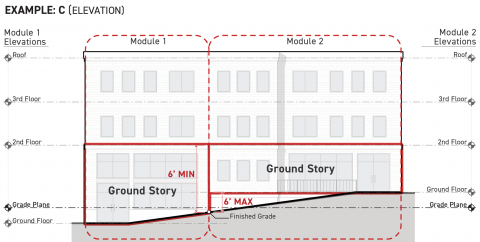
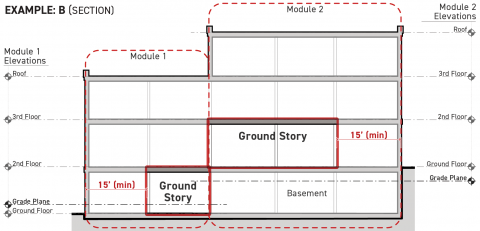
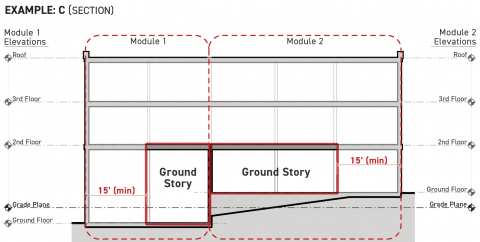
Ground Story Modules
Projects with very large buildings and those developed on lots with significant topographic variation may be required to designate a higher or lower story as the ground story for different portions of the building footprint. Where the ground story changes across the building footprint, the ground story shall meet the following standards:
-
A ground story shall be designated for all portions of a building footprint.
-
The ground story is the lowest story of a building or structure meeting the following standards:
-
The ground story shall meet the following standards for a minimum depth of 15 feet measured perpendicular to the specified facades:
-
The ground story facade shall be exposed a minimum of six feet above finished grade along the full width of each frontage applicable facade pursuant to Sec. 3A.2.2.B.3. (Frontage Applicable Facades).
-
The ground story finished floor shall be no more than six feet above finished grade for at least 75 percent of its applicable building perimeter pursuant to Sec. 14.2.9.B. (Applicable Building Perimeter), measured cumulatively.
-
The ground story shall comply with the ground story height and ground floor elevation standards specified by the applied Frontage District (Part 3B.).
-
-
For portions of a building footprint located 15 feet or greater from a frontage applicable facade pursuant to Sec. 3A.2.2.B.3. (Frontage Applicable Facades), the ground story shall be the story of a building or structure having its structural floor surface nearest to the grade plane elevation.
-
-
-
-
Ground Story Facade
The ground story facade is defined as the facade of the ground story for the full height of the ground story.
-
Ground Floor
The ground floor is defined as the finished floor elevation of the ground story.
-
Upper Story
The upper story is defined as any story of a building located above the ground story.
-
Upper Story Facade
The upper story facade is defined as the portions of the exterior building envelope at the perimeter of each upper story for the full height of the story.
-
Attic
Attic is defined as the clear height between the underside of the finished ceiling or exposed framing, whichever is lower, and the finished floor.
-
An attic that includes an occupiable floor area less than 50 percent of the floor area located on the story immediately below is not considered a story.
-
An attic that includes an occupiable floor area greater than or equal to 50 percent of the floor area located on the story immediately below is considered a story and shall comply with all standards applicable to upper story and upper story facades.
-
-
Basement
Basement is defined as an occupiable portion of a building located below the ground story.
-
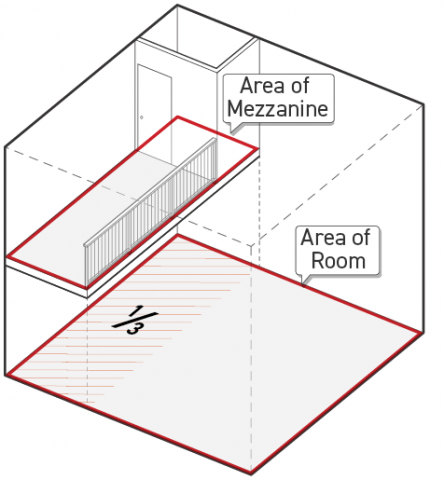
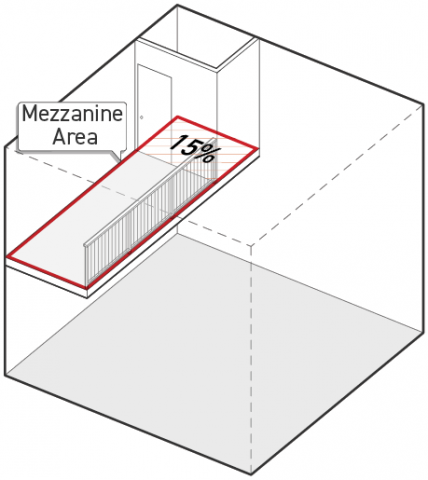
Mezzanine
Mezzanine is defined as an intermediate level within a story of a building.
-
A mezzanine is not considered a story provided it meets the following standards:
-
The mezzanine floor area shall not be greater than 1/3 of the floor area of the room or enclosed space it is included within.
-
The perimeter planes of the mezzanine shall consist of non-solid area, with the following exceptions:
-
Those portions of the mezzanine perimeter that are formed by the walls enclosing the larger room or space the mezzanine is included within;
-
Safety barriers that meet the standards outlined in Sec. 14.2.4. (Enclosure).
-
-
Regardless of enclosure rules in Subparagraph b., above, within the mezzanine floor area, a maximum of 15 percent of the mezzanine floor area may be enclosed.
-
-
A mezzanine that does not meet the standards in Paragraph 1., above, is considered an additional story.
-
Sec. 14.2.11. Lot
A lot is defined as one or more parcels of land identified for the purpose of development and meeting the standards below:
-
All parcels composing a lot shall be owned by the same person or entity.
-
For the purposes of Article 11. (Division of Land) all parcels composing a lot shall be identified on a final map and recorded with the Los Angeles County Recorder with a separate and distinct letter or number, or otherwise be on a recorded instrument that meet the requirement of the Subdivision Map Act.
-
For the purpose of meeting standards associated with the applied zoning districts, a lot composed of multiple parcels grouped together as a single lot through a lot tie affidavit filed and approved with the Department of Building and Safety shall be considered a single lot. When the involved parcels have different and conflicting applied zoning districts, each individual parcel must meet the standards associated with the applied zoning district on each parcel.
-
A lot does not include portions of a lot required for dedication of land (for example, proposed right-of-way), including dedication of land required by or included as part of the subdivision process, with the following exceptions:
-
As otherwise stated in Sec. 10.1.8. (Lots Affected by Street Widening).
-
In the case of new developments taking place on a lot with an existing, recorded dedication, or on lots with old permits where the building was never constructed, measurements of a lot may be taken from the lot lines that existed prior to the dedication of land, provided that clearance is obtained from the Department of Public Works indicating that the improvements or street widening associated with the recorded dedication have not taken place. If the associated improvements or street widening have already been completed, measurements of a lot do not include the portions of the lot required for dedication of land.
-
-
A lot shall include all portions of a lot allocated to City or utility easements.
-
A lot shall abut the public right-of-way, alley, or a private street contiguously for a minimum of 12 feet.
-
Access shall be provided from the lot to the public right-of-way through:
-
An access lane with a minimum width as specified in Div. 4C.2. (Automobile Access); or
-
A pedestrian accessway with a minimum width in accordance with Div. 4C.1. (Pedestrian Access); or
-
A private street with a minimum width as determined by the Advisory Agency.
-
Sec. 14.2.12. Lot Line Determination
-
General
-
Each lot line shall have one of the following designations as determined by the definitions in this Section (Lot Line Determination), and each lot line shall not have more than one of the following designations:
-
In addition to these required designations, lot lines may also be included into one of the following lot line categories:
-
For lot lines with curved or irregular lines which makes the dividing point between two types of lot line designations unclear, see Sec. 14.2.14.B. (Lot Line Determination for Curved Corner Lot Lines).
-
-
Lot Line Categories
-
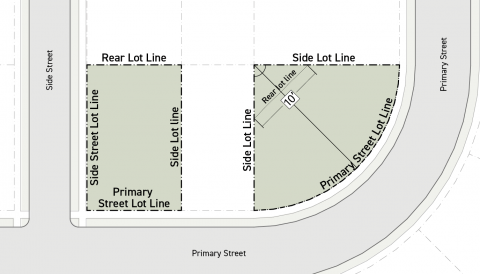
Frontage Lot Line
A frontage lot line is any lot line that triggers Frontage District (Part 3B.) requirements. Frontage lot lines include all primary street lot lines and side street lot lines.
-
Street Lot Line
A street lot line is any lot line that abuts a street right-of-way. Street lot lines include all primary street lot lines, side street lot lines, and alley lot lines.
-
Common Lot Line
A common lot line is any lot line shared by multiple lots. Common lot lines include all side lot lines and rear lot lines and may include special lot lines in Dual Frontage Districts (Div. 3B.8.).
-
-
Lot Line Designations
-
Primary Street Lot Line
A primary street lot line is a lot line that has been designated as a primary street lot line by following the criteria and standards listed below.
-
Each lot shall have at least one primary street lot line. However, if all street lot lines are mapped as special lot lines, then no primary street lot line is required.
-
When there is only one street lot line, it shall be designated as the primary street lot line, unless it is mapped as a special lot line.
-
When there is more than one street lot line, the primary street lot line shall be determined according to Subparagraph d. (Special Scenario Lots Abutting More Than One Street) and Subparagraph e. (Other Lots Abutting More Than One Street) below, except that:
-
Any lot line that has been mapped as a special lot line shall be considered a special lot line.
-
If all street lot lines are private streets, the primary street lot line shall be determined pursuant to Sec. 13B.3.1. (Administrative Review) using the established orientation of the block criteria pursuant to Subparagraph f. (Relief) below.
-
When the lot crosses the boundary of the City, its primary street lot line shall be determined pursuant to Sec. 13B.3.1. (Administrative Review) using the established orientation of the block criteria pursuant to Subparagraph f. (Relief) below.
-
-
Special Scenario Lots Abutting More Than One Street
In the following special scenarios, there may be more than one primary street lot line:
-
Any lot lines abutting a street that is mapped as a primary street pursuant to Sec. 1.5.3. (Primary Street Map), shall always be designated a primary street lot line, even if this results in more than one primary street lot line per lot.
-
On a lot with an applied Commercial-Mixed Use District (Div. 5B.5.), any lot line abutting an avenue or boulevard shall be a primary street lot line, even if this results in more than one primary street lot line per lot.
-
-
Other Lots Abutting More Than One Street
For lots that abut multiple streets where none of the lot lines are designated as a primary street lot line per the provisions in Subparagraph d. (Special Scenario Lots Abutting More Than One Street) above, the primary street lot line is designated using the following criteria, listed in order of priority:
-
The shortest lot line abutting a street, with the exception of:
-
Through lots, in which case the longest lot line abutting a street shall be the primary street lot line;
-
Lot lines under 20 feet, in which case the next shortest lot line shall be the primary street lot line;
-
Lots of 30,000 square feet or greater, for which the primary street lot line shall be determined using the subsequent criteria in this Subparagraph e. (Other Lots Abutting More Than One Street);
-
-
The lot line abutting the street or streets with the highest street designation;
-
The lot line abutting the longest face of the block which the lot touches;
-
The lot line abutting a street that faces a publicly accessible open space;
-
The lot line abutting the street that the lot takes its address from, as confirmed by the Bureau of Engineering;
-
-
Relief
Rather than designating a primary street lot line pursuant to Subparagraph a. (Primary Street Lot Line) through Subparagraph e. (Other Lots Abutting More Than One Street) above, the primary street lot line may be determined pursuant to Sec. 13B.3.1. (Administrative Review) using the established orientation of the block criteria below:
-
The lot line abutting the street the majority of buildings along the block accommodate pedestrian access from;
-
The primary street lot line designation of the majority of buildings along the block, either existing or approved;
-
The lot line abutting the street the majority of wall signs on the block are oriented toward.
-
-
-
Side Street Lot Line
A side street lot line is a lot line separating a lot from a side street right-of-way. Any street lot line not determined to be a primary street lot line is considered a side street lot line.
-
Special Lot Line
A special lot line is any lot line mapped as a special lot line on the Special Lot Line map, pursuant to Sec. 1.5.8. (Special Lot Line Map) and designated within an applied Form District (Part 2B.) or Frontage District (Part 3B.) that specifies standards for a special lot line.
-
Special lot lines are intended to identify lot lines that face, abut, or otherwise interact with active spaces such as pedestrian paths, open spaces, equine trails, or active pedestrian alleys.
-
Regardless of whether a lot line qualifies as any other lot line designation pursuant to Sec. 14.2.12.C. (Lot Line Designations), all lot lines that are mapped as a special lot line shall be designated as a special lot line.
-
-
Rear Lot Line
A rear lot line is a lot line that does not abut a street or alley right-of-way and is opposite and most distant from a primary street lot line, and meets the following criteria:
-
A lot shall have no more than one lot line designated as a rear lot line.
-
In the case of a through lot, a lot may have no rear lot line.
-
Where no lot line is clearly opposite to the primary street lot line, such as triangular lots or gore-shaped lots, the rear lot line is determined based on an imaginary line 10 feet wide, parallel to the primary street lot line that intersects two lot lines at its endpoints.
-
Where the primary street lot line is not straight, the rear lot line shall be the opposite and most distant lot line that is parallel to an imaginary line connecting the end points of the primary street lot line.
-
Where there are multiple primary street lot lines, the lot line having the highest portion of its length serving as the rear lot lines of abutting lots is the rear lot line.
-
-
Side Lot Line
A side lot line is any lot line not determined to be a primary street lot line, side street lot line, rear lot line, alley lot line, or special lot line.
-
Alley Lot Line
An alley lot line is any lot line that abuts an alley right-of-way. Even when a lot line qualifies as a rear lot line, or side lot line, alley right-of-way abutting lot lines shall be designated an alley lot line, except when the lot line qualifies as a special lot line.
-
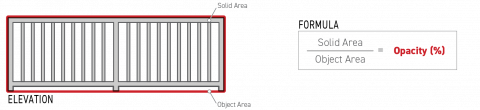
Sec. 14.2.13. Opacity (%)
Opacity is defined as the degree to which an object or material is impervious to rays of light or obstructs visibility.
-
Measurement
-
Opacity is measured as a percentage, calculated by dividing the solid portion of the object area by the total area of the object.
-
The total area of the object is measured as the smallest convex polygon containing all elements of the object or assembly.
-
-
Standards
-
Equivalent Transparency
Where an assembly includes materials or objects that are solid but transparent (including glass), the transparent portion of the solid area may be weighted by multiplying it by the visual light transmittance of the material specified by the manufacturer.
-
Visual Obstructions
Any permanent visual obstructions within a distance of five feet of the subject object, measured horizontal and perpendicular to the object area, renders otherwise non-solid areas solid for the purpose of measuring opacity.
-
Sec. 14.2.14. Irregular Lot lines
-
Parallel or Perpendicular to Irregular Lot Line
Where a lot line is curved, standards measured parallel or perpendicular to that lot line assume the angle of the lot line to be the same as an imaginary straight line connecting the endpoints of the curved lot line segment.
-
Lot Line Determination For Curved Lot Lines
-
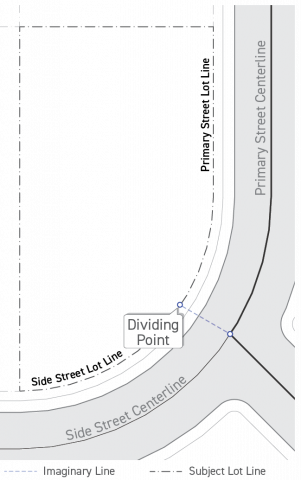
Street Lot Lines
Where a corner lot has a curved street lot line to which it makes the dividing point between two types of street lot lines unclear for the purposes of Sec. 14.2.12. (Lot Line Determination), that dividing point shall be identified as the nearest point on the lot perimeter to the intersection of the abutting street centerlines.
-
Common Lot Lines
Where a common lot line is curved to which it makes the dividing point between two types of lot lines unclear for the purposes of Sec. 14.2.12. (Lot Line Determination), the abutting lot line designation from the abutting lot or lots shall be utilized to assign a designation for the length of the lot line segment in question.
-
-
Building Setback Determination For Curved Lot Lines
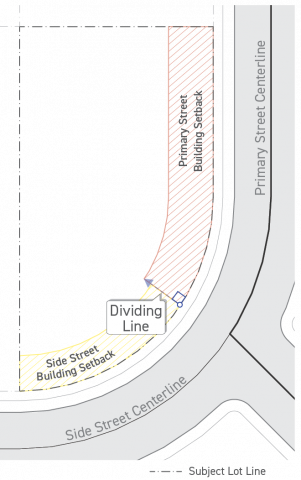
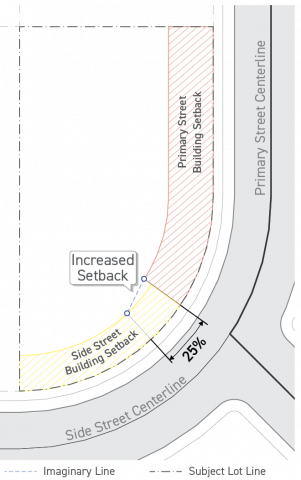
Where a corner lot has a curved street lot line which makes the dividing line between two types of building setbacks unclear for the purposes of Sec. 2C.2.2. (Building Setbacks), that dividing line shall be identified by the following:
-
Taking the dividing point established in Sec. 14.2.14.B.1. (Street Lot Lines), above, and drawing a line into the lot perpendicular to the lot line at the dividing point for the depth of the building setback.
-
The setbacks shall connect along the dividing line for the depth of the primary street building setback.
-
Where the depth of a primary street building setback and side street building setback differ at the dividing line established in Paragraph 1., above, the side street building setback shall be increased linearly for 25 percent of the side street lot line until it meets the primary street building setback.
-
-
Parking Setback Determination For Curved Lot Lines
Where a corner lot has a curved street lot line which makes the dividing line between two types of parking setback designations unclear for the purposes of Sec. 3C.2.1. (Parking Setback), that dividing line shall be the same as established in Subsection C. (Building Setback Determination For Curved Lot Lines) above.
-
Yard Determination For Curved Lot Lines
Where a corner lot has a curved street lot line which makes the dividing line between two types of yard designations unclear for the purposes of Sec. 14.2.6. (Yards), that dividing line shall be the same as established in Subsection C. (Building Setback Determination For Curved Lot Lines) above.
Sec. 14.2.15. Project Activities
-
Project
A project is defined as work involving any of the project activities listed in Subsection B. (Project Activities) below. A project may or may not require a building permit, and may or may not be one application in a series of applications (such as demolition followed by new construction). A Community Plan Implementation Overlay or Specific Plan may have its own definition for a project. Typically, more than one project activity will apply to a proposed project (for example, a street-facing addition concealing a portion of an existing building facade includes both new construction and an exterior modification).
-
Project Activities
A project activity describes the type of work composing a project. A project may be composed of one or more project activity. The following are types of project activities for the purposes of this Zoning Code (Chapter 1A):
-
New Construction
New construction is defined as work that includes the construction of a new building or structure on a lot, whether structurally detached or attached from other existing buildings or structures on the lot. New construction includes an addition to or relocation of an existing building or structure, or the relocation of existing floor area, to another location on the lot, or to any other lot. Relocation of existing buildings or structures includes any activity that lifts any portion of the building or structure off of its foundation. New construction does not include ground mounted signs or wall mounted signs.
-
Major Remodel
Major remodel is defined as work that includes significant removal, disassembly, or replacement of a building or structure or portions of a building or structure that does not add to or change the building footprint and meets the standards below:
-
Major remodel includes the removal or replacement of any of the following:
-
More than 50 percent of the perimeter wall framing; or
-
More than 50 percent of the roof framing; or
-
More than 50 percent of the structural members.
-
-
Major remodel may affect the exterior of a building or structure, in which case it would also be considered an exterior modification.
-
Remodeling that does not meet the thresholds within this Paragraph (Major Remodel) or another project activity would be considered maintenance & repair.
-
-
Lot Modification
Lot modification is defined as the modification of the lot lines of any existing lot through the Subdivision Map Act and Article 11. (Division of Land), including the division of land as defined in California Government Code, Title 7. (Planning and Land Use), Sec. 66424.
-
Site Modification
Site modification is defined as work including modifications to existing, or the addition of, new horizontal site improvements and landscaping, including trees, fences or walls, street furniture, lighting fixtures, grading, flatwork, ground mounted signs, and parking lot resurfacing or the reconfiguration of existing parking stalls.
-
Site modifications, such as grading, that expose additional foundation wall or facade areas are considered to be both a site modification and an exterior modification.
-
Any work whose principal aim is the provision of handicap accessibility for compliance with the Americans with Disabilities Act is not considered a site modification.
-
-
Exterior Modification
Exterior modification is defined as work to the exterior of a building or structure.
-
Facade Modification
Facade modification is an exterior modification that includes a change to a building facade involving a modification of its existing design or outward appearance.
Facade modifications include changes to any of the following:
-
Wall mounted signs beyond the maintenance & repair required pursuant to Sec. 4C.11.1.C.4. (Maintenance);
-
The amount of exterior foundation wall that is exposed above finished grade;
-
An architectural element or architectural feature attached to the facade;
-
Exterior wall finish materials on an applicable facade area in a Character Frontage District (Div. 3B.9.); or
-
In an Historic Preservation Overlay Zone, facade modification includes change of the exterior paint color.
-
General
Any exterior modification work that does not meet the definition and standards of facade modification.
-
-
Use Modification
Use modification is a change of use or an intensification of use.
-
Change of Use
Change of use is defined as work that includes a change or expansion in the permitted use of any portion of an existing building or lot from one use defined in Part 5D. (Use Definitions) to any other use defined in Part 5D. (Use Definitions). Change of use does not include any temporary uses. For temporary uses, see Paragraph 7. (Temporary Use) below.
-
Intensification of Use
Intensification of use is defined as work that increases the intensity of a use, such as an increase in dwelling units, seating capacity, or the number of people in care.
-
-
Temporary Use
Temporary use is defined as a use of a building or lot with any use defined in Part 5D. (Use Definitions) that does not exceed 180 days and meets the requirements of Chapter IX. (Building Regulations), Sec. 91.106.1.3. (Temporary Permits) of this Code.
-
Demolition
Demolition is defined as the removal of an entire structure or building.
-
Proposed demolition of a structure or building that results in a reduction of compliance of other structures or buildings on the lot with the requirements of this Zoning Code (Chapter 1A) is required to be accompanied by new construction or another project activity that maintains the level of compliance with the requirements of this Zoning Code (Chapter 1A) in place prior to the issuance of the demolition permit, except as described in Subparagraph b. below.
-
Regardless of the general rule in Subparagraph a. above, demolition permits may be issued for buildings or structures without accompanying new construction or other project activities when said building or structure has been determined by the Department of Building and Safety to be a present, imminent, extreme and immediate hazard or danger to life or limb, health or safety pursuant to Chapter IX. (Building Regulations), Sec. 91.8905. (Special Provisions for Vacating, Barricading, Removing or Demolishing Buildings or Structures Without Notice).
-
-
Renovation
Renovation is defined as a modification to the interior of any building or structure, including the basement, that does not expand the building or structure. Renovation includes interior remodels or tenant improvements.
-
Maintenance & Repair
Maintenance & repair is defined as work that does not qualify as a site modification, major remodel, exterior modification or new construction, and does not impact the project's ability to meet any applicable zoning requirements. Replacement of deteriorated or damaged parts of a building is considered maintenance & repair; however, in a Character Frontage District, CPIO, Conservation District, or Historic Preservation Overlay Zone, direct replacement may have additional requirements and processes. Maintenance & repair includes repair of site components such as restriping existing parking stripes, resealing parking lots, pothole repair, or replanting plants.
-
Sec. 14.2.16. Yards
-
General
-
All portions of a lot between exterior walls of a building and a property line shall be designated as one of the following yard designations, and no portions of a lot shall have more than one of the following designations, as established in Subsection B. (Yard Designations) below:
-
Individual yard designations may fall into one or more yard categories as provided in Subsection C. (Yard Categories) below.
-
-
Yard Designations
-
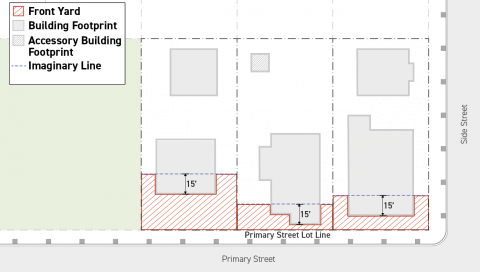
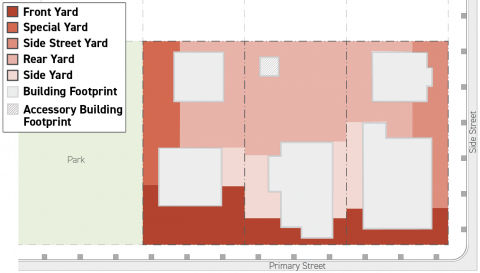
Front Yard
A front yard is the area between a primary street lot line and an imaginary line running parallel to the primary street lot line. The imaginary line shall be drawn 15 feet back from the portion of the primary street lot line-facing facade nearest to the primary street lot line, measured perpendicularly to the lot line.
-
Only yards abutting a primary street lot line shall be designated as front yards.
-
Portions of a lot that meet the criteria for front yard designation shall not be designated as any other yard, including portions of a lot that meet the criteria for front yard designation but also meet the criteria for any other yard designation.
-
-
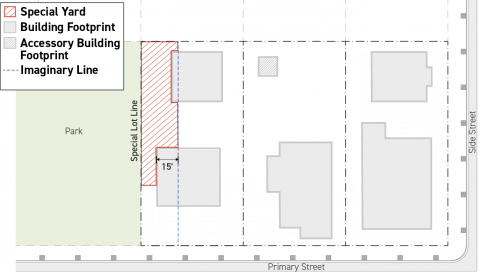
Special Yard
A special yard is the area between a special lot line and an imaginary line running parallel to the special lot line. The imaginary line shall be drawn 15 feet back from the portion of the special lot line-facing facade nearest to the primary street lot line, measured perpendicularly to the lot line.
-
Special yards include yards abutting a special lot line including but not limited to special river and special alley lot lines.
-
Portions of a lot that meet the criteria for special yard designation shall not be designated as a side street yard, rear yard, or side yard, including portions of a lot that meet the criteria for special yard designation but also meet the criteria for side street yard, rear yard, or side yard.
-
Portions of a lot that meet the criteria for special yard designation but also meet the criteria for front yard designation shall be designated as front yard.
-
-
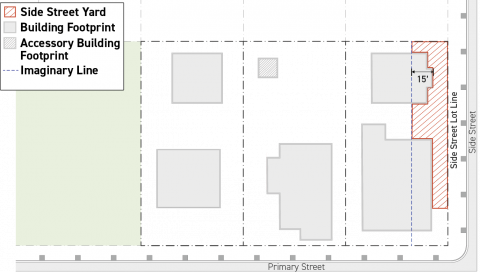
Side Street Yard
A side street yard is the area between a side street lot line and an imaginary line running parallel to the side street lot line. The imaginary line shall be drawn 15 feet back from the portion of the side street lot line-facing facade nearest to the side street lot line, measured perpendicularly to the lot line.
-
Only yards abutting a side street lot line shall be designated as side street yards.
-
Portions of a lot that meet the criteria for side street yard designation shall not be designated as a rear yard or side yard, including portions of a lot that meet the criteria for side street yard designation but also meet the criteria for rear yard or side yard.
-
Portions of a lot that meet the criteria for side street yard designation but also meet the criteria for front yard designation shall be designated as front yard.
-
Portions of a lot that meet the criteria for side street yard designation but also meet the criteria for special yard shall be designated as special yard.
-
Portions of a lot that meets all three criteria for side street yard designation, special yard designation, and front yard designation shall be designated as a front yard.
-
-
Rear Yard
A rear yard is the portion of a lot between a rear lot line and a principal structure. When there is more than one principal structure located on the same lot, rear yard includes the portions of a lot between the rear lot line and the principal structure that is located closest to the primary street lot line.
-
Portions of a lot that meet the criteria for rear yard designation shall not be designated as a side yard.
-
Portions of a lot that meet the criteria for rear yard designation but also meet the criteria for side street yard shall be designated as side street yard.
-
Portions of a lot that meets all three criteria for rear yard designation, side street yard designation, and special yard designation shall be designated as a special yard.
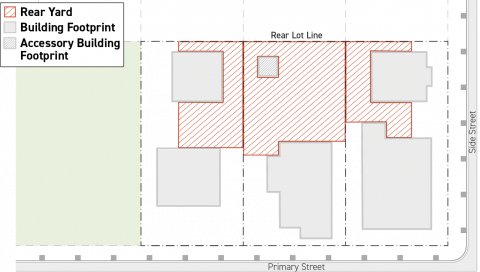
-
-
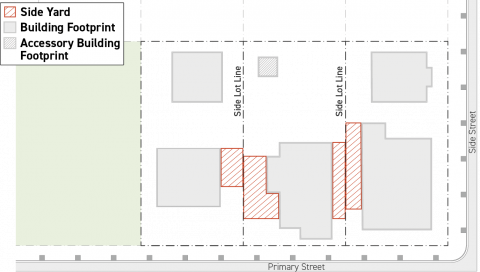
Side Yard
A side yard is the portions of a lot between a side lot line and a principal structure. All portions of a lot that do not meet the yard designation criteria for any other yard shall be designated as a side yard.
-
All Yards Graphic Illustration
The following illustration provides an example distribution of yard designations for three different lots.
-
-
Yard Categories
-
Frontage Yard
Frontage yard is a category of yards referring to all yards that abut a frontage lot line including:
-
Side street yards; and
-
Street Yard
Street yard is a category of yards referring to all yards that abut a street right-of-way including:
-
Front yards; and
-
-
Sec. 14.2.17. Public Access Easements
A public access easement is an easement, established between a lot owner or owners and the City of Los Angeles, as found on the Public Access Easement Map (Sec. 1.5.11.), affecting a lot or lots for the purpose of ensuring public access to the portions of the lot covered by the easement.
-
Standards
-
Public access easements affecting a lot shall be considered a part of the whole lot for the purposes of any standard or calculation which pertains to lot area or lot dimensions, unless stated otherwise as a condition of the easement.
-
No structures may be constructed within a public access easement.
-
When determining yard area, the yard area shall be measured from the interior edge of the easement rather than lot line.
-
-
Measurements
-
Building Setback
Buildings or structures to be constructed on a lot affected by a mapped public access easement shall measure the nearest required yard setback from the interior edge of the public access easement.
-
Lot Amenity Space
All portions of the public access easement area on a lot or lots may be calculated as part of the lot amenity space. When the public access easement is counted as lot amenity space, an accessway from the development on the lot must be ensured to the easement area. The required accessway must meet the minimum standards as established in Sec. 4C.1.1.C.2.A.i. (Linked).
-
Build-to depth
Where a lot includes a public access easement that abuts the frontage lot line, the build-to depth shall be measured to the front yard setback. The front yard setback is measured from the interior edge of the easement as established in Paragraph 1. (Building Setback) above.
-
Pedestrian Amenity Allowance
Where a lot includes a public access easement that abuts the frontage lot line, the pedestrian amenity shall be measured to the front yard setback. The front yard setback is measured from the interior edge of the easement as established in Paragraph 1. (Building Setback) above.
-
Parking Setback
Where a lot includes a public access easement that abuts the frontage lot line, the parking setback shall be measured to the front yard setback. The front yard setback is measured from the interior edge of the easement as established in Subsection A. (Standards) above.
-
Frontage Planting Area
Area within the public access easement shall not be used to meet planting area required by a frontage planting area, frontage screen, or transition screen.
-
Frontage Yard Fence & Wall
Where a lot includes a public access easement, fences and walls allowed by the applied Frontage District (Part 3B.) may be constructed and maintained on the interior edge of the public access easement, but shall not be constructed within the easement area nor on any lot line or portion of a lot line affected by the easement unless provided in the easement. A fence or wall shall not be constructed in a manner which obstructs public access to the easement area.
-
Frontage Screens and Transition Screens
Where a lot includes a public access easement, any required frontage screens and transition screens may be constructed and maintained on the interior edge of the public access easement, but shall not be constructed within the easement area nor on any lot line or portion of a lot line affected by the easement unless provided in the easement. A frontage screen or transition screen shall not be constructed in a manner which obstructs public access to the easement area.
-
Sec. 14.2.18. Slope
-
Average Natural Slope
Average natural slope is defined as the average of the ungraded slopes at selected contours within a given parcel of land divided by its area as computed from either the City Engineer’s topographic maps or a topographic map prepared by a registered civil engineer or land surveyor and meets all the following standards:
-
Regardless of which map is used, calculations cannot be derived or interpolated from a map that originally had contour intervals of greater than 25 feet for subdivisions or greater than five feet for parcel maps.
-
Average natural slope shall be computed by the following formula:
Where:
S = average natural slope in percent.
C = contour interval in feet, at no greater than 25-foot intervals for subdivisions or five-foot intervals for parcel maps, resulting in at least five contour lines.
L = total accumulated length of all contours of interval “C” in feet.
A = the area being considered in square feet.
-
Average natural slopes may be computed only by the entire subdivision or parcel map area. The calculation “L” (contour lengths) and “A” (area in square feet) can be computed by 500-foot grid increments, as shown on the City Engineer’s topographic maps. The “L” for each grid increment shall be added to the “L” for every other grid increment and the “A” for each grid increment shall be added to the “A” for every other grid increment to determine the “L” and the “A” for the entire subdivision or parcel map, prior to calculating the average natural slope for that subdivision or parcel map.
-
In any matter where the average natural slope is used to calculate density pursuant to Sec. 11.1.3. (Subdivision Design Standards) or Sec. 11.4.1.D. (Slope Density), the subdivision file shall contain copies of all maps and all calculations so that the figures can be verified. All maps and all calculations are required to be submitted at the time of the filing of a subdivision application or the application is deemed incomplete.
-
Div. 14.3. Glossary
The following terms, abbreviations, and symbols shall be used in construing this Zoning Code (Chapter 1A). For any term not defined in this glossary (or defined, but not for all purposes), see Sec. 14.1.1.A.4. (General).
Abbreviations & Symbols
': Feet.
": Inches
%: Percent
ac: Acres
ADU: Accessory Dwelling Unit.
AMI: Area Median Income.
CDO: Community Design Overlay.
CEQA: California Environmental Quality Act.
CPIO: Community Plan Implementation Overlay.
Div: Division.
DU: Dwelling Unit.
FAR: Floor Area Ratio.
FC: Footcandles.
HPOZ: Historic Preservation Overlay Zone.
JADU: Junior Accessory Dwelling Unit.
LAAC: Los Angeles Administrative Code.
LADBS: Los Angeles Department of Building and Safety.
LADOT: Los Angeles Department of Transportation.
LADWP: Los Angeles Department of Water and Power.
LAHD: Los Angeles Housing Department.
LAMC: Los Angeles Municipal Code.
LCP: Local Coastal Program.
LID: Low Impact Development.
max: Maximum.
Metro: Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority.
min: Minimum.
n/a: Not Applicable.
RAP: Department of Recreation and Parks.
Sec: Section.
SF: Square Feet.
TDM: Transportation Demand Management.
A
Abandoned Shopping Cart: Abandoned shopping cart is defined as a shopping cart located outside of the lot where the establishment that furnishes shopping carts for use by its patrons is located.
Abatement Radius: Abatement radius is defined as the area around a permitted lot designated by the Office of Community Beautification for the removal of graffiti, posters/handbills and any other illegal postings, as well as trash, debris, rubbish, and weeds from public property and right-of-ways.
Above-Grade: Above-grade is defined as located higher in elevation than the surrounding finished grade.
Abut: See abutting.
Abutting: Abutting is defined as to touch or have a common boundary with.
Access: Access is defined as a means of approaching or entering a place.
Access Lane: Access lane is defined as the lane accommodating automobile access onto a lot in accordance with Div. 4C.2. (Automobile Access).
Accessory Building: Accessory building is defined as a detached, subordinate building, the use and scale of which is supplementary to other buildings and uses on the lot.
Accessory Dwelling Unit: See Chapter I. (General Provisions and Zoning), Sec. 12.03. (Definitions) of this Code.
Accessory Material Coverage: Pursuant to Sec. 3D.10.2. (Accessory Material Coverage), accessory material coverage is defined as the building products used as an exterior wall finish material to accent or support the principal material.
Accessory Roof Form: Accessory roof form is defined as a portion of a roof structure that deviates from the principal roof form in either shape, color, or shape and color.
Accessory Structure: Accessory structure is defined as a detached, subordinate structure, the use and scale of which is supplementary to other buildings and uses on the lot.
Accessory Use: Pursuant to Sec. 5C.1.1. (Accessory To), accessory use is defined as a use that meets all standards in Sec. 5C.1.1 (Accessory To).
Active Space: For the purposes of Sec. 14.2.7.A.3. (Development Standards District 5) active space is defined as indoor occupiable spaces designed and intended for general commercial uses, public & institutional uses, or common indoor amenity spaces.
Active Wall Spacing: Pursuant to Sec. 3C.4.2. (Active Wall Spacing), active wall spacing is defined as the horizontal distance between widths of ground story facade and foundation wall with window or door openings.
Acts: Pursuant to Sec. 13B.5.5. (Reasonable Accommodation), acts is defined as the Federal Fair Housing Amendments Act of 1988 and California’s Fair Employment and Housing Act.
Acutely Low Income Household: An acutely low income household is a household whose annual income, adjusted for family size, does not exceed 15 percent of the area median income as designated for this category in California Health and Safety Code, Sec. 50063.5.
Adaptive Reuse Project: Adaptive reuse project is defined as any change of use to dwelling, or household business: joint living & work quarters, or any change in commercial use to another commercial use, in all or any portion of any eligible building according to Sec. 9.4.5. (Downtown Adaptive Reuse Program) or Sec. 9.4.6. (Citywide Adaptive Reuse Program), as long as the commercial use is allowed in the zone.
Addition: Addition is defined as any work that increases the floor area or the volume of enclosed space of an existing building, and is structurally attached to the existing building. The definition of addition is modified for the purposes of Historic Preservation (Div. 13B.8.), for which addition is defined as an extension or increase in floor area or height of a building or structure.
Additional Housing Units: Pursuant to 15.4.3.A. (Definitions), a net increase in the number of dwelling units or guest rooms to be added on a parcel or parcels of land by issuance of a building permit, after subtracting the number of dwelling units or guest rooms legally removed from the same parcel of real property during the year preceding the issuance of the building permit.
Additional Non-Residential Floor Area: For the purposes of Sec. 15.4.3.A. (Definitions), additional non-residential floor area is defined as the net increase in the amount of non-residential floor area to be added on a parcel or parcels of land by issuance of a building permit, less the amount of non-residential floor area legally removed from the same parcel of real property during the year preceding the issuance of the building permit.
Adjacent: See abutting.
Adjoining: See adjoining Lot.
Adjoining Lot: Adjoining lot is defined as abutting lots, lots separated from the subject lot by a street or alley right-of-way, and lots having a common corner with the subject property.
Administrative Guidelines: For the purposes of 5C.3.2.B.1. (Administrative Guidelines), the Department of City Planning or Office of Finance may promulgate regulations, which may include, but are not limited to, application requirements, interpretations, conditions, reporting requirements, enforcement procedures, and disclosure requirements, to implement the provisions, and consistent with the intent, of Sec. 5C.3.2. (Home-Sharing Program).
Advisory Agency: Advisory Agency is defined as the Director of Planning, who acts in the capacity of the Advisory Agency for the City pursuant to the Subdivision Map Act established in accordance with Sec. 13B.7.1.C. (Advisory Agency). The Advisory Agency is granted additional authority pursuant to Sec. 11.1.2. (Division of Land).
Affordable Housing Incentive Program: Affordable housing incentive program is defined as an incentive program established in Div. 9.2. (Affordable Housing Incentive Programs) to increase the production of affordable housing, consistent with City policies.
Affordable Housing Incentives Guidelines: Affordable housing incentives guidelines is defined as the guidelines approved by the City Planning Commission, pursuant to Sec. 13B.1.5. (Guidelines or Standards Adoption/Amendment), under which housing development projects for which a density bonus above 35 percent has been requested are evaluated for compliance with Div. 9.2. (Affordable Housing Incentive Programs).
Aggrieved Person: Aggrieved person is defined as any person or entity with standing to appeal an action on an application filed under this Zoning Code (Chapter 1A) under California law, or as provided in the provisions of this Zoning Code (Chapter 1A) relating to a particular appeal.
For the purposes of Sec. 13B.9.1. (Coastal Development Permit (Pre-Certification)), aggrieved person is defined as any person who, in person or through a representative, appeared at a hearing on the application for a Coastal Development Permit, or appeal hearing in connection with the decision or action appealed, or who, by other appropriate means prior to a hearing, informed the permit issuing authority, or appeal body of the nature of his or her concerns or who for good cause was unable to do either. "Aggrieved person" includes the applicant for a Coastal Development Permit.
Agricultural Use: Pursuant to Div. 5D.10. (Agricultural Uses), agricultural uses are defined as uses dedicated to the cultivation of plants or the keeping of animals.
Air Space Lot: Air space lot is defined as a division of the space above or below a lot with a finite width, length, and upper and lower elevation occupied or to be occupied by a use, or accessory use, any building or unit group of buildings, or portion of a use or building. An air space lot shall be identified on a final map recorded with the Los Angeles County Recorder with a separate and distinct number or letter. An air space lot shall have such access to a street or private street by means of one or more easements or other entitlements to use in a form satisfactory to the Advisory Agency and the City Engineer.
Airport: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.5.1. (Airport), an airport is defined as a runway landing area or other facility used for the landing and taking off of aircraft including all the necessary taxiways, aircraft storage and tie-down areas, hangars, passenger terminals, and warehousing facilities.
Alley: Alley is defined as a public way designated as an alley by the Circulation Element of the General Plan, and displayed on Zoning Information and Map Access System (ZIMAS) or NavigateLA.
Alley Lot Line: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.12.C.6. (Alley Lot Line), alley lot line is defined as any lot line that abuts an alley right-of-way. Even when a lot line qualifies as a rear lot line, or side lot line, alley right-of-way abutting lot lines shall be designated an alley lot line, except when the lot line qualifies as a special lot line.
Alley Lot Line-Facing Facade: Alley lot line-facing facade is defined as all portions of a building facade that are parallel to an alley lot line and meet the criteria outlined in Sec. 14.2.6.B. (Lot Line-Facing Facade).
Alteration: For the purposes of Div. 13B.8. (Historic Preservation), alteration is defined as any exterior change or modification of a building, structure, landscaping, natural feature or lot within a Historic Preservation Overlay Zone including but not limited to changing exterior paint color, removal of significant trees or landscaping, installation or removal of fencing, and similar projects, and including street features, furniture or fixtures.
Alternative Parking Strategy: Alternative parking strategy is defined as an alternative method of meeting parking requirements that meet the standards outlined in Sec. 4C.4.2. (Alternative Parking Strategies).
American Standard for Nursery Stock: American standard for nursery stock is defined as a publication by the American Horticulture Industry Association intended to provide buyers and sellers of nursery stock with a common terminology in order to facilitate commercial transactions involving nursery stock.
Amphitheater or Stadium: Amphitheater or stadium is defined as a use meeting the definition of either amphitheater or stadium: local or amphitheater or stadium: regional.
Amphitheater or Stadium: Local: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.4.1. (Amphitheater or Stadium: Local), amphitheater or stadium: local is defined as any outdoor or semi-outdoor assembly facility intended to accommodate a large number of spectators for performances or sporting events and having an associated seating capacity of less than 3,000 seats. This use does not include facilities with seating capacity of 3,000 seats or more, for such uses see Sec. 5D.4.1.B. (Amphitheater or Stadium: Regional).
Amphitheater or Stadium: Regional: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.4.1. (Amphitheater or Stadium: Regional), amphitheater or stadium: regional is defined as any outdoor or semi-outdoor assembly facility intended to accommodate a large number of spectators for performances or sporting events and having an associated seating capacity of 3,000 seats or more. This use includes an amphitheater or stadium associated with a school. This use does not include facilities with seating capacity of less than 3,000 seats, for such uses see Sec. 5D.4.1.A. (Amphitheater or Stadium: Local).
Angle of Elevation: Angle of elevation is defined as the angle of an elevation view, zero degrees (horizontal) being the angle of an elevation projection, and 90 degrees being vertical.
Animal Keeping: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.10.1. (Animal Keeping), animal keeping is defined as any agricultural use that includes the breeding, boarding, training, or raising of animals.
Animal Keeping: Bees: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.10.1. (Animal Keeping: Bees), animal keeping: bees is defined as any animal keeping use that includes the keeping of bees.
Animal Keeping: Dairy: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.10.1. (Animal Keeping: Dairy), animal keeping: dairy is defined as an animal keeping use that includes the storage, processing, or distribution of milk or milk products.
Animal Keeping: Equine, Commercial: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.10.1C. (Animal Keeping: Equine, Commercial), animal keeping: equine, commercial is defined as the keeping, breeding, raising, training, or boarding of more than two equines not owned by and registered to residents on the same lot as the equine use. Equine includes mules and donkeys.
Animal Keeping: Equine, Non-commercial: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.10.1.D. (Animal Keeping: Equine, Non-Commercial), animal keeping: equine, non-commercial is defined as the keeping, breeding, raising, training, or boarding of equines owned by and registered to residents on the same lot as the equine use. No more than two equines owned by or registered to persons not residing on the same lot shall be allowed. Equine includes mules and donkeys.
Animal Keeping: Livestock: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.10.1.E. (Animal Keeping: Livestock), animal keeping: livestock is defined as any animal keeping use that includes the breeding, raising, training, boarding, or keeping of animals such as alpacas, cattle, donkeys, goats, mules, sheep, swine, or similar livestock, typically for fiber, meat, milk, or other products. This use includes day-to-day care, selective breeding, raising, and selling of livestock.
Animal Keeping: Pets: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.10.1.F. (Animal Keeping: Pets), animal keeping: pets is defined as any animal keeping use that includes the keeping of domestic pets that are readily classifiable as being incidental to another use such as dogs, cats, rabbits, rodents, birds, poultry, fish, amphibians, and small reptiles. This use does not include those uses defined in Sec. 5D.10.1.G. (Animal Keeping: Small Animals). This use does not include those uses defined in Sec. 5D.6.1.B. (Animal Services: Kennel).
Animal Keeping: Small Animals: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.10.1.G. (Animal Keeping: Small Animals), animal keeping: small animals is defined as any animal keeping use licensed by the Department of Animal Services for the breeding, raising, training, or boarding of small domestic animals such as dogs, cats, rabbits, rodents, birds, poultry fish, amphibians, and reptiles. This use does not include the uses defined in Sec. 5D.10.1.G. (Animal Keeping: Wild Animals).
Animal Keeping: Wild Animals: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.10.1.H. (Animal Keeping: Wild Animals), animal keeping: wild animals is defined as any animal keeping use licensed by the Department of Animal Services pursuant to Chapter V. (Public Safety and Protection), Sec. 53.38. (Wild Animals - Keeping - Permit) for the keeping of wild, exotic, dangerous, or non-domestic animals.
Animal Products Processing: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.9.1. (Animal Products Processing), animal products processing is defined as a heavy industrial use involving one or more of the following: dressing or dyeing furs; preparing processed meat and meat byproducts; preparing, tanning, and finishing hides and skins; refining or rendering animal fat, bones, and meat scraps; and slaughtering animals.
Animal Services: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.1. (Animal Services), animal services is defined as a use involving the provision of services related primarily to domestic animal care and keeping.
Animal Services: General: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.1.A. (Animal Services: General), animal services: general is defined as animal services in which domestic dogs or cats are provided non-medical care, such as, grooming, training, supervision, or boarding. This does not include uses where the overnight boarding of dogs or cats exceeds 30 percent of the floor area of a facility, for such uses see Sec. 5D.6.1.B. (Animal Services: Kennel). This use does not include medical care of animals, for such uses see Sec. 5D.6.1.C. (Animal Services: Veterinary Care).
Animal Services: Kennel: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.1.B. (Animal Services: Kennel), animal services: kennel is defined as animal services in which four or more dogs or cats, at least four months of age, are sheltered for periods beyond 24 hours per day. This definition does not include retail establishments dedicated to the commercial sale of animals, for such uses see Sec. 5D.6.12.H. (Retail: Pet Shop). This use does not include the breeding and raising of animals, for such uses see Sec. 5D. 10.1.G. (Animal Keeping: Small Animals).
Animal Services: Veterinary Care: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.1.C. (Animal Services: Veterinary Care), animal services: veterinary care is defined as animal services in which animals or pets are given medical or surgical treatment and care. This use does not include the non-medical treatment and care of dogs and cats, for such uses see Sec. 5D.6.1.A. (Animal Services: General).
Apartment: Apartment is defined as a type of dwelling unit.
Appeal Board: For the purposes of Sec. 13B.7.8. (Subdivision Appeal), the Appeal Board is the Area Planning Commission where the map is located for any parcel map or tentative tract map that: (a) creates or results in less than 50,000 gross square feet of non-residential floor area; or (b) creates or results in fewer than 50 dwelling units, guest rooms, or combination of dwelling units and guest rooms; or (c) involves a lot with fewer than 65,000 square feet of lot area; or (d) where specifically provided by this Zoning Code (Chapter 1A). In all other cases, the Appeal Board for Subdivision Appeals (Sec. 13B.7.8.) is the City Planning Commission.
Appealable Area: For the purposes of Sec. 13B.9.2. (Coastal Development Permit (Post-Certification)), appealable area is defined as the area identified in Sec. 30603 of the Public Resources Code. the area that meets this criteria includes, but is not limited to, the area shown on the “Post-LCP certification Permit and Appeals Jurisdiction Map” certified by the Coastal Commission in accordance with the provisions of Sec. 13576 of Title 14 of the California Code of Regulations and attached as an exhibit in each certified coastal specific plan.
Appealable Development: For the purposes of Sec. 13B.9.2. (Coastal Development Permit (Post-Certification)), appealable development is defined in accordance with Sec. 30603(a) of the Public Resources Code, as any development that constitutes a major public works project or a major energy facility, or any development located in the Appealable Area.
Applicable Stories: Pursuant to Sec. 3C1.1. (Applicable Stories), applicable stories is defined as the number of stories that are required to meet build-to standards.
Applicable Story: See applicable stories.
Applicant: For the purposes of Sec. 13B.9.2. (Coastal Development Permit (Post-Certification)), applicant is defined as the person, partnership, corporation, or other entity or state or local government agency applying for the Coastal Development Permit.
For the purposes of Sec. 15.4.3. (Affordable Housing Linkage Fee), applicant is defined as any individual, person, firm, partnership, association, joint venture, corporation, limited liability company, entity, combination of entities or authorized representative thereof, who undertakes, proposes or applies to the City for a planning or zoning entitlement approval or building permit related to a development project.
Application: Application is defined as an application filed pursuant to Sec. 13A.2.3. (Applications) of this Zoning Code (Chapter 1A).
Approving Authority: For the purposes of Sec. 13B.9.2. (Coastal Development Permit (Post-Certification)), approving authority is defined as the initial decision maker and appeal body, including the Director, City Engineer, Zoning Administrator, City Planning Commission, Area Planning Commission, Board of Public Works, City Council or other applicable decision-making person or body within the City, which has the authority to approve a Coastal Development Permit pursuant to this Section or by reason of jurisdiction over other permits and approvals sought in conjunction with an application for a Coastal Development Permit.
Architectural Detail: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.5.A.1.a. (Architectural Details), architectural detail is defined as building elements attached to or integrated into the structure of a building, not intended for human occupation. Types of architectural details include, but are not limited to: cornices, belt courses, sills, lintels, pilasters, pediments, or chimneys.
Architectural Element: Architectural element is defined as any building component, either decorative or structural, which is outside of or comprises the building envelope. Examples include windows, walls, cornices, and parapets. For the purposes of Sec. 14.2.5.B. (Vertical Encroachments), architectural elements is defined as building elements attached to or integrated onto the roof of a building, not intended for human occupation. Examples of architectural elements may include, but are not limited to: skylights, steeples, spires, belfries, cupolas, domes, flagpoles, or lighting.
Architectural Feature: Architectural feature is defined as a structure or assembly of architectural elements attached to or integrated with a facade. Often architectural features include occupiable space. Examples include: bay windows, balconies, and entry features.
Area Median Income: Area median income is defined as the median income in Los Angeles County as determined annually by the California Department of Housing and Community Development, adjusted for household size.
Area of Overlap: Area of overlap is defined as the portion of a lot's area where the build-to zones of two intersecting frontage lot lines overlap. See Sec. 3C.1.2. (Build-To Depth). For an illustration of the area of overlap, see Sec. 3C.1.2.C.4. (Standards).
Area Planning Commission: Area Planning Commission is defined pursuant to Sec. 552. (Area Planning Commission) of the City Charter.
Articulating Element: Pursuant to Sec. 3D.6.5. (Articulating Element), articulating element is defined as permanent architectural details used to embellish a facade design to accentuate an articulation technique or facade composition.
At-Grade: At-grade is defined as a descriptor ascribed to something, such as a floor or entry, which is at the elevation of the ground where the ground meets the foundation of a building.
Attended Bicycle Parking Service: Attended bicycle parking service is defined as a service by which a bicycle is left in the care of an attendant(s) with provision for identifying the bicycle's owner. See Sec. 4C.3.2.C.7. (Attended Bicycle Parking Service) and Sec. 4C.3.3.C.5. (Attended Bicycle Parking Service).
Attic: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.10.F. (Attic), attic is defined as the clear height between the underside of the finished ceiling or exposed framing, whichever is lower, and the finished floor.
Automobile Access Package: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.2.1.C.1. (Automobile Access Packages), automobile access packages are defined as a combination of standards regulating automobile access between the public roadway and a lot.
Automobile Parking Stall: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.4.1. (Automobile Parking Stalls), automobile parking stalls are defined as a space within a building, or a private or public parking area, exclusive of driveways, ramps, columns, office, and work areas, for the parking of one automobile. Automobile parking stalls do not include bicycle parking.
Automotive Repair Garage: For the purposes of Sec. 13B.10.4. (Annual Inspection Monitoring (Type 2)), automotive repair garage is defined pursuant to Sec. 13B.10.4.A.3. (Definitions) as any use described by the definition of: 1) motor vehicle services: light 2) motor vehicle services: heavy 3) or motor vehicle services: large vehicle per Part 5D. (Use Definitions).
Avenue: Avenue is defined as any public right-of-way designated as an Avenue I, II, or III on the Citywide General Plan Circulation System maps of the Circulation Element of the General Plan.
Average Natural Slope: Average natural slope is defined as the average of the ungraded slopes at selected contours within a given parcel of land divided by its area as computed from either the City Engineer’s topographic maps or a topographic map prepared by a registered civil engineer or land surveyor and meets all the standards in Sec. 14.2.18.A. (Average Natural Slope).
Awning Sign: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.11.6.C.1. (Awning Sign), awning sign is defined as a sign painted, sewn, or otherwise adhered to the material of an awning as an integrated part of the awning itself.
B
Base-Top Articulation: Pursuant to Sec. 3D.6.2. (Base-Top Articulation), base-top articulation is defined as a requirement composed of two separate and coordinated articulating elements designed to visually break a building facade up into two separately legible layers.
Base, Middle & Top Articulation: Pursuant to Sec. 3D.6.1. (Base, Middle & Top Articulation), base, middle & top articulation is defined as a requirement composed of three separate and coordinated articulating elements designed to visually break a building facade up into three separately legible layers.
Basement: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.10.G. (Basement), basement is defined as an occupiable portion of a building located below the ground story.
Bee: Bee is defined as any stage of life of the common domestic honey bee (Apis Mellifera).
Beehive: Beehive is defined as a structure that houses a bee colony.
Belt Course: Pursuant to Sec. 3D.6.5.C.2. (Belt Course), belt course is defined as a horizontal course projecting beyond the face of the surrounding building facade often shaped to mark a division in the facade wall.
Bicycle Cage: Bicycle cage is defined as a locked bicycle parking area that has been fenced off to prohibit access by the general public, and contain bicycle racks that provide a means of securing the bicycle frame at two points to a securely anchored rack.
Bicycle Corral: Bicycle corral is defined as any on-street public bicycle parking space in which multiple short-term bicycle parking racks have been installed.
Bicycle Room: Bicycle room is defined as a locked bicycle parking area that has been walled off to prohibit access by the general public, and which, contain bicycle racks that provide a means of securing the bicycle frame at two points to a securely anchored rack.
Bicycle Share Dock: Bicycle share dock is defined as a device designed to receive a bicycle for locked storage as part of a system that directly rents bicycles on a short-term basis.
Bicycle Share Service Provider: Bicycle share service provider is defined as an entity operating a system that directly provides bicycles for rent on a short-term basis.
Bicycle Share Station: Bicycle share station is defined as a combination of multiple bicycle share docks, automated payment equipment, and related equipment associated with bicycle rentals on a short-term basis.
Bisecting Line: Bisecting line is defined as a line that equally divides the angle created by the projection of intersecting lot lines of a lot adjoining the street of a corner lot as illustrated in Sec. 4C.11.3.D. (Measurement).
Block: Block is defined as a lot or grouping of lots with public ways on all sides.
Block Face: Block face is defined as any number of lots that have a primary street lot line adjacent to one side of a segment of private or a public street that lies between two other streets or alleys.
Bollard: Bollard is defined a an upright post consisting of a piece of timber, concrete, metal or similar material fixed firmly in an upright position intended to impede various forms of traffic or circulation.
Bonus Building Width: [forthcoming].
Bonus FAR: See bonus floor area.
Bonus Floor Area: Bonus floor area is defined as the bonus floor area ratio granted pursuant to Sec. 2C.4.1.C.2. (Bonus).
Bonus Height: Bonus height is defined as the bonus height in feet granted pursuant to Sec. 2C.4.3.C.2. (Bonus) or bonus height in stories granted pursuant to Sec. 2C.4.4.C.2. (Bonus).
Booking Service: For the purposes of the Home-Sharing Program (Sec. 5C.3.2.), booking service is defined pursuant to Sec. 5C.3.2.B. (Definitions) as any reservation or payment service provided by a person that facilitates a short-term rental transaction between a person and a prospective guest or transient user, and for which the person collects or receives, directly or indirectly through an agent or intermediary, a fee in connection with the reservation or payment of services provided for the transaction.
Boulevard: Boulevard is defined as any public right-of-way designated as a Boulevard I or II on the Citywide General Plan Circulation System maps of the Circulation Element of the General Plan.
Build-To Depth: Pursuant to Sec. 3C.1.2. (Build-To Depth), build-to depth is defined as the depth of the build-to zone starting at the minimum building setback and continuing inward for the maximum build-to depth for the full width of the lot.
Build-To Width: Pursuant to Sec. 3C.1.3. (Build-To Width), build-to width is defined as the cumulative building width that shall occupy the build-to zone, relative to the width of the lot at the frontage lot line.
Build-To Zone: Build-to zone is defined as the area on a lot located behind the minimum frontage lot line building setback and continuing inward to the maximum build-to depth, and extending the full width of the lot.
Building: Building is defined as a covered and enclosed structure intended for human occupancy.
Building Break: Building break is defined as the minimum distance that structures are required to be separated in order to establish them as separate buildings.
Building Coverage: Pursuant to Sec. 2C.2.1. (Building Coverage), building coverage is defined as the percentage of lot area covered by buildings or structures.
Building Elevation: Building elevation is defined as an orthographic projection of the exterior face of a building, represented as a two-dimensional drawing of the building facade. Building elevations have an angle of elevation of zero degrees (horizontal).
Building Entrance: Building entrance is defined as a door providing access from the public realm to the interior of a building.
Building Envelope: Building envelope is defined as the physical barrier (including walls, roof, foundation, windows, and doors) that separates a building's interior from its exterior environment.
Building Facade: See facade.
Building Face: Building face is defined as the outer surface of a building facade, which would not include recesses or encroachments.
Building Footprint: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.1. (Building Footprint), building footprint building is defined as the area of a lot occupied by a building, measured horizontally. Also referred to as "structure footprint".
Building Frontage: Building frontage is defined as the projection of the exterior walls upon the street used for street frontage, as measured perpendicular to the edge of the street. For walls that are not parallel to the street, the building frontage shall include the wall that, other than open parking stalls, has direct and unimpeded access to the street.
Building Module: Building module is defined as sub-areas of a building footprint used in the building module method to determine grade plane elevation. See Sec. 14.2.9.D. (Grade Plane Elevation).
Building Perimeter: Building perimeter is defined as the perimeter of a building footprint, See Sec. 14.2.1. (Building Footprint).
Building Permit: Building permit is defined as a permit obtained pursuant to Chapter IX. (Building Regulations), Sec. 91.106.1.1. (Building Permit) of this Code.
Building Permit Application: For the purposes of Sec. 15.4.3. (Affordable Housing Linkage Fee), building permit application is defined as plans submitted to the Department of Building and Safety pursuant to Sec. 13B.10.1.B.2. (Vesting of Development Plan).
Building Setback: Pursuant to Sec. 2C.2.2. (Building Setback), building setback is defined as the area between a lot boundary and the minimum required setback, represented with a dotted white line and bounded by the buildable area.
Building Site: See lot.
Building Width: Pursuant to Sec. 2C.5.1. (Building Width), building width is defined as the horizontal dimension of any building or collection of abutting buildings on a lot.
Bulkhead: Pursuant to Sec. 3D.9.1.4.C.4. (Bulkhead), bulkhead is defined as a wall located beneath a display window on the ground story facade that elevates a window above the exterior finished grade and the interior finished floor surface.
C
California Coastal Act: California Coastal Act is defined by California Public Resources Code, Div. 20. (California Coastal Act), Sec. 30000., et seq.
California Environmental Quality Act: The California Environmental Quality Act (CEQA), is defined pursuant to the California Public Resources Code, Sec. 21000. et seq. and the CEQA Guidelines.
California Native Plant Library: California native plant library is defined as a library of native plants maintained by the Theodore Payne Foundation.
California State Accessibility Standards: California state accessibility standards is defined by the provisions established in the California Building Standards Code, Title 24. (Physical Access Regulations).
Caliper: Caliper is defined as the diameter measurement of the stem or trunk of nursery stock. For the measurement of caliper, see Sec. 4C.6.4.D.10. (Caliper).
Calvo Exclusion Area: Calvo exclusion area is defined as the lots identified as being in a Calvo Exclusion Area, as established in Sec. 1.5.7. (Coastal Zone Map).
Canes: Canes is defined as a primary stem which starts at a point not higher than 1⁄4 the height of the plant.
Caretaker Unit: Caretaker unit is defined as a dwelling unit designed for use solely by a watchman, manager, or caretaker (including their family) of a permitted use which requires 24-hour supervision and is located on the same lot with the permitted use.
Carpool: Carpool is defined as a vehicle carrying two to five persons to and from work on a regular schedule.
Categorically Excluded Development: For the purposes of Sec. 13B.9.2 (Coastal Development Permit (Post-Certification)), categorically excluded development is defined as a development, which is excluded from the Coastal Development Permit requirements pursuant to a categorical exclusion order adopted by the Coastal Commission that sets forth the specific categories of development that qualify for the exclusion within a specific geographic area, and which establishes that those categories of development in the specified geographic areas will have no potential for significant adverse effects, either individually or cumulatively on coastal resources or on public access to or along the coastline.
Cemetery: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.3.1. (Cemetery), cemetery is defined by California Health and Safety Code, Sec. 7003. (Definitions). A cemetery includes columbarium, crypt, and mausoleum facilities integrated within a burial ground. This use does not include crematoriums, for such uses see Sec. 5D.6.10. (Postmortem Services).
CEQA Clearance: CEQA clearance is defined as any determination, finding or certification authorized or required under CEQA to approve a project in compliance with CEQA. CEQA Clearances include, but are not limited to, (i) a determination that an approval does not require CEQA review, in whole or in part, either due to the applicability of an exemption or because the City action is not a project, (ii) a finding that the City may adopt a Negative Declaration or a Mitigated Negative Declaration, (iii) the certification of an Environmental Impact Report, or (iv) a finding that a project was adequately assessed in a prior adopted Negative Declaration or certified Environmental Impact Report, including through the use of an addendum.
CEQA Guideline: CEQA guideline is defined by California Code of Regulations, Title 14, Chapter 3, Sec. 15000, et seq.
Certificate of Appropriateness: For the purposes of Historic Preservation (Div. 13B.8.), certificate of appropriateness is defined as an approved certificate issued for the construction, additions over established thresholds outlined in Sec. 13B.8.4. (Review of Conforming Work), demolition, reconstruction, alteration, removal, or relocation of any publicly or privately owned building, structure, landscaping, natural feature, or lot within a Historic Preservation Overlay Zone that is identified as a contributing element in the historic resources survey for the zone, including street features, furniture or fixtures.
Certificate of Compatibility: For the purposes of Historic Preservation (Div. 13B.8.), certificate of compatibility is defined as an approved certificate issued for the construction of a new building or structure on a lot, demolition, or building replacement of an element, identified as noncontributing, or not listed, in the historic resources survey for the zone.
Certificate of Occupancy: Certificate of Occupancy is defined as a certificate issued by the Department of Building and Safety in accordance with Chapter IX. (Building Regulations), Sec. 91.109. (Certificate of Occupancy) of this Code authorizing the use of land, a building or structure or portion thereof, or a trailer park or portion thereof. See Sec. 1.4.2.C. (Certificate of Occupancy).
Chamfered Corner: Chamfered corner is defined as an architectural element at a corner of a building adjacent to a street intersection where a tertiary building face transitions between two otherwise intersecting primary building faces at an angle between 30 and 60 degrees measured from both primary building faces. For an illustrative example, see Sec. 3C.1.3.C.2. (Standards).
Change of Use: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.15.B.6.a. (Change of Use), change of use is defined as work that includes a change or expansion in the permitted use of any portion of an existing building or lot from one use defined in Part 5D. (Use Definitions) to any other use defined in Part 5D. (Use Definitions). Change of use does not include any temporary uses. For temporary uses, see Sec. 14.2.15.B.7. (Temporary Use).
Character Frontage: Character frontage is defined as a Frontage District established in Div. 3B.9. (Character Frontage District).
Citation: For the purposes of Sec. 5C.3.2. (Home-Sharing Program), citation is defined as any enforcement citation, order, ticket or similar notice of violation, relating to the condition of or activities at a person’s primary residence or property, issued by the Department of Building and Safety, Los Angeles Housing Department, Los Angeles Police Department, or Los Angeles Fire Department, including an Administrative Citation issued pursuant to Chapter I. (General Provisions and Zoning), Article 1.2. (Administrative Citations) of this Code.
City: City is defined as the City of Los Angeles, California.
City Council: City Council is established by City Charter, Sec. 200 (City Officers). See also Sec. 13A.1.2. (City Council).
City Engineer: City Engineer is defined pursuant to Article 6. (City Engineer) of the LAAC.
City Hall Height Restriction: Pursuant to Sec. 2C.4.4. (City Hall Height Restriction), City Hall height restriction is defined as a restriction to the vertical dimension of a building based on proximity and height relative to Los Angeles City Hall.
City Planning Commission: City Planning Commission is defined pursuant to City Charter, Sec. 551. (City Planning Commission).
Civic Facility: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.3.2. (Civic Facility), civic facility is defined as any publicly accessible facility that provides governmental or cultural services to the general public and is operated by or in partnership with a governmental institution. A civic facility includes a post office, civic center, community center, public museum, courthouse, government office, or library.
Civic Facility: Local: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.3.2.A. (Civic Facility: Local), civic facility: local is defined as a civic facility that occupies no more than 50,000 square feet of total floor area. This use does not include similar uses that occupy more than 50,000 square feet of total floor area; for such uses see Sec. 5D.3.2.B. (Civic Facility: Regional).
Civic Facility: Regional: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.3.2.B. (Civic Facility: Regional), civic facility: regional is defined as a civic facility that occupies more than 50,000 square feet of total floor area. This use does not include similar uses that occupy 50,000 square feet or less of total floor area; for such uses see Sec. 5D.3.2.A. (Civic Facility: Local).
Civic Fleet Services: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.3.3. (Civic Fleet Services), civic fleet services include maintenance, storage, and management of government or publicly operated motor vehicles, such as school buses, municipal transit vehicles, emergency response vehicles, public utility vehicles, or waste hauling vehicles, in service of any civic facility use. Where uses, such as dispatch, do not include motor vehicle maintenance or storage, they are allowed pursuant to Sec. 5D.3.2. (Civic Facility).
Clear Depth: Clear depth is defined as the horizontal dimension of the occupiable portion of a building or structure at the narrowest point.
Clear Height: Clear height is defined as the vertical dimension of the occupiable portion of a building or structure at the shortest point.
Clear Width: Clear width is defined as the horizontal dimension of the occupiable portion of a building or structure at the narrowest point (unless otherwise noted).
Coastal Bluff: For the purposes of Sec. 13B.9.2. (Coastal Development Permit (Post-Certification)), coastal bluff is defined as the upper termination of a bluff, cliff, or seacliff. In cases where the top edge of the cliff is rounded away from the face of the cliff as a result of erosional processes related to the presence of the steep cliff face, the bluff line or edge shall be defined as that point nearest the cliff beyond which the downward gradient of the surface increases more or less continuously until it reaches the general gradient of the cliff. In a case where there is a steplike feature at the top of the cliff face, the landward edge of the topmost riser shall be taken to be the cliff edge. The termini of the bluff line, or edge along the seaward face of the bluff, shall be defined as a point reached by bisecting the angle formed by a line coinciding with the general trend of the bluff line along the inland facing portion of the bluff. The minimum length of bluff line or edge used in making these determinations is 500 feet.
Coastal Development: For the purposes of Sec. 13B.9.2. (Coastal Development Permit (Post-Certification)), coastal development is defined as any of the following on land, in or under water: the placement or erection of any solid material or structure; the discharge or disposal of any dredged material or of any gaseous, liquid, solid or thermal waste; the grading, removing, dredging, mining or extraction of any materials; any change in the density or intensity of use of land, including, but not limited to, subdivisions pursuant to the Subdivision Map Act (commencing with California Government Code, Sec. 66410), and any other division of land, including lot splits, except where the land division is brought about in connection with the purchase of the land by a public agency for public recreational use; any change in the intensity of use of water or of access to the water; construction, reconstruction, demolition or alteration of the size of any structure, including any facility of any private, public or municipal utility; and the removal or harvesting of major vegetation other than for agricultural purposes, kelp harvesting, and timber operations, which are in accordance with a timber harvesting plan submitted pursuant to the provisions of the Z’bergNejedly Forest Practice Act of 1973 (commencing with Sec. 4511 of the Public Resources Code).
Coastal Zone: For the purposes of Sec. 13B.9.2. (Coastal Development Permit (Post-Certification)), coastal zone is defined as that land and water area specified on the maps cited in Sec. 30103 of the Public Resources Code, extending seaward to the State’s outer limit of jurisdiction, including all offshore islands, but with some additional criteria for special areas as specified in Sec. 30103.5 and 30166 of the Public Resources Code.
Collection Bin: Collection bin is defined as any box, canister, receptacle, or other container that can be opened and closed, and is used for collecting salvageable personal property, including, but not limited to, clothing, shoes, books, and household items for periodic off-site processing and/or redistribution. For purposes of this definition, salvageable personal property shall not include recyclable materials not intended for re-use, including, but not limited to, newspapers, plastic, glass, aluminum, electronics, toxic or hazardous materials, and solid waste; nor any personal property that, because of its size, does not fit inside the collection bin. See Sec. 13B.10.3.A.2. (Definitions).
Collector Street: Collector street is defined as any public right-of-way designated as a collector street on the Citywide General Plan Circulation System maps of the Circulation Element of the General Plan.
Commercial Message: For the purposes of Sec. 4C.11.1.E.3. (Original Art Murals, Vintage Original Art Murals & Public Art Installations), commercial message means any message that advertises a business conducted, services rendered, or goods produced or sold.
Commercial Vehicle: Commercial vehicle is defined as any vehicle, excluding household moving rental trucks and utility rental trailers, which when operated upon a highway is required to be registered as a commercial vehicle by the Vehicle Code of the State of California, or by any other jurisdiction, and that is used or maintained for the transportation of persons for hire, compensation, or profit, or designed, used, or maintained primarily for the transportation of property.
Commercial/Industrial Conversion Project: For the purposes of Div. 11.5. (Condominiums, Community Apartments, & Stock Cooperatives) commercial/industrial conversion project is defined as an existing building used exclusively for commercial or industrial purposes, or both, proposed for conversion to a condominium or stock cooperative to be used exclusively for commercial or industrial purposes, or both through approval of a tract map or parcel map. For purposes of this definition, the term existing means that the building was constructed prior to 1945, or if it was built after 1945, a Certificate of Occupancy was issued for the building prior to the time of map application.
Commercial/Industrial to Residential Conversion Project: For the purposes of Div. 11.5. (Condominiums, Community Apartments, & Stock Cooperatives) commercial/industrial to residential conversion project is defined as an existing building used exclusively for commercial or industrial purposes, or both, proposed for conversion to a condominium, stock cooperative or community apartment to be used exclusively for residential purposes through approval of a tract map or parcel map. For purposes of this definition, the term existing means that the building was constructed prior to 1945 or, if it was built after 1945, a Certificate of Occupancy was issued for the building prior to the time of map application.
Commissary Kitchen: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.2. (Commissary Kitchen), a commissary kitchen is defined as a kitchen facility used for cooking and preparing food to be primarily served and consumed off-site. This definition includes multi-tenant shared kitchen facilities, order fulfillment kitchens, and catering kitchen facilities. The following uses are allowed when incidential to the kitchen facility: research and teaching facilities, commercial food processing, and order fulfillment pick-up lobbies.
Common Indoor Amenity Space: Pursuant to Sec. 2C.3.3.C.5. (Common Indoor Amenity Space), common indoor amenity space is defined as a type of amenity space that is covered or enclosed, is legally required to be open to all tenants of a building, is intended to create opportunities for social and recreational activity for tenants, and meets all of the standards in Sec. 2C3.3.C.5. (Common Indoor Amenity Space).
Common Lot Line: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.12.B.3. (Common Lot Line), common lot line is defined as any lot line shared by multiple lots. Common lot lines include all side lot lines and rear lot lines and may include special lot lines in Dual Frontage Districts (Div. 3B.8.).
Common Outdoor Amenity Space: Pursuant to Sec. 2C.3.3.C.1. (Common Outdoor Amenity Space), common outdoor amenity space is defined as a type of amenity space that is outdoors, open to all tenants of a building, and meets the standards of Sec. 2C.3.3.C.1. (Common Outdoor Amenity Space).
Community Apartment Project: Community apartment project is defined pursuant to California Business and Professions Code, Sec. 11004.
Community Assembly: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.3.8. (Community Assembly), community assembly is defined as any non-residential and not-for-profit facility that is oriented around an assembly space used primarily for the temporary gathering of people for a shared social purpose. Access to the general public may be limited based on association. Community assembly includes any place of worship, community meeting room, private club, event space, assembly hall, social club, or union hall.
Community Assembly: Local: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.3.8.A. (Community Assembly: Local), community assembly: local is defined as any community assembly use that includes an assembly space 2,000 square feet or less. This use does not include similar uses that occupy more than 2,000 square feet of total assembly space floor area, for such uses see Sec. 5D.3.8.B. (Community Assembly: Regional).
Community Assembly: Regional: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.3.8.B. (Community Assembly: Regional), community assembly: regional is defined as any community assembly use that includes an assembly space larger than 2,000 square feet. This use does not include similar uses that occupy 2,000 square feet or less of total assembly space floor area, for such uses see Sec. 5D.3.8.A. (Community Assembly: Local).
Community Care Facilities: See community care facility.
Community Care Facility: Community care facility is defined as any place licensed by the State of California that is maintained and operated as a residential facility or as a social rehabilitation facility to provide non-medical residential care, day treatment, adult day care, or foster family agency services for persons in need of services, supervision, or assistance essential for sustaining the activities of daily living, as defined in the California Health and Safety Code, Sec. 1502 (a). (Definitions). The term includes halfway house, non-medical assisted living, and substance abuse treatment operation. For residential community care facility see Sec. 5D.2.4.A. (Supportive Housing: General). For non-residential community care facility see Sec. 5D.3.10. (Social Services).
Community Plan Implementation Overlay: Community Plan Implementation Overlay is defined as a zoning overlay adopted for a community plan area, which provides supplemental development regulations by defined subareas, which may include, public benefits incentives programs available, amount of floor area awarded for public benefits incentives programs, applicable local affordable housing incentive program sets, and development standards. See Sec. 8.2.2. (Community Plan Implementation Overlay).
Condominium: Condominium is defined pursuant to California Civil Code, Chapter 1, Sec. 783.
Contributing Element: For the purposes of Div. 13.B.8. (Historic Preservation), contributing element is defined as any building, structure, landscaping, natural feature identified on the historic resources survey as contributing to the Historic significance of the Historic Preservation Overlay Zone, including a building or structure which has been altered, where the nature and extent of the alterations are determined reversible by the historic resources survey.
Controlled Drilling Site: Controlled drilling site is defined as that particular location within an oil drilling district in an urbanized area upon which surface operations for the drilling, deepening, or operation of a hole or well associated with an oil, gas, or hydrocarbon well, or any incidental operation are permitted subject to the conditions prescribed by written determination by the Zoning Administrator.
Conversion Project: For the purposes of Article 11. (Division of Land), a conversion project is an existing building proposed for conversion to a condominium, stock cooperative, or community apartment through approval of a tract map or parcel map. For purposes of this definition, the term existing means that the building was constructed prior to 1945 or, where built after 1945, a Certificate of Occupancy was issued for the building prior to the time of map application. Conversion project includes residential conversion project, residential to commercial/industrial conversion project, and commercial/industrial to residential conversion project.
Corner Lot: Corner lot is defined as a lot situated at the intersection of two or more streets having an angle of intersection of not more than 135 degrees.
Covered: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.2.A.1. (Covered), covered is defined as a space or structure with less than 25 percent of its area open to the sky.
Covered Area: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.2. (Covered Area (%)), covered area is defined as the measurement of how open an occupiable space is to the sky.
Cultural: For the purposes of Historic Preservation (Div. 13B.8.), cultural is defined as anything pertaining to the concepts, skills, habits, arts, instruments or institutions of a given people at any given point in time.
Cultural Heritage Commission: Cultural Heritage Commission is defined pursuant to Article 1. (Cultural Heritage Commission) of the LAAC.
D
Day Laborer: Day laborer is defined as any person who offers themselves to be hired as a laborer for a day, or some other temporary basis.
Decision Maker: Decision maker is defined as the agency or official charged with rendering a formal decision on an application subject to Article 13. (Administration). For the purposes of Sec. 13B.11.1. (Environmental Review Procedures), see Sec. 13B.11.1.D.2. (Decision Maker).
Dedication of Land: Dedication of land is defined as a conveyance of land in fee simple or as an easement by its owner for public uses, reserving to themselves no other rights than such as are compatible with the full exercise and enjoyment of the public uses to which the property has been devoted.
Demolition: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.15.B.8. (Demolition), demolition is defined as the removal of an entire structure or building. For the purposes of Div. 13B.8. (Historic Preservation), demolition is defined as the removal of more than 50 percent of the perimeter wall framing, the removal of more than 50 percent of the roof framing, or the substantial removal of the exterior of a facade in the Street-Visible Area.
Density Bonus: Density bonus is defined as a density increase over the otherwise maximum allowable residential density under the applicable Zoning Code, and zoning designation, or Specific Plan, granted pursuant to Sec. 9.2.1. (Density Bonus).
Department: Department is defined as the Department of City Planning, unless otherwise indicated. See City Charter, Sec. 550. (Powers and Duties of the Department).
Department of Building and Safety: The Department of Building and Safety is defined pursuant to Sec. 22.20. (The Department) of the LAAC.
Department of City Planning: Department of City Planning is defined pursuant to City Charter, Sec. 550. (Powers and Duties of the Department).
Designated Historic Resource: Designated historic resource is defined as a building, structure, object, landscaping element, or natural feature listed or designated as a historic resource, either individually, or as a contributor to a historic district, at the local, state, or national level, including but not limited to listing in the National Register of Historic Places or California Register of Historical Resources, or designation as a Historic-Cultural Monument or as an Historic Preservation Overlay Zone.
Destroyed: Destroyed is defined as damaged so as to not be habitable, or having lost 75 percent of replacement value, as determined by the Department of Building and Safety.
Detention Facility: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.3.4. (Detention Facility), detention facility is defined as any facility where persons are incarcerated, or otherwise involuntarily confined under the jurisdiction and custody of a governmental entity. Detention facilities include correctional facilities and penal institutions.
Development: For the purposes of Sec. 13B.9.1. (Coastal Development Permit (Pre-Certification)), development is defined as: on land, in or under water, the placement or erection of any solid material or structure; discharge or disposal of any dredged material or of any gaseous, liquid, solid, or thermal waste; grading, removing, dredging, mining, or extraction of any materials; change in the density or intensity of the use of land, including, but not limited to, subdivisions pursuant to the Subdivision Map Act (commencing with Sec. 66410. of the California Government Code), and any other division of land, including, but not limited to, parcel maps and private street divisions, lot splits, lot reconfigurations, and mergers, except where the land division is brought about in connection with the purchase of such land by a public agency for public recreational use; change in the intensity of use of water, or of access thereto; construction, reconstruction, demolition, or alteration of the size of any structure, including any facility of any private, public, or municipal utility; and the removal or harvesting of major vegetation other than for agricultural purposes, kelp harvesting, and timber operations which are in accordance with a timber harvesting plan submitted pursuant to the provisions of the Z'berg-Nejedly Forest Practice Act of 1973 (commencing with Sec. 4511 of the California Public Resources Code). As used in this definition, "structure" includes, but is not limited to, any building, road, pipe, flume, conduit, siphon, aqueduct, telephone line, and electrical power transmission and distribution line.
Development Project: For the purposes of Article 15. (Fees), development project is defined as any activity involving or requiring the issuance of a building permit that results in additional housing units, additional non-residential floor area, additional single-family residential floor area, or a change of use from non-residential to residential.
Digital Display: Digital display is defined as a sign face, building face, or any building or structural component that displays still images, scrolling images, moving images, or flashing images, including video and animation, through the use of grid lights, cathode ray projections, light emitting diode displays, plasma screens, liquid crystal displays, fiber optics, or other electronic media or technology that is either independent of, attached to, integrated into, or projected onto a building or structural component, and that may be changed remotely through electronic means.
Direct Access: Direct access is defined as the ability of a person to move to and from a facility or space, without necessitating travel through any intermediate space.
Director: Director is defined as the Director of the Department of City Planning, or the Director’s designee. See Sec. 13A.1.6. (Director of Planning).
Disaster: For the purposes of Sec. 13B.9.2. (Coastal Development Permit (Post-Certification)), disaster is defined as fire, flood, wind, earthquake, or other natural or man-made disaster.
Distance: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.3.A.1. (Distance), distance is defined as the amount of space between two points.
District Boundary Height Transition: Pursuant to Sec. 2C.6.2. (District Boundary Height Transition), district boundary height transition is defined as a reduction in the maximum height of a building for a limited depth where abutting districts have substantially lower height allowances.
Divided-Lite: Divided-lite is defined as separate pieces of glass glazed between muntin bars.
Domestic Use: Domestic use is defined as for use or consumption within the household that cultivates, manufactures, or generates a good. Domestic use includes goods gifted outside of the household provided there is no reciprocal or monetary exchange.
Drilling & Production Site in the Los Angeles City Oil Field Area: Drilling & Production site in the Los Angeles City oil field area is defined as locations within an oil drilling district in the Los Angeles City Oil Field Area upon which surface operations for the drilling, deepening or operation of a hole or well associated with an oil, gas, or hydrocarbon well, or any operation incident thereto, are subject to the conditions prescribed by written determination by the Zoning Administrator.
Drip Line: Drip line is defined as a line which may be drawn on the ground around a tree, directly under its outermost branch tips, and which identifies that location where rainwater tends to drip from the tree.
Drive Aisle: Drive aisle is defined as an access lane in a parking area that accommodates vehicle circulation and access to parking stalls. Drive aisle may accommodate one-way or two-way vehicle traffic, depending on the drive aisle width provided in accordance with Sec. 4C.4.3. (Parking Area Design).
Drive-Through Facilities: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.2.2.C.3. (Drive-Through Facilities), a drive-through facility is defined a facility that provides goods or services to drivers in vehicles. Drive-through facilities include drive-through lanes consisting of queuing spaces.
Drive-Through Facility: See drive-through facilities.
Drive-Through Lane: A drive-through lane is defined as an automobile lane providing access to a service window through which goods or services are provided directly to drivers in vehicles.
Driveway: A driveway is defined as a space along a roadway that is designed to accommodate vehicle access to a drive aisle on a lot. Driveways are formed by a sloping break or cut in the curb along the roadway to allow a vehicle to drive over the curb and into the lot.
Dual Frontage: Pursuant to Div. 3B.8. (Dual Frontages), apply frontage standards along special frontage lot lines, in addition to primary and side street lot lines, on lots where multiple frontage lot lines are prioritized for a prescribed set of design and activation standards.
Dwelling: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.2.1. (Dwelling), a dwelling is defined as a housing accommodation serving as a primary residency or having an occupancy of greater than 30 consecutive days. A dwelling includes household dwelling unit, efficiency dwelling unit, and group dwelling.
Dwelling Unit: A dwelling unit is defined as a habitable residential unit serving as a residency having an occupancy of greater than 30 days consecutively.
Dwelling Units Per Lot: Pursuant to Sec. 6C.1.1. (Dwelling Units Per Lot), dwelling units per lot is defined as the maximum number of dwelling units allowed on a lot.
E
Easement: Easement is defined as a non-possessory right given to a person or entity to use another's property for a limited purpose, such as for access to other properties.
Eating & Drinking: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.3. (Eating & Drinking), eating & drinking is defined as the sale of prepared, ready-to-consume meals or drinks for consumption by the public.
Eating & Drinking: Alcohol Service: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.3.A. (Eating & Drinking: Alcohol Service), eating & drinking: alcohol service is a use that involves the serving and dispensing of alcoholic beverages primarily for consumption on-site. Eating & drinking: alcohol service includes the provision of alcoholic beverages to customers in a dining setting, while gathered at a bar or tasting room, or in conjunction with another use, such as an entertainment venue, stadium, hotel, indoor recreation, brewery or distillery. This use does not include the sale of alcoholic beverages for off-site consumption, without prepared food orders, for such uses see Sec. 5D.6.12.B. (Retail: Alcohol).
Eating & Drinking: General: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.3.A. (Eating & Drinking: General), eating & drinking: general is defined as an eating & drinking use that involves serving and sale of prepared food and drinks for on or off-site consumption. Eating & drinking: general uses includes table service at a restaurant, counter service for off-site consumption, and self-service cafeteria dining. This use does not include the dispensing of alcoholic beverages for consumption on-site, for such uses, see Sec. 5D.6.3.B. (Eating & Drinking: Alcohol Service). This use does not include the sale of alcoholic beverages for off-site consumption, without prepared food orders, for such uses see Sec. 5D.6.12.B. (Retail: Alcohol).
Efficiency Dwelling Unit: Efficiency dwelling unit is defined as a dwelling unit serving as a residency having an occupancy of greater than 30 days consecutively, and that contains only one habitable room, is limited to 455 square feet in floor area, may include a kitchenette, but may not include a full kitchen. The dwelling unit may include an exterior entry or an entry from a common interior corridor.
Electric Vehicle Charging Station: An electric vehicle charging station is defined as one or more electric vehicle charging spaces served by an electric vehicle charger or other charging equipment allowing charging of electric vehicles.
Elevation: Elevation is defined as the position or location of something along a vertical direction above or below a given vertical datum.
Elevation Projection: Elevation projection is defined as an orthographic projection of the exterior face of a building, represented as a two-dimensional drawing of the building facade. Elevation projections have an angle of elevation of zero degrees (horizontal).
Eligible Tenant: For the purposes of Div. 11.5. (Condominiums, Community Apartments, & Stock Cooperatives), eligible tenant is defined as any tenant who was a resident of the property both on the date of tentative tract map or preliminary parcel map application and the date of approval of such map, or at any time after that, and who does not intend to purchase a unit in the conversion project.
Emergency: For the purposes of Sec. 13B.9.2. (Coastal Development Permit (Post-Certification)) emergency is defined as a sudden, unexpected occurrence demanding immediate action to prevent or mitigate loss or damage to life, health, property or essential public services.
Enclosed: Pursuant to Sec. 14.1.4.A.1. (Enclosed), an enclosed space is considered to be enclosed when the perimeter of the space has an enclosure of at least 66.7 percent.
Enclosure: Pursuant to Sec. 14.1.4. (Enclosure), enclosure is defined as the measurement of how closed off an occupiable space is to its surroundings.
End Stall: An end stall is defined as the last parking stall in a row, beyond which the drive aisle does not continue.
Entertainment Venue, Indoor: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.4. (Entertainment Venue, Indoor), entertainment venue, indoor is defined as any indoor assembly use designed or intended for entertainment, includes live music venues, performing arts theaters, movie theaters, dance clubs, comedy clubs, karaoke lounges, and banquet halls.
Entertainment Venue, Indoor: Local: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.4.A. (Entertainment Venue, Indoor: Local), entertainment venue, indoor: local is defined as any entertainment venue, indoor use designed for an assembly capacity of less than 3,000 persons. For entertainment venue, indoors designed for an assembly capacity of 3,000 or greater, see Sec. 5D.6.4.B. (Entertainment Venue, Indoor: Regional). This use does not include activities established in Sec. 5D.6.13. (Sexually Oriented Business). For the inclusion of alcoholic beverages for on-site consumption, see Sec. 5D.6.3.B. (Eating & Drinking: Alcohol Service).
Entertainment Venue, Indoor: Regional: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.4.B. (Entertainment Venue, Indoor: Regional), entertainment venue, indoor: regional is defined as any entertainment venue, indoor use designed for an assembly capacity of 3,000 persons or greater. For entertainment venue, indoors designed for an assembly capacity of less than 3,000 persons, see Sec. 5D.6.4.A. (Entertainment Venue, Indoor: Local). This use does not include activities established in Sec. 5D.6.13. (Sexually Oriented Business). For the inclusion of alcoholic beverages for on-site consumption, see Sec. 5D.6.3.B. (Eating & Drinking: Alcohol Service).
Entrance Spacing: Pursuant to Sec. 3C.5.1.C.2. (Entrance Spacing), entrance spacing is defined as the distance between street-facing entrances meeting the standards of Sec. 3C.5.1.C.1. (Street-Facing Entrance General Standards).
Entry Feature: Pursuant to Sec. 3C.5.2. (Entry Feature), entry features are defined as improved design standards applied to each entrance along the public realm.
Entry Feature Option: Pursuant to Sec. 3C.5.2.C.2. (Entry Feature Options), entry feature options are defined as packages of design standards applied to each entrance along the public realm.
Environmentally Sensitive Habitat Area: For the purposes of Sec. 13B.9.2. (Coastal Development Permit (Post-Certification)) an Environmentally Sensitive Habitat Areas (ESHA) is defined as any officially mapped area in which plant or animal life or their habitats are either rare or especially valuable because of their special nature or role in an ecosystem and which could easily be disturbed or degraded by human activities and developments, and any area identified as a wetland, an environmentally sensitive habitat or as a sensitive coastal resource area, in a certified local coastal program, a certified land use plan or a certified Specific Plan.
Equine: Equine is defined as any horse, pony, donkey, burro, or mule which is 12 months of age or older, and is issued a current Equine License by the City Department of Animal Services. An animal which is under 12 months of age, and is the offspring of or is unweaned and being nursed by a female equine lawfully kept on the property where said animal is kept, shall not be considered an equine.
Evaluation Of Non-Compliance: Pursuant to Sec. 13B.6.1. (Evaluation Of Non-Compliance), evaluation of non-compliance is the procedure to modify, discontinue, or revoke any discretionary zoning approval where needed to remedy non-compliance with the conditions of any conditional use or similar quasi-judicial approvals.
Existing Building: An existing building is defined as a building lawfully constructed and completed under a building permit, if a building permit was required.
Existing Grade: Existing grade is defined as the grade prior to grading.
Existing Uses: An existing use is defined as any use enumerated in this Zoning Code (Chapter 1A) for which any lot or portion of a lot is used at the time the property is first classified in a zone, or subsequently allowed through Div. 13B.3. (Ministerial Action), Div. 13B.1. (Legislative Action), or Div. 13B.2. (Quasi-Judicial Review).
Extended Home-Sharing: For the purposes of Sec. 5C.3.2.B.4. (Extended Home-Sharing), extended home-sharing is defined as home-sharing that is permitted for an unlimited number of days in a calendar year.
Exterior Face: Exterior face is defined as the outermost surface of any object such as a window, wall, or building.
Exterior Material Option: Pursuant to Sec. 3D.10.3. (Exterior Material Options), exterior material option is defined as building products allowed for use as primary or accessory exterior wall finish material.
Exterior Modification: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.15.B.5. (Exterior Modification), exterior modification is defined as work to the exterior of a building or structure.
Exterior Wall: Exterior wall is defined as any wall which forms the envelope of a building, separating its interior from its exterior.
Extremely Low Income Household: A extremely low income household is a household whose annual income, adjusted for family size, does not exceed 30 percent of the area median income as designated for this category in California Health and Safety Code, Sec. 50106.
F
Facade: Facade is defined as the above-grade, non-roof portions of the exterior building envelope, which includes cornices, bay windows or architectural projections, of any exterior wall of a building.
Facade Area: Facade area is defined as any surface area of a facade.
Facade Modification: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.15.B.5.a. (Facade Modification) facade modification is an exterior modification that includes a change to a building facade involving a modification of its existing design or outward appearance.
Facade Plane: See Building Face.
Faces: See facing.
Facing: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.6. (Facing), facing is defined as the exterior portions of a structure that are exposed to a specified object or site element.
Feasible: For the purposes of Sec. 13B.9.1. (Coastal Development Permit (Pre-Certification)) and Sec. 13B.9.1.A.1. (Definitions), feasible is defined as capable of being accomplished in a successful manner within a reasonable period of time, taking into account economic, environmental, social and technological factors.
Fence: A fence is defined as a constructed vertical barrier of wood, masonry, wire, metal, or other manufactured material, or combination of materials erected to enclose, screen, or separate areas. A fence differs from a wall in not having a solid foundation along its entire length.
Fill: Pursuant to LAMC Chapter IX. (Building Regulations), Sec. 91.7003. (Definitions), fill is defined as a deposit of earth material placed by artificial means.
Final Map: A final map is defined as a map prepared in accordance with the provisions of Article 11. (Division of Land), and the Subdivision Map Act subject to e recordation with the Los Angeles County Recorder upon final approval by the City.
Final Tract Map: See final map.
Financial Services: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.5. (Financial Services), financial services is defined as professional services involving the investment, lending, or management of money and assets in a publicly accessible setting rather than a private office setting. For private office settings, see Sec. 5D.6.9. (Office).
Financial Services: Alternative: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.5.B. (Financial Services: Alternative), financial services: alternative is defined as financial services uses involving for-profit lending facility offering small, unsecured, short-term loans, such as bail bonds, or a use that primarily consists of check cashing services for a fee, or any business where articles of personal property may be left as security in exchange for a loan of money. Financial services: alternative include pawnshops, precious metal buyback centers, short-term credit lenders, and title loan centers. This use does not include remittance services, for such uses see Sec. 5D.6.5. (Financial Services: General).
Financial Services: General: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.5.A. (Financial Services: General), financial services: general is defined as financial services uses that provide retail banking services. Financial services: general include only those institutions engaged in the transfer and circulation of money, such as banks and credit unions. For uses such as check-cashing businesses and payday lenders, see Sec. 5D.6.5.B. (Financial Services: Alternative).
Finished Floor Elevation: Finished floor elevation is defined as the elevation of the uppermost surface of the structural floor.
Finished Grade: Finished grade is defined as the final grade of the lot which conforms to the approved plan, or where no grading work is proposed, the existing grade.
Fire Protection: For the purposes of Article 11. (Division of Land), fire protection is defined as such fire hydrants and other protective devices as required by the Chief Engineer of the Fire Department.
First Public Road Paralleling the Sea: For the purposes of Sec. 13B.9.2. (Coastal Development Permit (Post-Certification)), first public road paralleling the sea is defined as that road nearest to the sea, as defined in Sec. 30115 of the Public Resources Code, which: (a) is lawfully open to uninterrupted public use and is suitable for that use; (b) is publicly maintained; (c) is an improved, all-weather road open to motor vehicle traffic in at least one direction; (d) is not subject to any restrictions on use by the public except when closed due to an emergency or when closed temporarily for military purposes; and (e) does, in fact, connect with other public roads, providing a continuous access system, and generally parallels and follows the shoreline of the sea to include all portions of the sea where the physical features, such as bays, lagoons, estuaries and wetlands cause the waters of the sea to extend landward from the generally continuous coastline.
Flatwork: For the purposes Sec. 14.2.5.A. (Horizontal Encroachments), flatwork is defined as constructed objects 30 inches in height or less, measured from finished grade. Examples of flatwork may include, but are not limited to: pavement, sidewalk, multi-use path, patio, low deck, or stairs or ramps 30 inches in height or less.
For the purposes of Sec. 14.2.5.B. (Vertical Encroachments), flatwork is defined as constructed objects 30 inches in height or less. Examples of flatwork may include, but are not limited to: decking, walkways, patios, or planters.
Flood Hazard: Flood hazard is defined as a hazard to land or improvements due to overflow water having sufficient velocity to transport or deposit debris, scour the surface soil, dislodge or damage buildings, or erode the banks of water courses.
Floor Area: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.7. (Floor Area), floor area is defined as the cumulative amount of interior floor space on a lot, within a room, or within a covered and enclosed space.
Floor Area Ratio: Pursuant to Sec. 2C.4.1. (Floor Area Ratio (FAR)), floor area ratio or FAR is defined as the measurement of the total floor area of all buildings on a lot in relation to the size of the lot.
Focal Entry Feature: Pursuant to Sec. 3D.8.3. (Focal Entry Feature), focal entry features are design standards applied to enhance the primary entrance of a building frontage.
Focal Entry Feature Option: Pursuant to Sec. 3D.8.3.C.2. (Focal Entry Feature Options), focal entry feature options refer to packages of design standards options applied to enhance the primary entrance of a building frontage.
Food & Drink Preparation Area: Food & drink preparation area is defined as all floor area within an eating & drinking use where employees prepare food or beverages or are reserved for employee use, including kitchens, bartender stations, dishwashing facilities, storage, refrigeration closets, employee office, and break rooms.
Footcandle: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.10.1.D. (Measurement), a footcandle is a unit of illuminance. One footcandle is equivalent to one lumen per square foot and shall be measured using a light meter.
Foundation Inactive Wall Treatment Alternatives: Pursuant to Sec. 3C.4.2.E.3. (Foundation Inactive Wall Treatment Alternatives), foundation inactive wall treatment alternatives are defined as permanent design improvements located between exposed foundation walls and the public realm, designed to improve visual interest and the pedestrian experience.
Foundation Wall: A foundation wall is defined as any above-grade portion of a facade located below the finished ground story.
Freeway: Pursuant to Sec. 8.3.2. (Freeway), freeway is defined as any property owned by the California Department of Transportation (Caltrans) that is used for highway purposes.
Freight Loading Area: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.2.2.C.2. (Freight Loading Areas), freight loading area is defined as areas designated for the on-site loading and unloading of freight vehicles.
Freight Railway Facility: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.5.2. (Freight Railway Facility), a freight railway facility is defined as any railway facility accommodating the transportation of cargo by train on a railway network. Freight railway facilities include freight railway track networks and accompanying railway yards, stations, and maintenance facilities. This use does not include cargo transfer between vehicles; for such uses see Sec. 5D.5.3. (Freight Transfer Facility).
Freight Transfer Facility: Pursuant Sec. 5D.5.3. (Freight Transfer Facility), freight transfer facility is defined as a facility intended for the transshipment of freight between different modes of transport, including ship transport, rail transport, and road transport, and accompanying warehousing used in connection with such activities. This use does not include the storage of empty cargo containers; for such uses; see Sec. 5D.7.5.E. (Storage, Outdoor: Cargo Container).
Frequency: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.8. (Frequency), frequency is defined as the rate at which something occurs or is repeated over a given distance.
Front Yard: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.16.B.1. (Front Yard), a front yard is the area between a primary street lot line and an imaginary line running parallel to the primary street lot line. The imaginary line shall be drawn 15 feet back from the portion of the primary street lot line-facing facade nearest to the primary street lot line, measured perpendicularly to the lot line.
Frontage Lot Line: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.12.B.1. (Frontage Lot Line), a frontage lot line is any lot line that triggers Frontage District (Part 3B.) requirements. Frontage lot lines include all primary street lot lines and side street lot lines.
Frontage Planting Area: Pursuant to Sec. 3C.3.1. (Frontage Planting Area), a frontage planting area is defined as the area in a frontage yard designated and designed for plants.
Frontage Screen: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.8.1. (Frontage Screens), a frontage screen is defined as a device or combination of elements, including fences, walls, trees and other plants, along a frontage lot line that conceals, obstructs or protects the public realm from adjacent uses, activities, or site elements.
Frontage Screen Type: Pursuant to, Sec. 4C.8.1.C.2. (Frontage Screen Types), frontage screen types are defined as packages of standards for required frontage screens.
Frontage Yard: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.16.C.1. (Frontage Yard), frontage yard is defined as a category of yards referring to all yards that abut a frontage lot line, including front yards, side street yards, and special yards.
Frontage Yard Fence & Wall: Pursuant to Sec. 3C.3.2. (Frontage Yard Fence & Wall), frontage yard fence & wall is defined as fences, walls, and hedges that are allowed in a frontage yard.
Frontage Yard Fence & Wall Type: Pursuant to Sec. 3C.3.2.C.2. (Frontage Yard Fence & Wall Types), frontage yard fence & wall types refer to a package of standards, specified by the applied Frontage District (Part 3B.), that applies to fences, walls, and hedges located in a frontage yard.
Fueling Station: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.7.2. (Fueling Station), a fueling station is defined as any use dedicated to the sale and dispensing of vehicle fuel.
Fueling Station: Large Vehicle: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.7.2.B. (Fueling Station: Large Vehicle), fueling station: large vehicle is defined as any fueling station dedicated to dispensing fuel for large vehicles. Large vehicles include vehicles possessing three or more axles, such as trailer trucks, construction vehicles, motor homes, and recreation vehicles.
Fueling Station: Standard Vehicle: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.7.2.A. (Fueling Station: Standard Vehicle), fueling station: standard vehicle is defined as any fueling station dedicated to dispensing fuel for standard vehicles. Standard vehicles include vehicles possessing two or fewer axles, such as cars, motorcycles, sport utility vehicles, pickup trucks, and vans.
Full-service Grocery Store: Full-service grocery store is defined as a retail store which stocks a minimum inventory in the following food groups and non-perishable items: fresh and frozen meats and poultry; canned, fresh, and frozen fruits and vegetables; dairy products; cereals; canned fish; bread products; infant food and formula; shampoo; pain medication; diapers; and feminine hygiene products.
Fully Shielded Luminaire: Fully shielded luminaire is defined as a luminaire that allows no light emission above a horizontal plane through the luminaire.
Future Street or Alley: Future street or alley is defined as any real property which the owner has offered for dedication to the City for street or alley purposes, but which has been rejected by the City Council, subject to the right of the City Council to rescind its action and accept by resolution at any later date and without further action by the owner, all or part of the property as a public street or alley.
G
General Commercial Use: Pursuant to Div. 5D.6. (General Commercial Uses), general commercial uses are defined as uses that involve business activity serving the general public, including retail, professional and personal services, hospitality, and entertainment.
General Plan: The General Plan is the City’s comprehensive framework that sets forth policies, goals, and objectives to guide the physical development of the City, while outlining the vision and priorities of the City. It consists of 11 citywide elements in addition to a Land Use Element, composed of 34 Community Plans. The General Plan serves as the legal basis for all land use policy decisions. Preparation and maintenance of the General Plan is mandated by the State, pursuant to California Government Code, Title 7. (Planning and Land Use), Sec. 65300.
General Plan Land Use Designation: General Plan Land Use Designations are designations established in Appendix A to the Framework Element, which broadly identifies intensities, densities, heights, and general uses allowed where the designations are mapped on the General Plan Land Use Map, and implemented through the corresponding zoning districts from the Zoning Code, as shown in correspondence tables in Appendix A or as otherwise provided in the community plan.
Gore-Shaped Lot: A gore-shaped lot is defined as an irregularly shaped lot that includes an angle of 65 degrees or less between intersecting lot lines.
Grade: Grade is defined as the elevation or contour of the ground surface of a lot.
Grade Plane: See grade plane elevation.
Grade Plane Elevation: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.9. (Grade Plane Elevation), grade plane elevation is defined as a reference plane, representing the average elevation of the existing ground level adjoining a building and its exterior walls, from which the height of a building or structure shall be measured.
Grading: Grading is defined as any cut or fill, combination of cut and fill, or recompaction of soil, rock, or other earth materials.
Grocery Store: For the purposes of Article 15. (Fees), grocery store is defined as a project that is for a retail use of which greater than 1/2 of the floor area is devoted to the sale of food items intended for consumption or use off the premises, excluding alcoholic beverages.
Ground Floor: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.10.C. (Ground Floor), ground floor is defined as the finished floor elevation of the ground story.
Ground Floor Elevation: Pursuant to Sec. 3C.6.2. (Ground Floor Elevation), ground floor elevation is defined as the finished floor height associated with the story of a building having its finished floor elevation nearest to the finished grade.
Ground Story: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.10.A. (Ground Story), ground story is defined as the lowest story of a building meeting the criteria of either Continuous Ground Story (Typical) or Ground Story Modules pursuant to Sec. 14.2.10. (Story), depending on site and building conditions.
Ground Story Facade: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.10.B. (Ground Story Facade), ground story facade is defined as the facade of the ground story for the full height of the ground story.
Ground Story Height: Pursuant to Sec. 3C.6.1. (Ground Story Height), ground story height is defined as the floor-to-floor height of the story of a building having its finished floor elevation nearest to the finished grade.
Ground Story Inactive Wall Treatment Alternatives: Pursuant to Sec. 3C.4.2.E.3. (Ground Story Inactive Wall Treatment Alternatives), ground story inactive wall treatment alternatives are permanent design improvements located between segments of ground story active wall and the public realm, designed to improve visual interest and the pedestrian experience.
Ground Story Windows: Ground story windows are defined as any windows on the ground story facade.
Ground Surface: Ground surface is defined as any hardscape or softscape surface which is at-grade and is exterior to any building.
Ground-Mounted Equipment: Ground-mounted equipment is defined as any mechanical equipment or utility equipment that is fixed to the ground at or below grade in order to serve a building or facility on the same site. See Sec. 4C.12.2. (Ground-Mounted Equipment) for applicable development standards.
H
Habitable Room: Habitable room is defined as an enclosed space in a residential building commonly used for living purposes, but not including any lobby, hall, closet, storage space, water closet, bath, toilet, slop sink, general utility room, kitchen area, or service porch. A recess from a room or an alcove (other than a dining area), or a mezzanine having 50 square feet or more of floor area, and located where it could be partitioned off to form a habitable room, shall be considered a habitable room.
Habitable Space: Habitable space is defined as any occupiable space designed and intended for living, sleeping, eating, or cooking. Restrooms, toilet rooms, closets, halls, storage or utility spaces, and similar areas are not considered habitable spaces.
Health Center: For the purposes of Sec. 9.3.4.C.3. (Health Center Incentive Area), a health center is defined as a healthcare facility certified by the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) as a Federally Qualified Health Center (FQHC), or FQHC Look-Alike as defined by the HRSA.
Hearing Officer: A hearing officer is defined as any Department of City Planning staff member conducting a public hearing on behalf of the Director or the City Planning Commission.
Heavy Commercial Use: Pursuant to Div. 5D.7. (Heavy Commercial Uses), heavy commercial uses are defined as uses that involve the servicing and sale of motor vehicles, and businesses dedicated primarily to storage.
Heavy Industrial Use: Pursuant to Div. 5D.9. (Heavy Industrial Uses), heavy industrial uses are defined as uses involving manufacturing, processing of animal products, waste, or extraction activities, which requires siting away from the general public due to potentially adverse impacts on the immediate surroundings.
Height in Feet: Pursuant to Sec. 2C.4.2. (Height in Feet), height in feet is defined as the vertical dimension of a building or structure measured in feet.
Height in Stories: Pursuant to Sec. 2C.4.3. (Height in Stories), height in stories is defined as the vertical dimension of a building measured in stories.
Heliport: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.5.4. (Heliport), heliport is defined as any public-use, special-use, or personal-use airport, as defined by the California Code of Regulations, Title 21. Sec. 3527. (Definitions), suitable only for use by helicopters.
High-Rise Sign 1: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.11.6.C.2. (High-Rise Sign 1), a high-rise sign 1 is a sign located at least 100 feet above-grade and attached to the wall of a building.
High-Rise Sign 2: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.11.6.C.3. (High-Rise Sign 2), a high-rise sign 2 is a sign located at least 100 feet above-grade and attached to the wall of a building within close proximity to the top of the building.
Hillside Area: Pursuant to Sec. 1.5.6. (Hillside Area Map), a hillside area is defined as any area shown on the Hillside Area Map.
Historic: For the purposes of Historic Preservation (Div. 13B.8.), historic is defined as any building, structure, landscaping, natural feature, or lot, including street features, furniture or fixtures, which depicts, represents or is associated with persons or phenomena which significantly affect or which have significantly affected the functional activities, heritage, growth or development of the City, state, or nation.
Historic Preservation Overlay Zone: For the purposes of Historic Preservation (Div. 13B.8.), Historic Preservation Overlay Zone is defined as any area of the City containing buildings, structures, landscaping, natural features or lots having historic, architectural, cultural or aesthetic significance and designated as a Historic Preservation Overlay Zone.
Historic Resources Survey: For the purposes of Historic Preservation (Div. 13B.8.), a Historic Resources Survey is a document which identifies all contributing and non-contributing buildings, structures and all contributing landscaping, natural features and lots, individually or collectively, including street features, furniture or fixtures, and which is certified as to its accuracy and completeness by the Cultural Heritage Commission.
Historic-Cultural Monument: Pursuant to Sec. 22.171.10. (Procedures for Designation of Monuments) of the LAAC, a Historic-Cultural Monument (HCM) is defined as any building, structure, landscaping, natural feature, or lot designated by the City as a City Historic-Cultural Monument.
Historical Property Contract: For the purposes of Historic Preservation (Div. 13B.8.), a historical property contract is defined as a contract between an owner or owners of a Historical-Cultural Monument or a contributing element and the City, which meets all requirements of Sec. 50281 and 50282 of the California Government Code and Sec. 19.140 et seq. of the LAAC.
Historical Resource: As defined by California Public Resources Code, Sec. 21084.1., and as determined by the Director, in consultation with the Office of Historic Resources, a historical resource means those resources that meet the definition of a historical resource in Sec. 21084.1 (Historical Resources) of the Public Resources Code and Sec. 15064.5(a) (Determining the Significance of Impacts to Archaeological and Historical Resources) of the CEQA Guidelines.
Horizontal Band Articulation: Pursuant to Sec. 3D.6.3. (Horizontal Band Articulation), horizontal band articulation is defined as a continuous band of material running horizontally across a facade.
Horizontal Encroachment: Pursuant to Sec. 14.1.5.A. (Horizontal Encroachments), a horizontal encroachment is defined as a structure or assembly that extends horizontally into a space where structures are typically prohibited.
Horizontal Illuminance: Horizontal illuminance is defined as the amount of light falling on a horizontal plane, as measured with a light meter in units of footcandles.
Hospital: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.3.5. (Hospital), hospital is defined as an inpatient or outpatient healthcare facility that provides direct medical treatment to patients.
Hospital: Local: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.3.5.A. (Hospital: Local), hospital: local is defined as an inpatient or outpatient acute or subacute care facility with a capacity of 100 or fewer beds that provides direct medical treatment to patients. This use does not include outpatient facilities not providing acute or sub-acute care, for such uses see Sec. 5D.6.8. (Medical Clinic).
Hospital: Regional: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.3.5.B. (Hospital: Regional), hospital: regional is defined as an inpatient acute care and sub-acute care facility with a capacity of more than 100 beds that provides direct medical treatment to patients. This use does not include inpatient facilities providing sub-acute care with a capacity of fewer than 100 beds, for such uses see Sec. 5D.3.5.A. (Hospital: Local).
Host: For the purposes of Home-Sharing Program (Sec. 5C.3.2.), host is defined as an individual who is registered for home-sharing pursuant to Sec. 5C.3.2. (Home-Sharing Program).
Hosting Platform: For the purposes of Home-Sharing Program (Sec. 5C.3.2.), hosting platform is defined as a person that participates in short-term rental business by collecting or receiving a fee, directly or indirectly through an agent or intermediary, for conducting a booking service transaction using any medium of facilitation.
Household: Household is defined as one or more persons living together in a dwelling unit, with common access to, and common use of all living, kitchen, and eating areas within the dwelling unit.
Household Business: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.2.2. (Household Business), a household business is a use that combines a dwelling with productive uses and entrepreneurial activities within a unit or building.
Household Business: Family Child Care: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.2.2.A. (Household Business: Family Child Care), a household business: family child care is defined as the provision of non-medical care and supervision for children in the provider's primary residence for periods of less than 24 hours per day. No more than 14 children shall be in care, unless Use District standards specify otherwise. Any children under the age of 10 years who reside within the dwelling unit and are in care count toward the maximum number of children in care. This use shall comply with all regulations set forth in California Health and Safety Code, Sec. 1597.465. (Family Day Care Homes).
Household Business: Home Occupation: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.2.2.B. (Household Business: Home Occupation), household business: home occupation is defined as the incidental use of a dwelling unit for the intent of conducting a business enterprise by a primary resident of the dwelling unit. Home occupation business enterprises are limited to instructional services, personal services, office uses, and industrial homework.
Household Business: Home-Sharing: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.2.2.C. (Household Business: Home-Sharing), household business: home-sharing is defined as the use of a primary residence for lodging for periods of 30 days consecutively or less, and no more than 120 days annually. The use of a dwelling unit for home-sharing shall be in conjunction with a dwelling use. The use of a dwelling unit for home-sharing shall meet the registration and eligibility requirements pursuant to Sec. 5C.3.2. (Home-Sharing Program).
Household Business: Joint Living & Work Quarters: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.2.2.D. (Household Business: Joint Living & Work Quarters), household business: joint living & work quarters is defined as the adaptive reuse of a building or portion of a building, which is part of an adaptive reuse project, from commercial or industrial uses to household business: live/work use.
Household Business: Live/Work: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.2.2.E. (Household Business: Live/Work), household business: live/work is defined as the combination of a dwelling unit with a work space designated for productive uses and entrepreneurial activities within a single dwelling unit.
Household Dwelling Unit: Household dwelling unit is defined as a dwelling unit serving as a residency having an occupancy of greater than 30 days consecutively, and that includes a kitchen or kitchenette.
Housing Development Project: As the term "housing development" is defined in subdivision (i) of California Government Code, Sec. 65915., a development project with five or more dwelling units including mixed-use developments; and subdivisions or common interest developments as defined in California Civil Code, Sec. 4100.
I
Illuminated Canopy Sign: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.11.6.C.4. (Illuminated Canopy Sign), an illuminated canopy sign is defined as a sign integrated into an enclosed internally illuminated canopy that is attached to the wall of a building.
In-Kind: In-kind is defined as a replacement with the same material type, design, dimension, texture, detailing, and exterior appearance.
Inclusionary Housing Project: Inclusionary housing project is defined as a project involving the construction of 10 or more dwelling units which is subject to the requirements established in Sec. 5C.3.1. (Inclusionary Housing Program).
Individual with a Disability: For the purposes of Reasonable Accommodation (Sec. 13B.5.5.), as defined under the Acts, individual with a disability is any person who has a physical or mental impairment that limits one or more major life activities, anyone who is regarded as having that type of impairment or, anyone who has a record of that type of impairment.
Indoor Recreation: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.4.2. (Indoor Recreation), indoor recreation is defined as any indoor use providing sports, fitness, leisure, amusement, or recreational facilities. Indoor recreation includes the following uses when fully indoors: sports courts, health clubs, spas, fitness, martial arts, and dance studios, gymnasiums, aquatics centers, bowling alleys, billiard halls, gaming arcades, ice skating and roller rinks, skate parks, play facilities, and amusement rides.
Indoor Recreation: Commercial: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.4.2.B. (Indoor Recreation: Commercial), indoor recreation: commercial is defined as any indoor recreational use owned or operated by a private or commercial entity. This use does not include associated spectator facilities with seating capacity greater than 500 seats, for such uses see Sec. 5D.4.1. (Amphitheater or Stadium).
Indoor Recreation: Public: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.4.2.A. (Indoor Recreation: Public), indoor recreation: public is defined as any indoor recreational use owned or operated by or in partnership with a public institution.
Industrial Homework: Industrial homework is the same as defined in California Labor Code, Sec. 2650.
Instructional Services: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.6. (Instructional Services), instructional services are defined as any establishment primarily engaged in offering avocational or recreational educational courses to adults or children for the purposes of play, amusement, or relaxation, including education offered for the intent of teaching the fundamentals, skills, or techniques of a hobby or activity. Includes establishments offering programs in art, cooking, drama, driving, language, music, sewing, tutoring, or other similar forms of self-improvement. For vocational and other educational uses, see Sec. 5D.3.9. (School).
Integrated Parking: Integrated parking is defined as a parking structure within or attached to a building that is primarily used for a non-parking uses, such as residential or commercial uses. For a parking structure to be considered an integrated parking structure, the motor vehicle use area in a building shall not be greater than the floor area of the building.
Intensification of Use: Pursuant to Sec. 14.1.15.B.6.b. (Intensification of Use), intensification of use is defined as work that increases the intensity of a use, such as an increase in dwelling units, seating capacity, or the number of people in care.
Interim Lodging Unit Housing Project: Interim lodging unit housing project is defined as the physical re-purposing or adaptation of an existing lodging unit, for use as supportive housing or transitional housing for persons experiencing homelessness or those at risk of homelessness.
Interior: Interior is defined as all enclosed and covered areas included within surrounding exterior walls of a building.
Interior Wall: Interior wall is defined as any wall which is within the building envelope and that is not separating the building's interior from its exterior.
Inundation: Inundation is defined as ponded water, or water in motion, of sufficient depth to damage property due to the presence of the water or to the deposit of silt.
J
Junior Accessory Dwelling Unit: See Chapter I. (General Provisions and Zoning), Sec. 12.03. (Definitions) of this Code.
K
Kitchen: Kitchen is defined as an area designed to be used for the preparation of food that includes a sink and has all of the following standards: 1) a refrigerator rough-in greater than 30 inches in width; 2) a gas connection or 240V electrical connection; 3) an oven and range; and 4) counter space in excess of 10 square feet.
Kitchenette: Kitchenette is defined as an area designed to be used for the preparation of food that includes a sink and meets all of the following standards: 1) a refrigerator rough-in 30 inches in width or less; 2) no gas connection or 240V electrical connection; 3) counter space 10 square feet or less.
L
Landing Platform: Landing platform is defined as the portion of a floor adjacent to an elevator, ramp, stair, or door, designed to provide a stable space to stand.
Landscaping: For the purposes of Historic Preservation (Div. 13B.8.), landscaping is defined as the design and organization of landforms, hardscape, and softscape, including individual groupings of trees, shrubs, groundcovers, vines, pathways, arbors, etc. As the term is used in the remainder of this Zoning Code (Chapter 1A), landscaping is defined as any lot non-building structure features including; standalone fences and walls, site furniture, flatwork, ground treatments, vegetation, landforms, stormwater management features, outdoor lighting, water features, or outdoor access and circulation.
Large Species Tree: Large species tree is defined as a tree with a minimum 30-foot canopy spread at maturity.
Leachates: Leachates is defined as any liquid which has come into contact with or percolated through composting or curing materials and contains extracted or dissolved substances therefrom, or any other liquid which has been generated by the decomposition process.
Leader: Leader is defined as the tip of the main stem of a plant.
Light Industrial Use: Pursuant to Div. 5D.8. (Light Industrial), light industrial uses are defined as uses involving the production, warehousing, or manufacturing of goods, materials, and products in an intensive manner that require a significant separation from residential and commercial districts.
Light Trespass: Light trespass is defined as light that falls beyond the property it is intended to illuminate.
Linkage Fee: Pursuant to Sec. 15.4.3. (Affordable Housing Linkage Fee), linkage fee is defined as the fee assessed on certain development projects in order to mitigate the impact of the additional demand for affordable housing caused by such activity.
Living Wall: Living wall is defined as a system permanently attached to the exterior building facade, supporting vegetation with its growing medium and integrated irrigation system.
Loading Space: Loading space is defined as a designated space within a motor vehicle use area that accommodates the short-term parking of a vehicle for the purposes of loading and unloading passengers, goods, or materials.
Local Coastal Program: For the purposes of Sec. 13B.9.1. (Coastal Development Permit (Pre-Certification)), Local Coastal Program is the City's land use plans and other applicable general plan elements, zoning ordinances, zoning district maps, and proposed implementing actions, which when taken together, meet the requirements of, and implement the provisions and policies of, the California Coastal Act of 1976.
Local Public Agency: For purposes of Sec. 9.4.1. (Permanent Supportive Housing Incentive Program), Sec. 9.4.2. (Interim Conversions of Lodging Units Program), local public agency is defined as an agency, identified on a list maintained by the Department of City Planning, that funds supportive housing and transitional housing for persons experiencing homelessness or at risk of homelessness.
Local Street: Local street is defined as any public right-of-way designated as a local street on the Citywide General Plan Circulation System maps of the Circulation Element of the General Plan.
Lodging: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.7. (Lodging), lodging is defined as commercial overnight accommodations for transient occupancy, often for periods of 30 consecutive days, or less. Lodging uses shall not serve as a primary residence. Lodging uses include, hotels, motels, hostels, and bed and breakfast establishments. This use does not include uses defined in Sec. 5D.2.2.C. (Household Business: Home-Sharing). For residential housing accommodations see Div. 5D.2. (Residential Uses).
Lodging Unit: Lodging unit is defined as any habitable room or rooms, designed or used for transient occupancy by a single party, often for a period of 30 consecutive days or less. Lodging units must be associated with the lodging commercial use.
Los Angeles City Oil Field Area: Pursuant to Sec. 8.2.4.B.3.d. (Los Angeles City Oil Field Area) is defined as all land in the City within the areas identified on the maps in Ord. No. 156,166 located in Council File No. 80-3951, and shall include all oil producing zones beneath those areas, but no deeper than the third zone beneath the surface of the earth.
Los Angeles Fire Department Equipment: Los Angeles Fire Department Equipment is defined as any equipment owned or installed for the use of the Los Angeles Fire Department.
Lot: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.11. (Lot) a lot is defined as one or more parcels of land identified for the purpose of development and meets all the standards of Sec. 14.2.11. (Lot).
Lot Amenity Space: Pursuant to Sec. 2C.3.1. (Lot Amenity Space), lot amenity space is defined as an area on a lot designated to be used for active or passive recreation, including common outdoor amenity space, pedestrian amenity space, and public amenity space.
Lot Area: Pursuant to Sec. 2C.1.1. (Lot Area), lot area is defined as the amount of land area within the boundaries of a lot.
Lot Area Per Household Dwelling Unit: Pursuant to Sec. 6C.1.3. (Lot Area per Efficiency Dwelling Unit), lot area per efficiency dwelling unit is defined as the maximum number of efficiency dwelling units allowed on a lot based on lot area.
Lot Area Per Efficiency Dwelling Unit: Pursuant to Sec. 6C.1.2. (Lot Area per Household Dwelling Unit), lot area per household dwelling unit is defined as the maximum number of household dwelling units allowed on a lot based on lot area.
Lot Line: Lot line is defined as the legal boundaries of a lot, as determined pursuant to Sec. 14.2.12. (Lot Line Determination).
Lot Line-Facing Facade: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.6.B. (Lot Line-Facing Facade), lot line-facing facade is defined as the portions of any frontage applicable facade pursuant to Sec. 3A.2.2.C.3. (Frontage Applicable Facades) having no permanent structure (not including fences or walls) located between the building facade and a common lot line.
Lot Modification: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.15.B.3. (Lot Modification), lot modification is defined as the modification of the lot lines of any existing lot through the Subdivision Map Act and Article 11. (Division of Land), including the division of land as defined in California Government Code, Title 7. (Planning and Land Use), Sec. 66424.
Lot Tie: Lot tie is defined as a legally binding covenant to hold multiple lots as one.
Lot Width: Pursuant to Sec. 2C.1.2. (Lot Width), lot width is defined as the length of primary street lot lines bounding a lot.
Low Impact Development: Low impact development refers to the Low Impact Development (LID) program, which establishes requirements for stormwater and urban runoff control. The program is administered by LA Sanitation and Environment (LASAN) and is authorized by Chapter VI., Sec. 64.72. (Stormwater and Urban Runoff Pollution Control Measures for Development Planning and Construction Activities) of this Code.
Low Income Household: A low income household is a household whose annual income, adjusted for family size, does not exceed 80 percent of the area median income as designated for this category in the California Health and Safety Code, Sec. 50079.5.
Lower Income Household: A lower income household is a household whose annual income, adjusted for family size, does not exceed 80 percent of the area median income as designated for this category in California Health and Safety Code, Sec. 50079.5. Lower income households includes very low income households and extremely low income households.
Luminaire: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.10.1. (Outdoor Lighting), luminaire is defined as the complete lighting unit (fixture), consisting of a lamp or lamps, and ballasts (when applicable), together with the parts designed to distribute the light (reflector, lens, diffuser), to position and protect the lamps, and to connect the lamps to the power supply.
M
Machine Shop: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.8.1. (Machine Shop), a machine shop is defined as any facility engaged in the maintenance, repair, custom fabrication and finishing of products, parts, props, equipment, or machinery primarily using metal and woodworking machinery and tools. This use does not include the servicing of consumer goods when occupying less than 3,000 square feet in area; for such uses see Sec. 5D.6.10. (Personal Services). This use does not include motor vehicle repair and maintenance; for such uses see Sec. 5D.7.1. (Motor Vehicle Services). This use does not include the fabrication of heavy machinery used for manufacturing, motor vehicles, aircraft or watercraft; for such uses see Sec. 5D.9.2.A. (Manufacturing, Heavy: General).
Main Traveled Roadway of a Freeway: Main traveled roadway of a freeway is defined as the portion of a freeway, including interchange roadways connecting one freeway with another, which is designed for the movement of large volumes of vehicular traffic, efficiently and safely at high speed. Does not include service roadways, landscape areas, or ingress or egress ramps connecting the freeway with other streets.
Maintenance & Repair: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.15.B.9. (Maintenance & Repair), maintenance & repair is defined as work that does not qualify as a site modification, major remodel, exterior modification or new construction, and does not impact the project's ability to meet any applicable zoning requirements. Replacement of deteriorated or damaged parts of a building is considered maintenance & repair; however, in a Character Frontage District, CPIO, Conservation District, or Historic Preservation Overlay Zone, direct replacement may have additional requirements and processes. Maintenance & repair includes repair of site components such as restriping existing parking stripes, resealing parking lots, pothole repair, or replanting plants.
For the purposes of Historic Preservation (Div. 13B.8.), maintenance & repair is defined as any work done to correct the deterioration, decay of, or damage to a building, structure or lot, or any part thereof, including replacement in-kind where required, and which does not involve a change in the existing design, materials, or exterior paint color.
Major Remodel: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.15.B.2. (Major Remodel), major remodel is defined as work that includes significant removal, disassembly, or replacement of a building or structure or portions of a building or structure that does not add to or change the building footprint and meets the standards in Sec. 14.2.15.B.2. (Major Remodel).
Major Transit Stop: Pursuant to California Public Resources Code, Sec. 21155(b), California statute defines a "Major transit stop" as a site containing an existing rail transit station, a ferry terminal served by either a bus or rail transit service, or the intersection of two or more major bus routes with a frequency of service interval of 15 minutes or less during the morning and afternoon peak commute periods.
Majority: For the purposes of Article 13. (Administration), majority is defined as a majority number of the members of the respective body, not the majority of members present.
Manager Unit: See caretaker unit.
Manufacturing, Heavy: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.9.2. (Manufacturing, Heavy), manufacturing, heavy is defined as any heavy industrial use involving the making or processing of materials or components into finished products.
Manufacturing, Heavy: Chemical Products: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.9.2.B. (Chemical Products), manufacturing, heavy: chemical products is defined as any manufacturing, heavy use producing basic chemicals or manufacturing products by predominantly chemical processes. Includes, but is not limited to, production of acid, alkali, organic chemical, salt, dry color, pigment, synthetic fiber, fertilizer, explosives, or paint. This use does not include those uses defined in Sec. 5D.9.2.C. (Manufacturing, Heavy: Petroleum & Coal Products).
Manufacturing, Heavy: General: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.9.2.A. (Manufacturing, Heavy: General), manufacturing, heavy: general is defined as manufacturing that requires significant health, safety, or environmental precautions due to potential adverse impacts from the manufacturing process on immediate surroundings. This use includes, but is not limited to, the manufacturing of heavy machinery, motor vehicles, aircraft and watercraft, primary metal products, wood or paper products, metal fabrication, or manufacturing involving the processing, mixing, or refinement of inorganic raw materials. This use does not include those uses defined in Sec. 5D.9.2.B. (Manufacturing, Heavy: Chemical Products). This use does not include those uses defined in Sec. 5D.9.2.C. (Manufacturing, Heavy: Petroleum & Coal Products).
Manufacturing, Heavy: Petroleum & Coal Products: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.9.2.C. (Manufacturing, Heavy: Petroleum & Coal Products), manufacturing, heavy: petroleum & coal products is defined as any manufacturing, heavy use that processes petroleum, coal, plastic, or rubber materials into products, including the refining of petroleum, gas, or other hydrocarbons.
Manufacturing, Light: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.8.3. (Manufacturing, Light), manufacturing, light is defined as any light industrial use involving the making or processing of materials or components into new products.
Manufacturing, Light: Alcoholic Beverage: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.8.3.B. (Manufacturing, Light: Alcoholic Beverage), manufacturing, light: alcoholic beverage is defined as any manufacturing, light use where beer, wine, or other alcoholic beverages are fermented, distilled, and/or processed for distribution and sale on a wholesale basis. For retail sale of any alcoholic beverage, see Sec. 5D.6.12.B. (Retail: Alcohol).
Manufacturing, Light: Artistic & Artisanal: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.8.3.C. (Manufacturing, Light: Artistic & Artisanal), manufacturing, light: artistic & artisanal is defined as a small-scale manufacturing, light use where skilled craftspersons are integral to the creation of each product, materials, substances, or components, and may include, but are not limited to the use of hand tools or light mechanical equipment such as commercial mixers, sewing machines, wax melters, bottle sealers, paste filling machines, and button press machines. Manufacturing, light: artistic & artisanal uses are less than 5,000 square feet in area, for such uses larger than 5,000 square feet in area see Sec. 5D.8.2. (Manufacturing, Light: General).
Manufacturing, Light: Cosmetic & Pharmaceutical: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.8.2.D. (Manufacturing, Light: Cosmetic & Pharmaceutical), manufacturing, light: cosmetic & pharmaceutical is defined as any manufacturing, light use where cosmetics, soaps, or pharmaceutical drugs are produced. This use includes, but is not limited to, manufacturing of makeup products, deodorants, shampoos, hair dyes, perfumes, skin moisturizers, medications, or supplements.
Manufacturing, Light: Electronics: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.8.2.E. (Manufacturing, Light: Electronics), manufacturing, light: electronics is defined as any manufacturing, light use involved in the manufacturing or assembly of computer or electronic products, electrical equipment, appliances, fixtures, or electronic product components. This use includes testing and repair incidental to the product or component assembly.
Manufacturing, Light: Food & Drink: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.8.3.F. (Manufacturing, Light: Food & Drink), manufacturing, light: food & drink is defined as any manufacturing, light use where food or drink products are processed or manufactured. The food and beverage products manufactured in these facilities are typically sold to wholesalers or retailers for distribution to consumers. This use includes, but is not limited to, the processing and packaging of the following: sodas & juices, coffee & tea, ice, dairy products, fruit, nut, & vegetable products, grain & oilseeds, baked or fried goods, sugar and confectionery products, animal food, and tobacco products. This use includes food & drink products composed of previously rendered animal products. This use does not include meat processing, the rendering of animal products, or animal slaughtering, for such uses see Sec. 5D.9.1. (Animal Products Processing). This use does not include breweries, distilleries, and wineries, for such uses see Sec. 5D.8.2.B. (Manufacturing, Light: Alcoholic Beverage).
Manufacturing, Light: Garment & Accessory: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.8.3.G. (Manufacturing, Light: Garment & Accessory), manufacturing, light: garment & accessory is defined as any manufacturing, light use involving the cutting, stitching or assembly of materials to produce finished clothing, footwear, and accessories. Specific activities include, but are not limited to, sewing of finished textiles, printing or stenciling of designs on garments, assembly of accessories or footwear, or the knitting of finished garments. This use does not include those uses defined in Sec. 5D.8.2.H. (Manufacturing, Light: Textile).
Manufacturing, Light: General: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.8.2.A. (Manufacturing, Light: General), Manufacturing, light: general is defined as the manufacturing of finished goods intended to be sold as consumer goods to the general public, including devices and instruments used in a workplace. This use includes, but is not limited to, the manufacturing and assembly of the following: medical equipment and supplies; semiconductors and electronic instruments; signs and printed material; musical instruments; jewelry; toys; furniture; crates; boxes; and barrels. This use does not include those uses defined in Sec. 5D.9.2.A. (Manufacturing, Heavy: General).
Manufacturing, Light: Textile: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.8.3.H. (Manufacturing, Light: Textile), manufacturing, light: textile is defined as any manufacturing, light use involving mechanized production of fibers and fabrics used to create materials for the production of garments and accessories. Specific activities include, but are not limited to, textile spinning, weaving, dying, printing, or finishing. This use does not include those uses defined in Sec. 5D.8.2.G. (Manufacturing, light: Garment & Accessory).
Marquee Sign: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.11.6.C.5. (Marquee Sign), a marquee sign is defined as a sign attached to the periphery of a marquee.
Mayor: Mayor is defined pursuant to Sec. 200. (City Officers) of the City Charter.
Mechanical Equipment: Mechanical equipment is defined as any building mechanical services equipment including heating, cooling, and ventilation equipment; electrical systems, plumbing or piping; or any sustainable energy systems.
Mechanical Exhaust Outlet: Mechanical exhaust outlet is defined as any pneumatic conveyor or port which expels any air or gas as part of the function of any building mechanical systems.
Medical Clinic: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.8. (Medical Clinic), medical clinic is defined as an outpatient healthcare facility that provides direct medical, dental, or therapeutic services to patients. This use does not include healthcare facilities providing acute, subacute or inpatient healthcare; for such uses see Sec. 5D.3.8.A. (Hospital: Local) and Sec. 5D.3.8.B. (Hospital: Regional).
Mezzanine: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.10.H. (Mezzanine), mezzanine is defined as an intermediate level within a story of a building.
Mineral & Ore Extraction: Pursuant to 5D.9.6. (Mineral & Ore Extraction), mineral & ore extraction is defined as any use engaged in the extraction of metallic minerals, nonmetallic minerals, or other natural compounds. This use includes the exploration or development of any lot for such purposes, and any preparation of those resources until the point of shipment from the producing property. This use includes metal ore mining, nonmetallic mineral mining, and quarrying. This use does not include extraction, recovery, or production of oil, natural gas, or any other hydrocarbon materials, for these activities see Sec. 5D.9.7. (Oil, Gas, or Hydrocarbon Well).
Ministerial Action: See ministerial decision.
Ministerial Decision: Ministerial decision is defined as a decision based on the non-discretionary application of objective standards. See Sec. 13A.2.1.B. (Procedural Categories).
Mobile Home: Mobile home is defined as a structure transportable in one or more sections, designed and equipped to be used as a dwelling unit or accessory dwelling unit. This structure shall comply with all applicable provisions of the California Health and Safety Code, Div. 13. (Housing), Part 2. (Manufactured Housing). The term “mobile home” shall not include a factory-built home, recreational vehicle, or commercial coach.
Mobile Home Park: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.2.3. (Mobile Home Park), mobile home park is defined as any lot or portion of a lot used to provide rental or lease sites for two or more individual manufactured homes, mobile homes, or park trailer used to provide housing accommodations.
Model Dwelling: Model dwelling is defined as a structure designed to be temporarily used as an example of a dwelling unit which have been built or are proposed to be built in the same subdivision or multiple unit development. See Sec. 11.1.3.M. (Model).
Moderate Income Household: A moderate income household is a household whose annual income, adjusted for family size, does not exceed 120 percent of the area median income as designated for this category in California Health and Safety Code, Sec. 50093.
Module: Module is defined as each of a set of parts or independent units that can be used to construct, or as a construct for, a more complex system. See Sec. 14.2.10.A.2. (Ground Story Modules). See Sec. 2C.4.3. (Height in Stories). See Sec. 14.2.9.D. (Building Module Method).
Monument: For the purposes of Div. 13B.8. (Historic Preservation), monument is defined as any building, structure, landscaping, natural feature, or lot designated as a City Historic-Cultural Monument.
Monument Sign: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.11.6.C.6. (Monument Sign), monument sign is defined as a freestanding sign which is wholly independent of a building for support, erected directly upon the original grade or finished grade, or that is raised no more than 12 inches from the grade to the bottom of the sign.
Motor Vehicle: Motor vehicle is the same as defined in the Code of Federal Regulations, Title 40., Sec. 85.1703. (Definition of Motor Vehicle).
Motor Vehicle Sales & Rental: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.7.3. (Motor Vehicle Sales & Rental), motor vehicle sales & rental is defined as any heavy commercial use that sells, rents, or leases motor vehicles.
Motor Vehicle Sales & Rental: Household Moving Truck Rental: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.7.3.C. (Motor Vehicle Sales & Rental: Household Moving Truck Rental), motor vehicle sales & rental: household moving truck rental is defined as any motor vehicle sales & rental use involving the rental of household moving rental trucks or utility trailers. This use does not include the outdoor storage of vehicles that do not comprise an establishment's rental inventory, for such uses see, Sec. 5D.7.5.C. (Storage, Outdoor: Large Vehicle).
Motor Vehicle Sales & Rental: Large Vehicle: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.7.3.B. (Motor Vehicle Sales & Rental: Large Vehicle), motor vehicle sales & rental: large vehicle is defined as any motor vehicle sales & rental use involving indoor or outdoor display of three or more new or used large vehicles for sale, rental, or lease. Large vehicles include vehicles possessing three or more axles, such as trailer trucks, construction vehicles, motor homes, and recreational vehicles, in addition to recreational boats and watercraft. This use does not include the outdoor storage of vehicles that do not comprise an establishment's sale or rental inventory, for such uses see, Sec. 5D.7.5.C. (Storage, Outdoor: Large Vehicle).
Motor Vehicle Sales & Rental: Standard Vehicle: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.7.3.A. (Motor Vehicle Sales & Rental: Standard Vehicle), motor vehicle sales & rental: standard vehicle is defined as any motor vehicle sales & rental use involving indoor or outdoor display of three or more new or used standard vehicles for sale, rental, or lease. Standard vehicles include vehicles possessing two or fewer axles, such as cars, motorcycles, sport utility vehicles, pickup trucks, and vans. This use does not include the outdoor storage of vehicles that do not comprise an establishment's sale or rental inventory, for such uses see, Sec. 5D.7.5.B. (Storage, Outdoor: Standard Vehicle).
Motor Vehicle Services: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.7.1. (Motor Vehicle Services), motor vehicle services are defined as a use involving the diagnosing of malfunctions, repair, or maintenance of motor vehicles.
Motor Vehicle Services: Car Wash: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.7.1.D. (Motor Vehicle Services: Car Wash), motor vehicle services: car wash is defined as any motor vehicle services use engaged in cleaning, washing, or waxing of motor vehicles, such as passenger cars, trucks, vans, and trailers. This use does not include wash facilities for large vehicles, for such uses see Sec. 5D.7.1.C. (Motor Vehicle Services: Large Vehicle).
Motor Vehicle Services: Heavy: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.7.1.B. (Motor Vehicle Services: Heavy), motor vehicle services: heavy is defined as any motor vehicle services use involving auto body repair or rebuilding, painting, or servicing of standard motor vehicles. This use includes the repair or rebuilding of a vehicle’s frame, roof, doors, fenders, bumpers, hood, trunk, automobile painting, and electric vehicle battery reconditioning and replacement.
Motor Vehicle Services: Large Vehicle: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.7.1.C. (Motor Vehicle Services: Large Vehicle), motor vehicle services: large vehicle is defined as any motor vehicle services use performed for large vehicles, classified for this purpose as a vehicle having three or more axles, such as trailer trucks, construction vehicles, motor homes, and recreation vehicles.
Motor Vehicle Services: Light: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.7.1.A. (Motor Vehicle Services: Light), motor vehicle services: light is defined as any motor vehicle services use involving the mechanical or electrical repair, diagnosis, maintenance or servicing of standard motor vehicles. This use includes automotive emissions testing; electrical diagnostic, battery testing, and charging; tire removal, replacement, and repair; mechanical adjustment; oil change; lubrication; sound system or alarm service and installation; and window repair. This use does not include uses defined in the following Sections: Sec. 5D.7.1.B. (Motor Vehicle Services: Heavy), Sec. 5D.7.1.C. (Motor Vehicle Services: Large Vehicle), or Sec. 5D.7.1.D. (Motor Vehicle Services: Car Wash).
Motor Vehicle Use Area: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.2.2. (Motor Vehicle Use Area), motor vehicle use area is defined as portions of a lot designed and intended for use by motor vehicles, including areas to be used by motor vehicles for circulation, maneuvering, loading, staging, queuing, service areas and areas to be used for the sale or storage of motor vehicles.
Movable Tiny House: See Chapter I. (General Provisions and Zoning), Sec. 12.03. (Definitions) of this Code.
Multi-Story Building: Multi-story building is defined as a building with one or more stories constructed above the ground story.
N
Native Plant: Native plant is defined as any plant species listed on Calscape as occurring in the South Coast region.
Natural Feature: For the purposes of Div 13B.8. (Historic Preservation), natural feature is defined as any significant tree, plant life, geographical or geological feature identified individually or collectively on the historic resources survey as contributing to the cultural or historic significance of the Historic Preservation Overlay Zone.
Nature Reserve: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.4.3. (Nature Reserve), nature reserve is defined as an area managed so as to protect its flora, fauna, and physical features. Nature reserve includes ecological preserve, marine preserve, natural resource preserve, and water conservation area.
New Construction: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.15.B.1. (New Construction), new construction is defined as work that includes the construction of a new building or structure on a lot, whether structurally detached or attached from other existing buildings or structures on the lot. New construction includes an addition to or relocation of an existing building or structure, or the relocation of existing floor area, to another location on the lot, or to any other lot. Relocation of existing buildings or structures includes any activity that lifts any portion of the building or structure off of its foundation. New construction does not include ground mounted signs or wall mounted signs.
Non-Contributing Element: For the purposes of Div. 13B.8. (Historic Preservation), non-contributing element is defined as any building, structure, natural feature, lot, or landscaping, that is identified in the historic resources survey as a non-contributing element, or not listed in the historic resources survey.
Non-Solid Area: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.4.A.5. (Non-Solid Area), non-solid area is defined as the portions of the perimeter planes along the perimeter of a space that have no permanent structure or component obstructing the space from its surroundings. For the purpose of measuring the enclosure of a space, portions of the perimeter plane are considered non-solid area where no permanent structure or component is located within five feet of the perimeter plane, measured perpendicular to the perimeter plane and away from the subject space.
Non-Urbanized Area: Pursuant to Sec. 8.2.4.B.2.a. (Non-Urbanized Area), non-urbanized area is defined as all those portions of the City which the City Planning Commission or City Council has determined will not be detrimentally affected by the drilling, maintenance, or operation of oil, gas, or hydrocarbon wells. In making its determination, the City Planning Commission, or the City Council on appeal, shall give due consideration to the amount of land subdivided, the physical improvements, the density of population, and the zoning of the district.
Nonconforming: See nonconforming lot, nonconforming structure, nonconforming use, nonconforming sign, or nonconforming yard.
Nonconforming Building: See nonconforming structure.
Nonconforming Lot: Nonconforming lot is defined as a lot that conformed to the zoning regulations, if any, at the time it was established, but does not conform to current requirements of this Zoning Code (Chapter 1A). See Sec. 12.8.2. (Lot Area).
Nonconforming Sign: Nonconforming sign is defined as a sign that conformed to the zoning regulations, if any, at the time it was established, but does not conform to current requirements of this Zoning Code (Chapter 1A). See Sec. 12.4.2. (Sign Exceptions).
Nonconforming Structure: Nonconforming structure is defined as a structure that conformed to the regulations, if any, at the time it was established, but does not conform to current requirements of this Zoning Code (Chapter 1A). See Div. 12.1. (General Nonconforming Provisions).
Nonconforming Use: Nonconforming use is defined as a use that conformed to the zoning regulations, if any, at the time it was established, but does not conform to current requirements of this Zoning Code (Chapter 1A). See Div. 12.5.1. (Use Exceptions).
Nonconforming Yard: Nonconforming yard is defined as an existing yard that conformed to the zoning regulations, if any, at the time it was established, but does not conform to current requirements of this Zoning Code (Chapter 1A). See Div. 12.1. (General Nonconforming Provisions).
O
Occupiable: See occupiable space.
Occupiable Space: Occupiable space is defined as any area designed and intended for human occupancy with a minimum clear height of seven feet.
Off-Site Sign: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.11.3. (Off-Site Signs), off-site sign is defined as a sign that displays any message directing attention to a business, product, service, profession, commodity, activity, event, person, institution, or any other commercial message, which is generally conducted, sold, manufactured, produced, offered or occurs elsewhere than on the premises where the sign is located.
Office: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.9. (Office), office is defined as any workspace accommodating administrative, creative and business services. Office uses may be operated independently or combined with other uses, provided each of the other uses is permitted and meets the applicable standards. An office use includes workspace accommodating the following activities: administrative, clerical, legal, accounting, design, consulting, graphics and sound editing, and dry lab research.
Oil Drilling District (O): An oil drilling district established pursuant to Sec. 8.2.4. (Oil Drilling Districts).
Oil Well Class I or A: Oil well class I or A is defined as any well associated with an oil, gas, or hydrocarbon well drilled, conditioned arranged, used or intended to be used for the production of petroleum.
Oil Well Class II or B: Oil well class II or B is defined as any well associated with an oil, gas, or hydrocarbon well drilled, conditioned, arranged, used or intended to be used only for the subsurface injection into the earth of oil field waste, gases, water or liquid substances.
Oil, Gas, or Hydrocarbon Well: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.9.7. (Oil, Gas, or Hydrocarbon Well), oil, gas, or hydrocarbon wells are defined as any well or hole already drilled, being drilled or to be drilled into the surface of the earth which is used or intended to be used in connection with coring or the drilling for prospecting for or producing petroleum, natural gas or other hydrocarbon substances, or is used or intended to be used for the subsurface injection into the earth of oil field waste, gases, water or liquid substances, including any such existing hole, well or casing which has not been abandoned in accordance with the requirements of Chapter V. (Public Safety and Protection), Sec. 57.5706.3.16. (Abandonment of Oil Wells) and the mitigation monitoring program and well plugging and abandonment mitigation measures adopted with Ordinance No. 187,709 (Oil and Gas Drilling Ordinance). This use does not include any well operated by a public utility regulated by the California Public Utilities Commission.
On-Site Sign: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.11.4. (On-Site Signs), on-site sign is defined as a sign that is other than an off-site sign.
Opacity: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.13. (Opacity (%)), opacity is defined as the degree to which an object or material is impervious to rays of light or obstructs visibility.
Open Space & Recreation Use: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.4. (Open Space & Recreation), open space & recreational uses are defined as uses that provide opportunities for recreation, sport, and the enjoyment of open space and nature.
Open Space, Public: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.4.4. (Open Space, Public), open space, public is defined as publicly accessible, outdoor areas for passive recreation, which include spaces such as parks, plazas, walking trails, lawns, and picnic benches.
Open to the Sky: Open to the sky is defined as having no intervening structure between the finished floor or ground surface and the sky.
Opposing Lot Line: Opposing lot line is defined as lot lines that do not intersect at any point. Determinations as to whether irregular lot lines are opposing shall be made in accordance with Sec. 14.2.14. (Irregular Lot Lines).
Original Art Mural: Original art mural is defined as a one-of-a-kind, hand-painted, hand-tiled, or digitally printed image on the exterior wall of a building that does not contain any commercial message.
Outdoor Dining: Outdoor dining is defined as any covered or uncovered portion of an eating and drinking establishment which is unenclosed and which is used primarily for the consumption of food or drinks by the patrons of the eating and drinking establishment. Includes outdoor dining areas that are on or above the ground story. Does not include rooftop dining.
Outdoor Dining Area: Outdoor dining area is defined as any portion of any eating & drinking use on private property designed and intended for the service and consumption of food and drinks, that has less than 75 percent enclosure (regardless of covered area percentage), or less than 25 percent covered area (regardless of enclosure percentage).
Outdoor Display: Outdoor display is defined as any exhibition of goods for retail sale which are outdoors.
Outdoor Furniture: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.5.A.1.n. (Outdoor Furniture), outdoor furniture is defined as permanent or movable furniture not located within an enclosed space. Examples of outdoor furniture may include, but are not limited to: benches, tables, or bike or scooter parking racks.
Outdoor Recreation: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.4.5. (Outdoor Recreation), outdoor recreation is defined as any outdoor use providing sports, fitness, leisure, amusement, or recreation facilities. Outdoor recreation includes the following uses when outdoors: sports courts and fields, aquatic centers, skate parks, play facilities, and amusement rides.
Outdoor Recreation: Commercial: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.4.5.B. (Outdoor Recreation: Commercial), outdoor recreation: commercial is defined as any outdoor recreational use owned or operated by a private or commercial entity. This use does not include associated spectator facilities with seating capacity greater than 500 seats, for such uses see Sec. 5D.4.1. (Amphitheater or Stadium).
Outdoor Recreation: Golf Course: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.4.5.C. (Outdoor Recreation: Golf Course), outdoor recreation: golf course is defined as an area of land designed and intended for the game of golf with a series of holes each including tee, fairway, and putting green, and often one or more natural or artificial hazards. A outdoor recreation: golf course use includes any course having a total par of 65, or greater. This use also includes a clubhouse incidental to a standard-sized golf course. This use does not include miniature golf, pitch & putt, driving range, or 3-par courses, for such uses see Sec. 5D.4.5.A. (Outdoor Recreation: Public) or Sec. 5D.4.5.B. (Outdoor Recreation: Commercial).
Outdoor Recreation: Public: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.4.5.A. (Outdoor Recreation: Public), outdoor recreation: public is defined as any outdoor recreational use owned or operated by or in partnership with a public institution.
Outdoor Storage Screening: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.8.3. (Outdoor Storage Screening), outdoor storage screening is defined as fences or walls surrounding outdoor storage areas in which goods, material, and equipment, new or used, are held outside of a building for future use.
Owner: For the purposes of Div. 13B.8. (Historic Preservation), owner is defined as any person, association, partnership, firm, corporation or public entity identified as the holder of title on any property as shown on the records of the City Engineer or on the last assessment roll of the County of Los Angeles, as applicable. For purposes of this Div. 13B.8. (Historic Preservation), “owner” also refers to an appointed representative of an association, partnership, firm, corporation, or public entity which is a recorded owner.
P
Parallel Parking: For purposes of on-site parking, parallel parking is defined as a parking stall having its length parallel to its access drive aisle.
Parcel: Parcel is defined as a piece of land with defined boundaries intended for the purpose of ownership, lease, or finance.
Parcel Map: Parcel map is defined as a map for the division of land meeting the requirements of Sec. 11.4.5. (Parcel Map).
Park Fee: Park fee is defined as Quimby in-lieu fees and park mitigation fees pursuant to Sec. 10.4.2. (Types of Fees).
Park Trailer: Park trailer is the same as defined in California Health and Safety Code, Sec. 18009.3.
Parking: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.3.6. (Parking), parking is defined as a facility intended for the temporary storage of operable vehicles belonging to a site's occupants, employees, or visitors and is designed to meet the standards of Sec. 4C.4.4. (Parking Area Design). Includes parking structures and surface parking lots. This use does not include long term vehicle storage, for such uses see Sec. 5D.7.5. (Storage, Outdoor).
Parking Area: Parking area is defined as a motor vehicle use area which is used for parking vehicles. Examples include, parking lots and parking structures.
Parking Bay: For a double-loaded aisle, parking bay is defined as the width of two rows of parking stalls including the width of the access drive aisle in-between. For a single-loaded aisle, parking bay is defined as the width of a single row of parking stalls including the width of the access drive aisle.
Parking Garage: Parking garage is defined as any parking structure that is primarily used for parking. For a parking structure to be considered a parking garage, motor vehicle use area in a building shall be greater than or equal to the floor area of the building. See Sec. 4C.4.6. (Parking Structure Design).
Parking Lot: Parking lot is defined as a parking area that has no floor area below or above it.
Parking Setback: Pursuant to Sec. 3C.2.1. (Parking Setback), parking setback is defined as an area on a lot along a frontage lot line where motor vehicle use areas are prohibited, including primary street parking setbacks, side street parking setbacks, and special lot line parking setbacks.
Parking Stall: See automobile parking stall.
Parking Structure: Parking structure is defined as a building that includes parking uses. Parking structure includes parking garages and integrated parking structures. See Sec. 4C.4.6. (Parking Structure Design).
Parkway: Parkway is defined as the area between the edge of the roadway and the adjacent property line excluding any area occupied by a sidewalk. Parkway shall also include any area within a roadway which is not open to vehicular travel.
Passenger Loading Area: Passenger loading area is defined as areas designated for the on-site or curbside loading and unloading of passenger vehicles.
Passenger Transit Facility: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.5.5. (Passenger Transit Facility), a passenger transit facility is defined as any facility that includes a structure accommodating publicly accessible passenger transport vehicles which regularly load and unload passengers along a fixed route. A passenger transit facility include bus terminals, light rail stations and right-of-ways, subway stations and right-of-ways, and passenger train stations and right-of-ways.
Pedestrian Access: Pedestrian access is defined as a means of approaching or entering a lot from the public right-of-way as a pedestrian in accordance with Div. 4C.1. (Pedestrian Access).
Pedestrian Access Package: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.1.1.C.1. (Pedestrian Access Packages), pedestrian access package is defined as a combination of standards regulating pedestrian access from the public sidewalk into and through a site.
Pedestrian Accessway: Pedestrian accessway is defined as a pedestrian path designed to accommodate pedestrian access from the public right-of-way into a lot and to one or more building entrances, in accordance with Div. 4C.1. (Pedestrian Access).
Pedestrian Amenity & Public Amenity-Facing Facade: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.6.C. (Pedestrian Amenity & Public Amenity-Facing Facade), pedestrian amenity & public amenity-facing facade is defined as the portions of any frontage applicable facade pursuant to Sec. 3A.2.2.C.2. (Frontage Applicable Facade) having no permanent structure (not including fences or walls) located between the building facade and a pedestrian amenity space or public amenity space.
Pedestrian Amenity Allowance: Pursuant to Sec. 3C.1.4. (Pedestrian Amenity Allowance), pedestrian amenity allowance is defined as the width of pedestrian amenity space in the build-to zone that can be counted toward the build-to width requirement.
Pedestrian Amenity Space: Pursuant to Sec. 2C.3.3.C.2. (Pedestrian Amenity Space), pedestrian amenity space is defined as a type of amenity space that is outdoors, located at ground-level, is accessible to pedestrians and all tenants of a building, and meets all the standards in Sec. 2C.3.3.C.2. (Pedestrian Amenity Space). See Div. 3C.1. (Build-To) for additional provisions related to pedestrian amenity spaces.
Pedestrian Amenity-Facing Facade: See pedestrian amenity & public amenity-facing facade.
Pedestrian Passageway: Pedestrian passageway is defined as a publicly accessible pedestrian pathway that provides pedestrian through access from the public right-of-way into and directly through a lot, in accordance with Sec. 4C.1.1.C.3.a. (Pedestrian Passageway).
Pedestrian Sign: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.11.6.C.7. (Pedestrian Sign), pedestrian sign is defined as a small sign attached perpendicular to the building facade that hangs from a bracket or support.
Pedestrian Walkway: Pedestrian walkway is defined as any public right-of-way designated as a pedestrian walkway on the Citywide General Plan Circulation System maps of the Circulation Element of the General Plan.
Perennial: Perennial is defined as a plant that lives more than two years, including woody species and other plants that do not die back annually.
Perimeter Plane: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.4.A.3. (Perimeter Plane), perimeter plane is defined as an imaginary vertical plane along the perimeter of a space used to measure the enclosure of a space. A perimeter plane shall be projected for a height of eight feet measured from the floor or ground surface of the space.
Permanent Supportive Housing: Permanent supportive housing is defined by Div. 10. (Contracts), Article 25. (Permanent Supportive Housing and Facilities Infrastructure Stabilization Ordinance), Sec. 10 51.1.(j). (Definitions) of the LAAC.
Permission Level: A permission level is a letter or symbol provided within a Use District table to indicate how an individual use is permitted, as established in Div. 5A.3. (Use Permissions).
Permit: For the purposes of Sec. 13B.9.1. (Coastal Development Permit (Pre-Certification)), permit is defined as any license, certificate, approval, or other entitlement for use granted, conditionally granted, or denied by any public agency, which is subject to the provisions of Sec. 13B.9.1. (Coastal Development Permit (Pre-Certification)).
Perpendicular Line: For the purposes of Sec. 4C.11.3.D.1. (Lots with Multiple Street Frontages), perpendicular line is defined as, a straight line between the point on a sign face that is closest to the street and the point where the line intersects the street lot line at a 90 degree angle, as illustrated in Sec. 4C.11.3.D.1. (Lots with Multiple Street Frontages).
Person: For the purposes of the Home-Sharing Program (Sec. 5C.3.2.), person shall have the same meaning as that term is defined in Chapter II. (Licenses, Permits, Business Regulations), Sec. 21.7.2. (Definitions) of this Code. As the term is used in the remainder of this Zoning Code (Chapter 1A) person means, an individual, joint venture, joint stock company, partnership, association, club, company, corporation, business trust, or organization and any other legal or natural person, or the manager, lessee, agent, servant, officer, or employee of any of them.
Personal Services: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.10. (Personal Services), personal services are defined as any commercial use providing an in-person service directly to individuals seeking cosmetic services, counseling services, document services, or servicing of consumer goods. Personal services include: cosmetic services such as hair cutting and styling, nail salon, day spas, licensed massage therapy, tattooing and piercing; counseling services, such as non-medical counseling, legal counseling, financial counseling, psychic counseling; document services such as printing, form and application assistance, notary services, photo developing, visa and passport services; garment services, such as garment tailoring and alterations, laundromat, dry cleaning; and consumer goods repair services when occupying less than 3,000 square feet in area, such as electronics repair, jewelry repair, shoe repair, appliance repair, furniture restoration, and bicycle repair. This use does not include consumer goods repair services when occupying 3,000 square feet in area, or greater, for such uses see Sec. 5D.8.1. (Machine Shop). This use does not include maintenance and repair of motor vehicles, for such uses see Sec. 5D.7.1. (Motor Vehicle Services).
Plant Cultivation: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.10.2. (Plant Cultivation), plant cultivation is defined as any agricultural use that includes the growing of plants.
Plant Cultivation: Community Garden: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.10.2.A. (Plant Cultivation: Community Garden), plant cultivation: community garden is defined as a plant cultivation use designed and intended for multiple households or organizations to cultivate plants for domestic use. This use may include shared facilities for storage and maintenance or services incidental to the agricultural use such as an educational space.
Plant Cultivation: Farming: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.10.2.B. (Plant Cultivation: Farming), plant cultivation: farming is defined as the cultivation of produce, ornamental plants, herbs, seeds, or fungi, for off-site sale or distribution. This use includes, but is not limited to, truck gardening, indoor farming, or vertical farming. For the sale of produce on-site beyond a farm stand pursuant to Sec. 5C.2.8.G.1. (Supplemental Standards), see Sec. 5D.6.12.E. (Retail: Food & Beverage).
Planting Area: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.6.4.C.2. (Planting Areas), planting area is defined as an area on a lot designated and designed for plants.
Planting Hole: Planting hole is defined as a hollow space dug within a planting area to accommodate the placement of a plant.
Platform Agreement: For the purposes of Sec. 5C.3.2. (Home-Sharing Program), platform agreement is defined as a signed agreement between a hosting platform and the City, which, among other things, provides that the platform will collect and submit the Transient Occupancy Tax to the City on behalf of hosts and persons listed for short-term rentals.
Pole Sign: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.11.6.C.8. (Pole Sign), pole sign is defined as a freestanding sign that is wholly independent of a building for support, permanently affixed to the ground using one or more poles or posts.
Postmortem Services: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.11. (Postmortem Services), postmortem services are defined as any establishment engaged in the provision of services involving the care, preparation, or arrangement of human or animal remains, and conducting memorial services. Postmortem service establishments include crematoriums, funeral homes, mortuaries, and pet crematoriums. This use does not include a cemetery, for such uses see Sec. 5D.3.1. (Cemetery).
Preliminary Parcel Map: Preliminary parcel map is defined as a map made for the purpose of showing the design of a proposed subdivision creating four or fewer parcels, four or fewer condominiums, or four or fewer units in a community apartment project or stock cooperative and prepared pursuant to Sec. 11.4.2. (Preliminary Parcel Map Standards).
Prepare: Whenever this Zoning Code (Chapter 1A) directs an agency or official to prepare a document, prepare means prepare directly or cause to be prepared.
Primary Residence: For the purposes of the Home-Sharing Program (Sec. 5C.3.2.), primary residence is defined as the sole residence from which the host conducts home-sharing and in which the host resides for more than six months of the calendar year. For all other purposes in this Zoning Code (Chapter 1A), primary residence is defined as a place of residence for an individual or group of individuals to live for more than six months out of the year.
Primary Roof Form: Primary roof form is defined as the form of the roof which covers at least 80 percent of the building footprint.
Primary Street: See primary street lot line.
Primary Street Lot Line: Primary street lot line is defined as a lot line that has been designated as the primary street lot line per Sec. 14.2.12.C.1. (Primary Street Lot Line).
Primary Use: For the purposes of Article 5. (Use), primary use is defined as the principal or predominant use of a lot relative to any other uses sharing the same lot as determined by the use that occupies the most floor area on a lot, or the use that covers the most lot area when concerning outdoor uses.
Principal Material Coverage: Pursuant to Sec. 3D.10.1. (Principal Material Coverage), principal material coverage is defined as the building products used as the primary exterior wall finish materials of the exterior building facade.
Principal Structure: Principal structure is defined as any structure that is not an accessory structure.
Private Club: Private club is defined as any facility organized solely for the promotion of some common interest and which is accessible to club members and their guests only. Private club includes business, fraternal, political, and social organizations.
Private Outdoor Amenity Space: Pursuant to Sec. 2C.3.3.C.4. (Private Outdoor Amenity Space), private outdoor amenity space is defined as a type of amenity space that is uncovered or unenclosed and is available to an assigned unit or tenant space, and meets all the standards in Sec. 2C.3.3.C.4. (Private Outdoor Amenity Space).
Private Road Easement: Private road easement is defined as a parcel of land not dedicated as a public street, over which a private easement for road purposes is proposed to be, or has been, granted to the owners of property contiguous or adjacent to the road, that intersects or connects with a public street or a private street. The instrument creating such easement shall be, or shall have been, duly recorded with the Los Angeles County Recorder.
Private Street: Private street is defined as a private road easement as defined herein which has been determined by the Advisory Agency or the Director to be adequate for access and for the purposes set forth in Article 10. (Streets & Parks), or Article 11. (Division of Land) of this Zoning Code (Chapter 1A).
Problem Areas: Problem areas are defined as those portions of the City determined by resolution of the Board of Public Works to be actually or potentially dangerous by reason of geological conditions, being subject to inundation or overflow by storm water, or because of any other potentially dangerous condition, including areas subject to rapid spread of fire.
Producing Zone (Oil Drilling Districts): Producing zone (Oil Drilling Districts) is defined as a reservoir or series of reservoirs of sufficient thickness and productivity of hydrocarbons as to form an economic source of supply and which is segregated from other reservoirs, or series of reservoirs, by natural boundaries or barriers to such an extent as to make its separate development either economically or mechanically desirable in accordance with good oil field practice.
Project: As the term is used in this Zoning Code (Chapter 1A) project is defined by Sec. 14.2.15.A. (Project). The definition for project is modified for the purposes of the following Sections:
-
For the purposes of Sec. 13B.11.1. (Environmental Review Procedures), project is defined by the California Public Resources Code, Sec. 21065. and CEQA Guidelines, Sec. 15378.
-
For the purposes of Historic Preservation (Div. 13B.8.), see Sec. 13B.8.1.C. (Definitions) or Sec. 8.2.6.B.1. (Definition of Project).
-
For the purposes of Sec. 8.2.2. (Community Plan Implementation Overlay (CPIO)) see Sec. 8.2.2.B.1. (Definition of Project).
-
For the purposes of Sec. 8.2.3. (Sign District (SN)) see Sec. 8.2.3.B.1. (Definition of Project).
-
For the purposes of Sec. 8.2.5. (Community Design Overlay (CDO)) see Sec. 8.2.5.B.1. (Definition of Project).
-
For the purposes of Sec. 8.2.7. (Conservation Districts (CD)) see Sec. 8.2.7.B.1. (Definition of Project).
-
For the purposes of Sec. 8.2.8. (Transportation Communication Network District (TCN)) see Sec. 8.2.8.B.1. (Definition of Project).
Project Activities: See project activity.
Project Activity: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.15. (Project Activities), project activity is defined as the type of work composing a project. A project may be composed of one or more project activity.
Project Adjustment: For the purposes of review of a project for compliance with a Specific Plan, project adjustment is defined as a decision on a project by the Director granting a minor adjustment from certain Specific Plan regulations, subject to the limitations specified by Div.13B.4. (Specific Plan Implementation).
Project Compliance: For the purposes of review of a project for compliance with a Specific Plan, project compliance is defined as a decision by the Director that a project complies with the regulations of the applicable Specific Plan, either as submitted, or with conditions imposed to achieve compliance.
Project Exception: For the purposes of review of a project for compliance with a Specific Plan, project exception is defined as a decision on a project by the Area Planning Commission granting relief from applicable Specific Plan regulations.
Project Site: Project site is defined as the lot on which a project is located.
Projecting Balcony: Pursuant to Sec. 3D.7.1.D. (Projecting Balcony), projecting balcony is defined as an unenclosed occupiable platform, located at an elevation above the ground story, that is fixed to or integrated with an exterior building facade and projects beyond the floor area of the story immediately below. Balconies include protective barriers such as railings or parapets and may be covered or uncovered.
Projecting Sign: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.11.6.C.9. (Projecting Sign), projecting sign is defined as a sign attached approximately perpendicular to the building facade that does not meet the standards for a pedestrian sign.
Projection: For the purposes of signs, projection is defined as the distance by which a sign extends beyond the building face. See Div. 4C.11. (Signs).
Proposed Use: For the purposes of Article 5. (Use), proposed use is defined as any project activity involving the establishment of a new use, the modification of an existing use, expansion of floor area dedicated to an existing use, or relocation of an existing use.
Protected Vegetation: Protected vegetation is defined as any protected tree or shrub as defined in Chapter IV. (Public Welfare), Sec. 46.01. (Definition) of this Code.
Protective Barrier: Protective barrier is defined as a building component or assembly located at, or near, the open sides of elevated floor surfaces, that is designed to reduce the risk of fall from the occupiable space. Protective barrier includes guardrails, railings, and parapets.
Public & Institutional Use: Pursuant to Div. 5D.3. (Public & Institutional Uses), public & institutional uses are defined as uses dedicated to serving the public through the provision of government services, utilities, healthcare, education, and culture.
Public Access Easement: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.17. (Public Access Easements), public access easement is an easement, established between a lot owner or owners and the City of Los Angeles, as found on the Public Access Easement Map (Sec. 1.5.11.), affecting a lot or lots for the purpose of ensuring public access to the portions of the lot covered by the easement.
Public Amenity Space: Pursuant to Sec. 2C.3.3.C.3. (Public Amenity Space), public amenity space is defined as a type of amenity space that is outdoors and, although privately owned, is open to the public, and meets all the standards in Sec. 2C.3.3.C.3. (Public Amenity Space).
Public Amenity-Facing Facade: See pedestrian amenity & public amenity-facing facade.
Public Art Installation: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.11.1.E.3.d. (Public Art Installation), public art installation is defined as a facility, amenity or project that does not contain any commercial message and which is either an "approved public arts project" as defined by Sec. 19.85.4. (Direct Expenditure on Approved Public Arts Projects) of the LAAC or approved pursuant to Chapter IX. (Building Regulations), Sec. 91.107.4.6. (Arts Development Fee) of this Code.
Public Facility: Public facility is defined as any facility, including, but not limited to, buildings, property, recreation areas, and roads, which are owned, leased, or otherwise operated, or funded by a governmental body or public entity. See Sec. 9.3.4.C.7. (Civic Facility Incentive Area).
Public Project: For the purposes of Div. 13B.9. (Coastal Development), public project is defined as any development initiated by the Department of Public Works or any of its bureaus, any development initiated by any other department or agency of the City, and any development initiated or to be carried out by any other governmental agency which is required to obtain a local government permit. Public project shall not include any development by any department or agency of the City or any other governmental entity which otherwise requires action by or approval of the City Planning Commission, Area Planning Commission or the Office of Zoning Administration, or any development by any department or agency of the City or any other government entity for which a permit from the Department of Building and Safety is required. Public project shall also not include any development on tidelands, submerged lands, or on public trust lands, whether filled or unfilled. (Definition Amended by Ord. No. 173,268, eff. 7/1/00, Oper. 7/1/00.).
Public Right-of-Way: Public right-of-way is defined as the area on, below, or above any surface owned by, or under the control of the City for the purpose of providing public access for a mode of transportation or mobility. Public right-of-way includes roadway, alley, median, sidewalk, parkway, bicycle path, and recreational trail.
Public Safety Facility: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.3.7. (Public Safety Facility), public safety facility is defined as any government facility that provides public safety services. Public safety facility includes fire stations and police stations.
Public Sidewalk: Public sidewalk is defined as any sidewalk within a public right-of-way.
Public Way: Public way is defined as a street, alley, or other parcel of land leading to a street or public right-of-way, that has been deeded, dedicated, or otherwise permanently appropriated to the public, for public use, that has a clear width and height of not less than 10 feet. Public way includes any street, channel, viaduct, subway, tunnel, bridge, easement, public right-of-way, or other way, in which a public agency or the public has a right of use.
Publicly Accessible: Publicly accessible is defined as the ability of the public to access a facility.
Q
Qualified Nonprofit Housing Corporation: Qualified nonprofit housing corporation is defined pursuant to Sec. 501(c)(3) of the Internal Revenue Code that has received a welfare exemption under Sec. 214.15 of the Revenue and Taxation Code for properties intended to be sold to low-income families who participate in a special no-interest loan program.
Qualified Permanent Supportive Housing Project: Qualified permanent supportive housing project is defined as a use where all dwelling units meet the standards of Sec. 9.4.1. (Permanent Supportive Housing Incentive Program).
Quasi-Judicial Approval: Quasi-judicial approval is defined as an action that applies rules to specific facts and is subject to procedural due process principles and includes but is not limited to the approvals provided for in Div. 13B.2. (Quasi-Judicial Review), Div. 13B.4. (Specific Plan Implementation), and Div. 13B.5. (Quasi-Judicial Relief).
Queuing: Queuing is defined as the channeling of vehicle traffic into lanes to accommodate the temporary stopping of two or more vehicles that are waiting to enter into an area or obtain goods or services from a drive-through facility.
Queuing Depth: Queuing depth is defined as the portion of a drive aisle which is designated for ingress vehicular traffic on a site, and meets the standards of Sec. 4C.2.1.C.2.b. (Queuing Depth).
Queuing Space: Queuing space is defined as the space within a drive-through lane needed to accommodate the temporary stopping of a single vehicle.
R
Rear Lot Line: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.12.C.4. (Rear Lot Line), rear lot line is defined as a lot line that does not abut a street or alley right-of-way and is opposite and most distant from a primary street lot line, and meets the criteria pursuant to Sec. 14.2.12.C.4. (Rear Lot Line).
Rear Yard: See Sec. 14.2.16.B.4. (Rear Yard).
Reasonable Accommodation: For the purposes of Sec. 13B.5.5. (Reasonable Accommodation), reasonable accommodation is defined as providing an individual with a disability or developers of housing for an individual with a disability, flexibility in the application of land use and zoning regulations or policies (including the modification or waiver of certain requirements), when it is necessary to eliminate barriers to housing opportunities.
Reconstruction: For the purposes of Div. 13B.8. (Historic Preservation), reconstruction is defined as the act or process of reproducing by new construction the exact form, features and details of a vanished building, portion of a building, structure, landscape, natural feature, or object as it appeared at a specific period of time, on its original or a substitute lot.
Recorded Parcel Map: Recorded parcel map is defined as a parcel map that has been recorded in accordance with Sec. 11.4.5. (Parcel Map).
Recreational Vehicle: Recreational vehicle is defined pursuant to California Health and Safety Code, Sec. 18010.
Recyclable Materials: Recyclable materials are defined as items or materials to be recycled or reused, including yard waste, paper, plastic, glass, metal, newspaper, and cardboard.
Recycling Area: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.12.7. (Recycling Areas), recycling area is defined as an outdoor enclosure or a room within a building which is designated for the collection of recyclable materials generated by the use(s) on a lot.
Recycling Center: Pursuant to Sec. 13B.10.3. (Annual Inspection Monitoring (Type 1)), recycling center is defined as any recycling collection or buyback site, recycling sorting facility, or other recycling oriented site which does not do any processing other than mechanical compaction to reduce the volume of recyclable containers for economy of storage.
Recycling Chute: Recycling chute is defined as any vertical smooth shaft used to convey recyclable materials from the upper floors of a building to a recyclable storage bin or room at the bottom end of the chute.
Recycling Facility: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.9.4. (Recycling Facility), recycling facility is defined as any use that includes the recovery and processing of recyclable or reusable materials.
Recycling Facility: Collection: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.9.4.A. (Recycling Facility: Collection), recycling facility: collection is defined as any recycling facility use where recyclable materials including, but not limited to, paper, plastic, glass, metal, newspaper, or cardboard, are deposited or redeemed for monetary value. This use includes baling or crushing operations for the purposes of efficient storage and transfer, but shall not include sorting or processing activities other than for temporary storage purposes. This use includes reverse vending machines and buyback centers.
Recycling Facility: Sorting & Processing: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.9.4.B. (Recycling Facility: Sorting & Processing), recycling facility: sorting & processing is defined as any recycling facility use that accepts recyclable materials for on-site sorting or processing. For the purpose of this definition, processing shall mean the process of changing the physical characteristics of a recyclable material, including the shredding, smelting, grinding and crushing of cans, bottles, and other materials, other than for temporary storage purposes. This use includes the transfer and processing of scrap metals.
Recycling Receptacle: Recycling receptacle is defined as a container which is suitable for the collection of recyclable materials.
Registered Civil Engineer: Registered civil engineer is defined as a civil engineer licensed and registered by the State of California.
Rehabilitation: Pursuant to Div. 13B.8. (Historic Preservation), rehabilitation is defined as the act or process of returning a property to a state of utility, through repair or alteration, which makes possible an efficient contemporary use while preserving those portions or features of the property which are significant to its historical, architectural and cultural values.
Renovation: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.15.B.9. (Renovation), renovation is defined as a modification to the interior of any building or structure, including the basement, that does not expand the building or structure. Renovation includes interior remodels or tenant improvements.
Rental Unit: For the purposes of Home-Sharing Program (Sec. 5C.3.2.), rental unit is defined as a dwelling unit or residential structure, or portion thereof. For all other purposes in this Zoning Code (Chapter 1A) rental unit is defined as a dwelling unit available for rent.
Renter: For the purposes of Historic Preservation (Div. 13B.8.), renter is defined as any person, association, partnership, firm, corporation, or public entity which has rented or leased a dwelling unit or other structure within an HPOZ for a continuous time period of at least three years. The “renter” also refers to an appointed representative of an association, partnership, firm, corporation, or public entity which is a renter. See Sec. 13B.8.1.C. (Definitions).
Research & Development: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.8.3. (Research & Development), research & development is defined as any light industrial use requiring a wet laboratory where chemicals, drugs, or other material or biological matter are handled in liquid solutions or volatile phases, requiring direct ventilation, and specialized piped utilities. Research & development does not include uses requiring a dry laboratory, for these uses see Sec. 5D.6.9. (Office).
Resident: Resident is defined as one who legally resides at the subject building or lot.
Residential: See residential use.
Residential Amenity Space: Pursuant to Sec. 2C.3.2. (Residential Amenity Space), residential amenity space is defined as an area which is designed and intended to be used by occupants of dwelling units for recreational, domestic, or vocational purposes.
Residential Building: Residential building is defined as a building, or portion of a building, designed or used for human habitation.
Residential Care Facility for Elderly: Residential care facility for elderly is defined pursuant to California Code of Regulations, Title 22. (Social Security), Div. 6. (Licensing of Community Care Facilities), Sec. 87101 (r)(5) (Definitions).
Residential Conversion Project: Residential conversion project is defined as an existing apartment house, apartment hotel, hotel, or multiple dwellings used exclusively for residential purposes, proposed for conversion to a condominium, stock cooperative, or community apartment project to be used exclusively for residential purposes through approval of a tract map or parcel map. For purposes of this definition, the term existing means that the building was constructed prior to 1945 or, where built after 1945, a Certificate of Occupancy has been issued for the building prior to the time of map application.
Residential Project: Residential project is defined as a project containing any number of dwelling units.
Residential to Commercial/Industrial Conversion Project: Residential to commercial/industrial conversion project is defined as an existing hotel or multiple dwellings used exclusively for residential purposes proposed for conversion to a condominium or stock cooperative which is to be used exclusively for commercial or industrial purposes through approval of a tract map or parcel map. For purposes of this definition, the term existing means that the building was constructed prior to 1945 or, where built after 1945, a Certificate of Occupancy was issued for the building prior to the time of map application.
Residential Use: Pursuant to Div. 5D.2. (Residential Uses) residential uses are uses that provide housing accommodations, residential support services, and home-based enterprise. See.
Restoration: For the purposes of Div. 13B.8. (Historic Preservation), restoration is defined as the act or process of accurately recovering the form, features and details of a property as it appeared at a particular period of time by means of the removal of later work or by the replacement of missing earlier work.
Restaurant: An eating & drinking establishment that provides a dining environment where customers are seated and served made-to-order meals prepared in a full-service kitchen on-site.
Restricted Affordable Unit: Restricted affordable unit is defined as a dwelling unit for which rental amounts or mortgage amounts are restricted through enforceable covenant or other legal restriction so as to be affordable to and occupied by an acutely low income household, extremely low income household, very low income household, low income household, or moderate income household as verified by the Los Angeles Housing Department.
Retail: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.12. (Retail), retail is defined as a commercial use involved in the sale or dispensing of consumer goods to the general public, including any associated indoor or outdoor display and point of sales.
Retail: Alcohol: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.12.B. (Retail: Alcohol), retail: alcohol is defined as a retail use involving the sale or dispensing of alcoholic beverages for off-site consumption and are licensed or seeking a license to sell or otherwise dispense alcoholic beverages for off-site consumption, as defined by the California State Alcoholic Beverage Control Act (ABC). This use does not include the on-site consumption of alcoholic beverages, for such uses see Sec. 5D.6.3.B. (Eating & Drinking: Alcohol Service).
Retail: Farmers' Market, Certified: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.12.C. (Retail: Farmers' Market, Certified), retail: farmers' market, certified is defined as a retail use involved in the sale or dispensing of agricultural products by producers or certified producers directly to consumers or to individuals, organizations, or entities that subsequently sell or distribute the products directly to end users and is certified by the Los Angeles County Agricultural Commissioner.
Retail: Firearms: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.12.D. (Retail: Firearms), retail: firearms is defined as a retail use where firearms, ammunition, or related accessories are sold.
Retail: Food & Beverage: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.12.E. (Retail: Food & Beverage), retail: food & beverage is defined as a retail use primarily involved in the retail sale of food and beverages for off-site consumption. Retail: food & beverage includes grocery stores, produce markets, seafood and meat markets, bakeries, delis, and on-site seating areas for dining accessory to the primary retail use. This use does not include alcoholic beverage sales; for such uses see Sec. 5D.6.12.B. (Retail: Alcohol).
Retail: General: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.12.A. (Retail: General), retail: general is defined as any retail use primarily involved in the sale or rental of new or used consumer goods to the general public. Retail: general includes but is not limited to, the sale or rental of household goods, clothing, books, toys, art supplies, pet supplies, house plants, medicine, consumer electronics, appliances, hardware, building supplies, mattresses, and furniture. This use does not include the sale or rental of motor vehicles, for such uses see Sec. 5D.7.3. (Motor Vehicle Sales & Rental).
Retail: Large Format: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.12.F. (Retail: Large Format), retail: large format is defined as any retail use with a non-residential tenant size of 100,000 square feet or greater. This use may include but is not limited to any of the following types of retail when occupying a non-residential tenant size of 100,000 square feet or greater: superstore, department store, wholesale club, furniture store, and home improvement store. This use does not include any retail use with a non-residential tenant size of less than 100,000 square feet, for such uses see Sec. 5D.6.12.A. (Retail: General).
Retail: Merchant Market: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.12.G. (Retail: Merchant Market), retail: merchant market is defined as a retail use that includes ten or more tenants or vendors within a shared facility with common entrances and walkways, where goods, products, groceries, and prepared food are offered or displayed for sale or exchange, and may include on-site seating areas for dining as incidental to the market use.
Retail: Pet Shop: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.12.H. (Pet Shop), retail: pet shop is defined as a retail use possessing a pet shop permit issued by the Department of Animal Services where domestic animals such as dogs, cats, rabbits, rodents, birds, fish, amphibians, and small reptiles are kept and offered for commercial sale, for hire, or adoption. This use does not include uses where the overnight keeping of dogs or cats exceeds 30 percent of the floor area of a facility, for such uses see Sec. 5D.6.1.B. (Animal Services: Kennel). This use does not include the breeding and raising of animals, for such uses see Sec. 5D.10.1.G. (Animal Keeping: Small Animals).
Retail: Seasonal Market: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.12.I. (Seasonal Market), retail: seasonal market is defined as a retail use involving the seasonal outdoor retail sale of ornamental holiday decor, primarily ornamental pumpkins and Christmas trees.
Retail: Smoke & Vape Shop: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.12.J. (Smoke & Vape Shop), retail: smoke & vape shop is defined as a retail use primarily involving the sale of tobacco products, substances intended for smoking, or smoking accessories, including but not limited to cigars, pipes, vaporizing devices, or other smoking paraphernalia. The use may include an enclosed smokers’ lounge that is solely dedicated to smoking tobacco products. This use does not include medicinal or recreational cannabis establishments, for such uses see the Department of Cannabis Regulation.
Retaining Wall: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.9.2. (Retaining Walls), retaining wall is defined as a freestanding continuous structure, as viewed from the top, intended to support earth, which is not attached to a building.
Reverse Vending Machine: Reverse vending machine is defined as an automated mechanical device which accepts one or more types of empty beverage containers including aluminum cans, glass and plastic bottles, and which issues a cash refund or a redeemable credit slip with a value not less than the container’s redemption value, as determined by the State of California. A reverse vending machine may sort and process containers mechanically, provided that the entire process is enclosed within the machine. See Sec. 5D.9.4.A. (Collection).
Reviewing Agency: Reviewing agency is defined as the agency or official charged with reviewing an application for an approval under this Zoning Code (Chapter 1A) which includes the Zoning Administrator, the Director of Planning, or the Department of City Planning.
Revised Tentative Tract Map: Revised tentative tract map is defined as a tract map for which a tentative tract map has been previously approved which involves a revised arrangement of the streets, alleys, easements, or lots within property or a modification of the boundary of the property pursuant to Article 11. (Division of Land).
Right-of-way: For the purposes of Historic Preservation (Div. 13B.8.) right-of-way is defined as the dedicated area that includes roadways, medians, and/or sidewalks. For the remainder of this Zoning Code (Chapter 1A) see public right-of-way.
Roadway: Roadway is defined as that portion of a public right-of-way for a street or alley used for, or intended to accommodate, the movement of vehicles, including provided or planned on-street bike lanes.
Roof Form: Pursuant to Sec. 3D.11.1. (Roof Form), roof form is defined as the shape of the external upper covering of a building, including the frame for supporting the roofing.
Roof Projection: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.5.A.1.b. (Roof Projection), roof projections are defined as roof elements that overhang or cantilever beyond the building footprint and do not include posts or columns. Types of roof projections include, but are not limited to: eaves, roof overhangs, gutters, awnings, or canopies.
Roof Sign: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.11.6.C.10. (Roof Sign), a roof sign is defined as a sign erected on a roof of a building.
Roof Sign: Open Panel: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.11.6.C.11. (Roof Sign: Open Panel), a roof sign: open panel is defined as a sign erected on a roof of a building consisting of channel letters, graphic segments, open lighting elements, or other open forms affixed to a non-solid panel sign support structure.
Roof Structure: A roof structure is defined as the structure forming the upper covering of a building.
Roof-Mounted Equipment: Roof-mounted equipment is defined as all mechanical equipment or utility equipment located on a roof, with the exception of solar panels and their required appurtenances. See Sec. 4C.12.1. (Roof-Mounted Equipment).
Roofline Cornice: Pursuant to Sec. 3D.6.5.C.4. (Roofline Cornice), a roofline cornice is defined as a continuous molded projection that crowns a wall, often as part of a parapet.
Rooftop Planting Area: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.6.4.C.2.b. (Rooftop Planting Area Standards), rooftop planting areas are defined as areas where plants are provided on or over a built structure, including but not limited to, a roof, a bridge, a balcony or a parking structure, and complies with all of the standards in Sec. 4C.6.4.C.2.b. (Rooftop Planting Area Standards).
Root Ball: Root ball is defined as the intact ball of earth or growing medium containing the roots of a nursery plant.
Root Collar: A root collar is defined as the line of junction between the root of a plant and its stem or trunk.
Root Flare: A root flare is defined as the area at the base of the plant’s stem or trunk where the stem or trunk broadens to form roots; the area of transition between the root system and the stem or trunk.
Root Mass: Root mass is defined as a plant's overall amount of root growth.
S
Safety Barrier: For the purposes of vertical encroachments pursuant to Sec. 14.2.5.B.1.e. (Safety Barriers), a safety barrier is defined as a vertical barriers that is 45 inches in height or less and required for safety and protection by Chapter IX. (Building Regulations) of this Code to protect occupants from falling from walking surfaces including but not limited to parapets, railings, or banisters. For the purposes of the remainder of this Zoning Code (Chapter 1A), a safety barrier is defined as anything put in place to prevent people from moving easily from one place to another for the purpose of mitigating risk including fences, walls, parapets, and railings.
Sales Floor Area: Sales floor area is defined as the interior floor area of a retail use devoted to the retail sale of merchandise where customers can view, select, and carry merchandise from an inventory display to the point of sale. Areas not included in sales floor area include, showrooms, restrooms, office space, storage areas, open-air retail areas.
Salvage Yard: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.9.3. (Salvage Yard), a salvage yard is defined as any heavy industrial use having any portion of the use located outdoors where a junk dealer or automobile dismantler operates, or where partially dismantled, obsolete, or wrecked automobiles are stored. This use does not include motor vehicle storage, for such uses see Sec. 5D.7.5. (Storage, Outdoor).
School: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.3.9. (School), school is defined as an institution of academic learning and social development that provides facilities for teaching and instruction to accommodate a student body such as preschool, K-12, post-secondary education, and associated athletic and recreational facilities. This use does not include avocational, recreational, or other educational or instruction-based uses, for such uses see Sec. 5D.6.6. (Instructional Services). This use does not include a campus auditorium or stadium facilities with a seating capacity greater than 3,000 seats, for such uses see Sec. 5D.4.1. (Amphitheater or Stadium).
School: K-12: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.3.9.B. (School: K-12), school: K-12 is defined as an institution of learning which offers instruction in grades Kindergarten through 12th grade, and associated recreation and athletic facilities serving its students.
School: Post-Secondary: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.3.9.C. (School: Post-Secondary), school: post-secondary is defined as an institution offering a formal educational program beyond K-12, including programs whose intent is academic, vocational, or continuing professional education. School: post-secondary includes college, technical school, trade school, and university.
School: Preschool/Daycare: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.3.9.A. (School: Preschool/Daycare), school: preschool/daycare is defined as a facility providing care, supervision, and educational services to children during the day. A school: preschool/daycare includes all forms of early childhood education, daycare, and after school supervision. This use does not include in-home child care, for such uses see Sec. 5D.2.2.A. (Household Business: Family Child Care).
Screening: Screening is defined as an arrangement of structures, vegetation, or site elements that are intended to block or obscure views into a lot or structure. See Div. 4C.8. (Screening).
Screening Plants: Screening plants are defined as plants that are arranged for the purposes of obscuring views into a lot or structure.
Screening Structure: A screening structure is defined as a structure obstructing visibility from outside an enclosed area to another space, object, or structure.
Sea: For the purposes of Sec. 13B.9.1. (Coastal Development Permit (Pre-Certification)) sea is defined as the Pacific Ocean and all harbors, bays, channels, canals, estuaries, salt marshes, sloughs and other areas subject to tidal action through any connection with the Pacific Ocean, excluding nonestuarine rivers, streams, tributaries, creeks, and flood control and drainage channels.
Senior Care Facility: Senior care facility is defined as any assisted living, senior independent living, or skilled nursing home for senior citizens. See Sec. 9.4.3. (Senior Care Facilities Incentive Program).
Senior Citizen: Senior citizen is defined as an individual at least 62 years of age, except that for projects of at least 35 units that are subject to Div. 9.2. (Affordable Housing Incentive Programs), a senior citizen may be a person of 55 years of age.
Senior Citizen Housing Development: As defined pursuant to California Civil Code, Sec. 51.3 (b)(4), a housing development project for senior citizens that has at least 35 dwelling units.
Sensitive Use: Unless otherwise provided in this Code or City guidelines for a specific purpose, sensitive use is defined as any permitted use in the residential use group, a hospital use, a school use, or any use in the open space & recreation use group shall be considered a sensitive use.
Service Floor Area: Service floor area is defined as all indoor floor area within an eating & drinking use where the customer can be served, including an indoor dining or lounge area, bar-top and bar seating area, service counter, customer waiting area, customer restrooms, and indoor paths of travel accessible to customers.
Service Road: A service road is defined as that part of a major or secondary highway, containing a roadway that affords access to abutting property, but is adjacent and approximately parallel to, and separated from the principal roadway.
Sexually Oriented Business: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.13. (Sexually Oriented Business), sexually oriented business is defined as any commercial use involving the retail sale, rental or exhibition, of any goods or services that are characterized by an emphasis on the exposure or display of specified sexual activities or specified anatomical parts. Each sexually oriented business use shall constitute a separate sexually oriented business, even if operated in conjunction with another sexually oriented business at the same establishment, for the intent of meeting applicable use standards.
Sexually Oriented Business: General: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.13.A. (Sexually Oriented Business: General), sexually oriented business: general is defined as any sexually oriented business use, other than a sexually oriented business: sexual encounter establishment. This use includes but is not limited to adult arcades, adult bookstores, adult cabaret theaters, adult motion picture theaters, or striptease venues.
Sexually Oriented Business: Sexual Encounter: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.6.13.B. (Sexually Oriented Business: Sexual Encounter), sexually oriented business: sexual encounter is defined as any sexually oriented business use, other than lodging offering public accommodations, which, for any form of consideration, provides a place where two or more persons may congregate, associate or consort in connection with specified sexual activities or the exposure of specified anatomical parts. This use does not include a use where a medical practitioner, psychologist, psychiatrist, or similar professional licensed by the State of California engages in sexual therapy, for such uses see Sec. 5D.6.8. (Medical Clinic).
Sheltered: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.2.A.3. (Sheltered) a space or structure is considered sheltered if no portion of its area is open to the sky.
Sheltering Structure: Sheltering structure is defined as any structure, including entry features, canopies, or roofs, that creates a covered, unenclosed space.
Shopfront Cornice: Pursuant to Sec. 3D.6.5.C.3. (Shopfront Cornice), shopfront cornice is defined as a continuous molded projection located above a series of display windows on the ground story facade.
Shopping Cart: A shopping cart is defined as a basket of any size, mounted on wheels, rollers or a similar device, including parts, provided by a retail establishment for the purpose of transporting groceries or merchandise of any kind within a retail establishment or associated parking area.
Shopping Cart Containment Plan: Shopping cart containment plan is defined as a plan sheet that includes a specific written plan with a corresponding site plan that identifies areas of shopping cart containment to prevent customers from removing shopping carts from the premises. See Sec. 4C.12.8. (Shopping Cart Containment).
Shopping Cart Corral: Shopping cart corral is defined as a stable structure that provides an enclosure for the collection of shopping carts on a lot.
Shoreline Project: Shoreline project is defined as any development in streams, wetlands, and other waters of the United States, and may include depositing of fill and dredged material, jetties, marinas, and piers.
Short-Term Rental: For the purposes of the Home-Sharing Program (Sec. 5C.3.2.), short-term rental is defined as a rental unit, rented in whole or in part, to any person(s) for use of 30 consecutive days or less. Rental units within City-approved lodging uses shall not be considered a short-term rental.
Showroom Area: Showroom area is defined as the interior floor area of a retail use devoted to the display of heavy/large goods, such as furniture, mattresses, major household appliances, carpet, cars, or wholesale fabric where the assistance of a sales associate, special order, or delivery of goods is required.
Shrub: Shrub is defined as a small to medium sized perennial woody plant. Unlike herbaceous plants, shrubs have persistent woody stems above the ground. They are distinguished from trees by their multiple stems and shorter height and for purposes of this Zoning Code (Chapter 1A) are less than 15 feet.
Side Lot Line: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.12.C.5. (Side Lot Line), side lot line is defined as any lot line not determined to be a primary street lot line, side street lot line, rear lot line, alley lot line, or special lot line.
Side Street Lot Line: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.12.C.2. (Side Street Lot Line), side street lot line is defined as a lot line separating a lot from a side street right-of-way. Any street lot line not determined to be a primary street lot line is considered a side street lot line.
Side Street Yard: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.16.B.3. (Side Street Yard), side street yard is defined as the area between a side street lot line and an imaginary line running parallel to the side street lot line. The imaginary line shall be drawn 15 feet back from the portion of the side street lot line-facing facade nearest to the side street lot line, measured perpendicularly to the lot line.
Side Yard: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.16.B.5. (Side Yard), side yard is defined as the portions of a lot between a side lot line and a principal structure. All portions of a lot that do not meet the yard designation criteria for any other yard shall be designated as a side yard.
Sidewalk Grade: Sidewalk grade is defined as the elevation of the sidewalk surface at any given point.
Sign: Sign is defined as any whole or part of a display board, wall, screen, or object, used to announce, declare, demonstrate, display, or otherwise present a message and attract the attention of the public.
Sign Face: Sign face is defined as the surface upon which the sign message is placed.
Significant Tree: Significant tree is defined as any tree which measures 12 inches or more in diameter at 4.5 feet above the average natural grade at the base of the tree or is more than 35 feet in height.
Sill: Pursuant to Sec. 3D.9.2.C.4. (Sill), sill is defined as the bottommost horizontal exterior surface of a window opening including a ledge or other architectural detail that projects from the surrounding building facade.
Simulated Divided-Lite: Simulated divided-lite is defined as a way to create the look of authentic divided lites, simulated divided-lite bars are permanently adhered to both sides of glass. See Sec. 3D.9.1.C.5. (Symmetrical Lite Pattern).
Site: See project site.
Site Modification: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.15.B.4. (Site Modification), site modification is defined as work including modifications to existing, or the addition of, new horizontal site improvements and landscaping, including trees, fences or walls, street furniture, lighting fixtures, grading, flatwork, ground mounted signs, and parking lot resurfacing or the reconfiguration of existing parking stalls.
Skilled Nursing Home: Skilled nursing home is defined as residential housing that is licensed by the California Department of Health, and provides acute, intermediate, or long-term skilled nursing care, and consists only of efficiency dwelling units for its residents. Full-time medical services may be provided on the premises. It may be a component of a senior care facility. See Sec. 5D.2.4.B. (Supportive Housing: Medical Care).
Slope: Slope is defined as the plane or incline of land, usually expressed as a percentage:
vertical distance
% slope = ----------------- x 100
horizontal distance
Small Species Tree: Small species tree is defined as a tree with a minimum 15-foot canopy spread at maturity.
Social Service Center: Social service center is defined as any facility that provides services for the benefit of the community, on a voluntary basis, including the following: employment services, job training, business incubation, youth development, educational services, medical and mental health care, substance abuse treatment, food aid, or other similar services. See Sec. 9.3.4.C.6. (Social Service Incentive Area).
Social Services: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.3.10. (Social Services), social services are defined as publicly accessible administrative services and governmental services that support public welfare through social programs. Social services may be operated by a government entity, a non-profit or a non-governmental organization, and includes welfare service, foster family services, day treatment, adult day care, special needs care, and all other non-residential community care facilities.
Soil Depth: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.6.4.D.4. (Soil Depth), soil depth is defined as the shortest vertical dimension of growing medium provided, for all portions of a planting area.
Soil Volume: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.6.4.D.5. (Soil Volume), soil volume is defined as the total volume of growing medium provided. Drainage layers and other elements located within a container or planter that are not growing medium are not included in the calculation of soil volume.
Solid Area: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.4.A.4. (Solid Area), solid area is defined as the portions of the perimeter planes that have a permanent structure or component physically obstructing the space from its surroundings. For the purpose of measuring the enclosure of a space, portions of the perimeter plane are considered solid area where a permanent structure or component is located within five feet of the perimeter plane, measured perpendicular to the perimeter plane and away from the subject space.
Solid Perimeter: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.4.A.6. (Solid Perimeter), solid perimeter is defined as the length of a perimeter of a space that consists of solid area for the entire height of the perimeter plane.
Soundstages & Backlots: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.8.4. (Soundstages & Backlots), soundstages & backlots are defined as any light industrial use providing facilities for the construction and use of indoor or outdoor filming sets and adjoining backlot facilities, including supporting office workspace, machine shops, and warehousing related to filming or film production.
Special Lot Line: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.12.C.3. (Special Lot Line), special lot line is defined as any lot line mapped as a special lot line on the Special Lot Line map, pursuant to Sec. 1.5.8. (Special Lot Line Map) and designated within an applied Form District (Part 2B.) or Frontage District (Part 3B.) that specifies standards for a special lot line.
Special Lot Line-Facing Facade: Special lot line-facing facade is defined as any facade which faces a special lot line.
Special Use Program: Special use program is defined as programs established for uses that require a detailed and prescriptive set of performance standards for safe, orderly, and efficient operation, in addition to any general use standards and supplemental standards that may be included in the Use District table. See Div. 5C.3. (Special Use Programs).
Special Yard: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.16.B.2. (Special Yard), special yard is defined as the area between a special lot line and an imaginary line running parallel to the special lot line. The imaginary line shall be drawn 15 feet back from the portion of the special lot line-facing facade nearest to the primary street lot line, measured perpendicularly to the lot line.
Special Zone: A Special Zone is a set of self-contained development regulations, adopted by ordinance, tailored and applied to a designated area having unique characteristics that may not lend themselves to established zoning districts and regulations. See Div. 8.3. (Special Zones).
Specific Plan: Specific Plan is defined as a zoning tool, adopted by ordinance, to provide detailed standards, and regulations, together with a map or description defining the locations where such standards, and regulations apply.
Specified Anatomical Parts: The same as defined in Chapter X. (Business Regulations), Sec. 103.01. (Definitions) of this Code.
Specified Sexual Activities: The same as defined in Chapter X. (Business Regulations), Sec. 103.01. (Definitions) of this Code.
Spread at Maturity: Spread at maturity is defined as the horizontal width of a shrub or the crown of a tree at maturity. See Sec. 4C.6.4.D.3. (Canopy Diameter, Spread, and Height at Maturity).
Standard Hillside Limited Street: Standard hillside limited street is defined as a street (public or private) with a minimum width of 36 feet, and paved to a minimum roadway width of 28 feet, as determined by the Bureau of Engineering.
Standards Package: Standards package is defined as a group of related development standards which is applied through Development Standards Districts (Part 4B.).
Stock Cooperative: The same as defined in California Business and Professions Code, Sec. 11003.2.
Storage, Indoor: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.7.4. (Storage, Indoor), storage, indoor is defined as the indoor holding of goods, merchandise, supplies, material, machinery, equipment, or other items for future use.
Storage, Indoor: General: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.7.4.A. (Storage, Indoor: General), storage, indoor: general is defined as any storage, indoor use that is incidental to another use. This use does not include storage, indoor: self-service for such uses see Sec. 5D.7.4.B. (Storage, Indoor: Self-Service). This use does not include indoor storage that functions as the primary use on a lot and is not incidental to another use, for such uses see Sec. 5D.8.6. (Wholesale Trade & Warehousing).
Storage, Indoor: Self-Service: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.7.4.B. (Storage, Indoor: Self-Service), storage, indoor: self-service is defined as any storage, indoor use that offers secure self-storage for household goods in individual rooms, compartments, lockers, or containers, to which clients bring goods for storage and retrieve them at any time during normal business hours.
Storage, Outdoor: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.7.5. (Storage, Outdoor), storage, outdoor is defined as the outdoor holding of goods, merchandise, supplies, material, machinery, equipment, vehicles, or other items for future use. Includes contractors' equipment storage yards and lumber yards.
Storage, Outdoor: Cargo Container: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.7.5.E. (Storage, Outdoor: Cargo Container), storage, outdoor: cargo container is defined as any storage, outdoor use involving the keeping of empty cargo containers. Storage, outdoor: cargo container may include storage of container chassis and commercial truck cabs, repair facilities, warehouses, and offices, incidental to the movement or storage of cargo containers. This use does not include the storage of cargo containers that are not empty, or uses which are part of any freight transfer, for such uses see Sec. 5D.5.3. (Freight Transfer Facility).
Storage, Outdoor: Donation Bin: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.7.5.D. (Storage, Outdoor: Donation Bin), storage, outdoor: donation bin is defined as any storage, outdoor use, involving a box, canister, receptacle, or other container that can be opened and closed, and is used for collecting salvageable personal property, including, but not limited to, clothing, shoes, books, and household items for periodic off-site processing or redistribution. For purposes of this definition, salvageable personal property shall not include recyclable materials not intended for re-use, including, but not limited to, newspapers, plastic, glass, aluminum, electronics, toxic or hazardous materials, and solid waste. For purposes of this definition, donation bins are limited dimensionally to 82-inches in height, 50-inches in depth, and 60-inches in width. For bins that are larger in size, see Sec. 5D.9.4.A. (Recycling Facility: Collection).
Storage, Outdoor: General: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.7.5.A. (Storage, Outdoor: General), storage, outdoor: general is defined as any storage, outdoor use that is in conjunction with another use. This use does not include the keeping of empty cargo containers, for such uses see Sec. 5D.7.5.E. (Storage, Outdoor: Cargo Container). This use does not include inactive large vehicles, for such uses see Sec. 5D.7.C. (Storage, Outdoor: Large Vehicle). This use does not include towing and storage for official motor vehicle impound, for such uses see Sec. 5D.7.5.F. (Storage, Outdoor: Official Motor Vehicle Impound). This use does not include inactive standard vehicles, for such uses see Sec. 5D.7.5.B. (Storage, Outdoor: Standard Vehicle).
Storage, Outdoor: Large Vehicle: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.7.5.C. (Storage, Outdoor: Large Vehicle), storage, outdoor: large vehicle is defined as the outdoor storage of large vehicles that are not actively used by the site's occupants, employees, or visitors. Large vehicles include vehicles possessing three or more axles, such as trailer trucks, construction vehicles, motor homes, and recreational vehicles as well as recreational boats and watercraft. This use includes storage of inoperable vehicles. This use does not include uses where vehicles are actively used by the site's occupants, employees, or visitors; for such uses see Sec. 5D.3.6. (Parking).
Storage, Outdoor: Official Motor Vehicle Impound: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.7.5.F. (Storage, Outdoor: Official Motor Vehicle Impound), storage, outdoor: official motor vehicle impound is defined as any vehicle towing and storage service that involves City-approved vendors that support the public safety mission of the Los Angeles Police Department and Department of Transportation.
Storage, Outdoor: Standard Vehicle: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.7.5.B. (Storage, Outdoor: Standard Vehicle), storage, outdoor: standard vehicle is defined as the outdoor storage of standard vehicles that are not actively used by the site's occupants, employees, or visitors. Standard vehicles include vehicles possessing two or fewer axles, such as cars, motorcycles, sport utility vehicles, pickup trucks, and vans. Includes storage of inoperable vehicles. This use does not include uses where vehicles are actively used by the site's occupants, employees, or visitors; for such uses see Sec. 5D.3.6. (Parking).
Stories: See story.
Story: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.10. (Story), story is defined as the portion of a building or structure included between the upper surface of a floor and the upper surface of the floor next above, except that the top most story is that portion of a building or structure included between the upper surface of a floor and the upper surface of the ceiling structure above.
Street Centerline: Street centerline is defined as a line that is aligned to the center of a street as established and maintained by the Department of Public Works, Bureau of Engineering.
Street Designation: Street designation is defined as the classification assigned to a roadway or other public right-of-way based on Citywide General Plan Circulation System maps of the Circulation Element for the purposes of providing dimensional and performance standards.
Street Frontage: For the purposes of Div. 4C.11. (Signs), street frontage is defined as the length of a line separating a lot from one street.
Street Lot Line: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.12.B.2. (Street Lot Line), street lot line is defined as any lot line that abuts a street right-of-way. Street lot lines include all primary street lot lines, side street lot lines, and alley lot lines.
Street Step-Back: Pursuant to Sec. 2C.6.1. (Street Step-Back), street step-back is defined as a step-like recess in the massing of a building that requires upper stories to be pushed back from the lower stories from the street.
Street Visible Area: For the purposes of Historic Preservation (Div. 13B.8.), street visible area is defined as any portion of the front, side, and rear facades that can be seen from any adjacent street, alley, or sidewalk, or that would be visible but are currently obstructed by landscaping, fencing, or freestanding walls. It also includes undeveloped portions of the lot where new construction would be visible from the adjacent street or sidewalk; facades that are generally visible from non-adjacent streets due to steep topography; or second stories visible over adjacent one story structures.
Street Wall: Street wall is defined as the condition created along a street by the fronts and consistent setbacks of buildings, and enhanced by the continuity and the height of the buildings.
Street Yard: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.16.C.2. (Street Yard), street yard is defined as a category of yards referring to all yards that abut a street right-of-way including front yards and side street yards.
Street-Facing Entrance: Pursuant to Sec. 3C.5.1. (Street-Facing Entrance), street-facing entrance is defined as a door providing access from the public realm to the interior of a building.
Street-Facing Facade: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.6.D. (Street-Facing Facade), street-facing facade is defined as the portions of any frontage applicable facade, pursuant to Sec. 3A.2.2.C.2. (Frontage Applicable Facades), having no permanent structure (not including fences or walls) located between the building facade and a street lot line or special lot line.
Structural Floor: Structural floor is defined as the assembly of building components that compose a floor, which includes any structural members, subfloor, and similar elements. Structural floor does not include finish or underlayment materials such as carpets, tiles, or membranes.
Structural Modification: Structural modification is defined as any change to the existing load-bearing members of a building or structure, including bearing walls, columns, beams, or girders.
Structure: Structure is defined as any constructed object more than 30 inches in height. For constructed objects 30 inches or lower in height, see flatwork.
Structure Footprint: See building footprint.
Subdivider: The same as defined in California Government Code, Sec. 66423. (Subdivider).
Subdivision: The same as defined in California Government Code, Sec. 66424. (Subdivision). Subdivision includes a stock cooperative project.
Subdivision Approval: Subdivision approval is defined as any approval under Div. 13B.7. (Division of Land).
Subdivision Committee: Pursuant to Sec. 13B.7.1.D. (Subdivision Committee), subdivision committee is defined as an advisory committee composed of the following officers of the City or their duly authorized representatives: the City Engineer; the Superintendent of Building; the Chief Engineer of the Department of Fire; the Chief Engineer and General Manager of the Department of Water and Power; the General Manager of the Department of General Services; the General Manager of the Department of Recreation and Parks; the General Manager of the Department of Transportation; and the Director of the Bureau of Street Lighting of the Department of Public Works.
Subdivision Design: Subdivision design is defined as a set of design features, elements, and infrastructure incorporated into a subdivision including: street alignments, grades and widths; drainage and sanitary facilities and utilities, including alignments and grades; location and size of all required easements and right-of-ways; fire roads and firebreaks; lot and size configuration; traffic access; grading; dedication of land for park and recreation purposes; and such other specific requirements in the General Plan and configuration of the entire subdivision as may be necessary or convenient to insure conformity to or implementation of the General Plan or any adopted Specific Plan.
Subdivision Improvement: The same as defined in California Government Code, Title 7. (Planning and Land Use), Sec. 66419. (Improvement). For standards to subdivision improvements see Sec. 11.3.3. (Subdivision Improvements).
Subdivision Map Act: The Subdivision Map Act, California Government Code, Title 7. (Planning and Land Use), Div. 2. (Subdivisions), commencing with California Government Code, Sec. 66410.
Subject Use: As used in Article 5. (Use), a "subject use" refers to a use that is subject to applicable use rules, permissions, standards, supplemental findings, or special use programs.
Substandard Hillside Limited Street: Substandard hillside limited street is defined as a street which does not meet the minimum requirements of a standard hillside limited street (public or private), because it has a width less than 36 feet or is paved to a roadway width of less than 28 feet, as determined by the Bureau of Engineering.
Supergraphic Sign: Supergraphic sign is defined as a sign, consisting of an image projected onto a wall or printed on vinyl, mesh or other material, with or without written text, supported and attached to a wall by an adhesive, by using stranded cable and eye-bolts, or with other materials and methods, and that does not comply with the following provisions of this Zoning Code (Chapter 1A): Sec. 4C.11.6.C.9. (Projecting Signs), Sec. 4C.11.6.C.5. (Marquee Signs), Sec. 4C.11.2. (Temporary Signs), Sec. 4C.11.1.E.2. (Original Art Murals, Vintage Original Art Murals and Public Art Installations).
Superintendent: Pursuant to Sec. 13B.10.3.A.2. (Definitions), Superintendent is defined as the Superintendent of Building or his or her authorized representative.
Supplemental District: Supplemental District is defined as a limited set of topic-specific development regulations, adopted by ordinance, and is indicated in a third zoning bracket in the zone string, and applied to a designated area in order to establish additional regulations that build upon and enhance regulations applied through zoning districts. See Div. 8.2. (Supplemental Districts).
Supportive Housing: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.2.4. (Supportive Housing), supportive housing is defined as a residential use that provides housing accommodations and support services on a voluntary basis to residents on an ongoing basis.
Supportive Housing: General: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.2.4. (Supportive Housing: General), supportive housing: general is defined as a residential use with no limit on length of stay for persons with low incomes and/or who have one or more disabilities who may require support from on-site or off-site supportive services for daily living. Eligible populations may include seniors, children within the foster care system, emancipated minors, families with children, elderly persons, young adults aging out of the foster care system, individuals exiting from institutional settings, individuals receiving rehabilitation or mental health support, veterans, and persons or families experiencing homelessness. The housing accommodations are linked to on-site or off-site supportive services, including, but not limited to: subsidized, permanent housing; intensive case management; medical or mental health care; substance abuse treatment; employment services; benefits advocacy; or other services or service referrals necessary to obtain and maintain housing. Any floor area used for office workspace accommodating the administration of supportive services shall be incidental to the residential use. Medical services shall not be provided on the premises, unless otherwise permitted by the applied Use District. Supportive housing: general includes a residential community care facility, assisted living, and permanent supportive housing. Residential uses with six or fewer beds shall be classified as a dwelling rather than supportive housing: general. This use does not include non-residential community care facilities, for such uses see Social Services (Sec. 5D.3.10.).
Supportive Housing: Medical Care: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.2.4.B. (Supportive Housing: Medical Care), supportive housing: medical care is defined as a residential use of long, and short-term occupation, which may be licensed by the California Department of Health, to provide 24-hour non-acute medical services and supportive care on the premises. Supportive housing: medical care includes congregate living health facilities, skilled nursing homes, residential mental health facilities, and hospice care. Any floor area used for office workspace accommodating the administration of medical services and supportive care shall be incidental to the residential use. Supportive housing: medical care facilities may include dwelling units, common dining areas, or other community rooms.
Supportive Housing: Transitional: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.2.4.C. (Supportive Housing: Temporary), Supportive housing: temporary is defined as a facility providing temporary housing accommodations or services, including low barrier navigation, to persons or families experiencing homelessness. Supportive housing: temporary may provide housing for persons or families experiencing homelessness for a time period not to exceed six months within a calendar year. Supportive housing: temporary shall be provided by a government agency or private non-profit organization which provides, or contracts with recognized community organizations to provide, emergency or temporary shelter or services for persons or families experiencing homelessness.
Supportive Services: Supportive services are defined as services that are provided on a voluntary basis to residents of supportive housing or transitional housing, including, but not limited to, intensive case management, medical and mental health care, substance abuse treatment, employment services, benefits advocacy, and other services or service referrals necessary to obtain and maintain housing. See Sec. 9.4.1. (Permanent Supportive Housing Incentive Program).
Surrounding Grade: Surrounding grade is defined as the elevation of finished grade measured along the perimeter of an object, assembly, or structure.
Surveyed Historic Resource: Surveyed historic resource is defined as any building, structure, object, site, landscape, or natural feature identified through an historic resources survey as potentially eligible for listing as either an individual resource, or as a contributor to a historic district, under a local, state or federal designation program, including but not limited to listing in the National Register of Historic Places or California Register of Historical Resources, or designation as a historic-cultural monument or as an Historic Preservation Overlay Zone. This term does not include a non-contributor to an eligible historic district.
Surveyor: Surveyor is defined as a licensed land surveyor authorized to practice in California.
Sustainable Energy Systems: Sustainable energy systems is defined as any equipment which uses renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, to generate electricity, heating or cooling.
Symmetrical Lite Pattern: Pursuant to Sec. 3D.9.1.C.5. (Symmetrical Lite Pattern), symmetrical lite pattern is defined as window panes that are arranged or designed so that the left-side of the window composition is a mirror image of the right-side of the window composition.
T
Target Population: For the purposes of Article 9. (Public Benefit Systems), target population is defined as persons with qualifying lower incomes who:
-
Have one or more disabilities, including mental illness, HIV or AIDS, substance abuse, or other chronic health condition, and are homeless as defined by any Los Angeles City, Los Angeles County, State of California, or federal guidelines; or
-
Are chronically homeless, as defined by any Los Angeles City, Los Angeles County, State of California, or federal guidelines.
Targeted Planting Area: Targeted planting area is defined as a planting area with boundaries established pursuant to Sec. 1.5.5.B. (Boundaries).
Targeted Planting List: Targeted planting list is defined as the document containing planting requirements established to implement the Targeted Planting Areas Map. See Sec. 1.5.5. (Targeted Planting Map).
Temporary Construction Wall: Temporary construction wall is defined as a temporary solid fence or barrier of wood or similar material that provides protection for pedestrians and is erected and maintained on the perimeter of a construction or demolition site, which may be required by Chapter IX. (Building Regulations), Sec. 91.3306. (Protection of Pedestrians) of this Code.
Temporary Sign: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.11.2. (Temporary Signs), temporary sign is defined as any sign that is to be maintained for a limited duration, including paper signs, posters, pennants, banners, ribbons, streamers, spinners, and other signs that are not permanently affixed to the ground or building.
Temporary Use: Pursuant to Sec.14.2.15.B.7. (Temporary Use), temporary use is defined as a use of a building or lot with any use defined in Part 5D. (Use Definitions) that does not exceed 180 days and meets the requirements of Chapter IX. (Building Regulations), Sec. 91.106.1.3. (Temporary Permits) of this Code.
Tentative Tract Map: Tentative tract map is defined as a map made for the purpose of showing the design of a proposed subdivision creating five or more parcels, five or more condominiums, or five or more units in a community apartment project or stock cooperative and prepared pursuant to Sec. 11.2. (Tentative Tract Maps).
Through Lot: Through lot is defined as a lot abutting two parallel or approximately parallel streets, a lot situated at the intersection of two streets having an angle of intersection of 35 degrees or less, or a lot abutting three or more streets. A through lot does not include those lots abutting a street and also abutting a navigable public canal or waterway parallel or approximately parallel to said street.
Tract Map: Tract map is defined as either a tentative tract map or final tract map.
Transient: For the purposes of the Home-Sharing Program (Sec. 5C.3.2.), transient shall have the same meaning as that term is defined in Chapter II. (Licenses, Permits, Business Regulations), Sec. 21.7.2. (Definitions) of this Code.
Transit Stop/Major Employment Center: For purposes of Sec. 9.2.1. (Density Bonus) transit stop/major employment center is defined as any one of the following:
-
A station stop for a fixed transit guideway or a fixed rail system that is currently in use, or whose location is proposed and for which a full funding contract has been signed by all funding partners, or one for which a resolution to fund a preferred alignment has been adopted by Metro; or
-
A Metro rapid bus stop located along a Metro rapid bus route; or, for a housing development project consisting entirely of restricted affordable units, any bus stop located along a Metro rapid bus route; or
-
The boundaries of the following three major economic activity areas, identified in the General Plan Framework Element: Downtown, LAX, and the Port of Los Angeles; or
-
The boundaries of a college or university campus with an enrollment exceeding 10,000 students.
Transition Screen: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.8.2. (Transition Screens), transition screen is defined as a device or combination of elements along a common lot line that conceals, obstructs or protects abutting lots from impactful uses, activities, or site elements.
Transitional Housing: Transitional housing is defined as a building where housing linked to supportive services is offered, usually for a period of up to 24 months, to facilitate movement to permanent housing for persons with low incomes who may have one or more disabilities, and may include but are not limited to, adults, emancipated minors, families with children, elderly persons, young adults aging out of the foster care system, individuals exiting from institutional settings, veterans, and persons or families experiencing homelessness.
Transmit: See transmitted.
Transmitted: Transmitted is defined as a notification of a decision in writing, by mail, or electronically. See Sec. 13A.2.5.D. (Transmittal).
Transparent Area: Pursuant to Sec. 3C.4.1. (Transparent Area), transparent area is defined as the amount of transparent area on a building facade.
Transportation Demand Management: Transportation demand management is defined as the modification of travel behavior through programs of incentives, services, and policies, including encouraging the use of alternatives to single-occupant vehicles such as public transit, cycling, walking, carpooling/vanpooling, and changes in work schedule that move trips out of the peak period or eliminate them altogether (such as telecommuting or compressed work weeks).See Div. 4C.5. (Transportation Demand Management).
Transportation Use: Pursuant to Div. 5D.5. (Transportation Uses), transportation use is defined as uses that facilitate major modes of transportation for the loading or unloading of passengers and freight.
Trash Chute: Trash chute is defined as any vertical smooth shaft used to convey rubbish, trash, or garbage from the upper floors of a building to a trash storage bin or room at the bottom end of the chute.
Tree Expert: Tree expert is defined as a person with at least four years of experience in the business of transplanting, moving, caring for, and maintaining trees and who is a certified arborist with the International Society of Arboriculture, and who holds a valid California license as an agricultural pest control advisor; or a landscape architect; or a registered consulting arborist with the American Society of Consulting Arborists.
Trip Reduction: For the purposes of Article 9. (Public Benefit Systems) trip reduction is defined as the reduction in the number of work-related trips made by single-occupant vehicles.
U
Uncovered: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.2.A.2. (Uncovered), uncovered is defined as an instance where 25 percent or more of a space or structure's area is open to the sky. Areas containing overhead, non-solid structures, such as lattice and pergolas, may be considered uncovered provided that 25 percent or more of their area is open to the sky.
Underground Parking: Underground parking is defined as motor vehicle use areas located below the finished floor elevation of the ground story.
Underground Structure: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.5.A.1.j. (Underground Structures), underground structure is defined as a covered structure located entirely below finished grade. Examples of underground structures include, but are not limited to: cellars, basements, underground parking structures, stormwater storages, or cisterns.
Unenclosed: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.4.A.2. (Unenclosed), unenclosed is defined as an instance when the perimeter of a space has an enclosure of less than 66.7 percent.
Unified Development: Unified development is defined as a development consisting of multiple lots within a common site plan which is unified by a combination of functional linkages, such as pedestrian or vehicular connections, common architectural and landscape features which constitute distinctive design elements of the development, and when viewed from adjoining streets appears to be a consolidated whole. A unified development may include lots that abut or are separated only by an alley or are located across the street from any portion of each other. See Sec. 14.2.1. (Lot) for clarification on lot ties.
Uniformity Ratio: Uniformity ratio is defined as a ratio of the average illumination to minimum illumination.
Upper Story: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.10.D. (Upper Story), upper story is defined as any story of a building located above the ground story.
Upper Story Facade: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.10.E. (Upper Story Facade), upper story facade is defined as the portions of the exterior building envelope at the perimeter of each upper story for the full height of the story.
Upper Story Height: Pursuant to Sec. 3D.5.2. (Upper Story Height), upper story height is defined as the floor-to-floor height of any story of a building located above the ground story.
Urbanized Area: Pursuant to Sec. 8.2.4.B.3.b. (Urbanized Area), urbanized area is defined as all land in the City, except land in the Heavy Industrial 1 Use District, and land which has been determined to be non-urbanized area by the City Planning Commission or City Council, or land located in the Los Angeles City Oil Field Area.
Use: Use is defined as the purpose for which land or a building is arranged, designed, or intended, or for which land or a building is, or may be, occupied or maintained.
Use Category: Use category is defined as a group of use groups.
Use District: Use District is defined as the fourth component in a zone string established in Part 5B. (Use Districts), which regulates land uses by assigning permission levels for defined uses as well as citing applicable performance standards, supplemental procedures for conditional uses, and special use programs.
Use District Table: Use District table is defined as a table provided for each Use District established in Part 5B. (Use Districts) that contains a list of uses and their assigned permission levels, along with any applicable performance standards, conditional use procedures, and special use programs that apply to uses within a Use District.
Use Group: Use group is defined as a group of individual uses with common use characteristics and similar activities.
Use Modification: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.15.B.6. (Use Modification), use modification is defined as a change of use or an intensification of use.
Used Vehicle Sales Area: Pursuant to Sec. 13B.10.4. (Annual Inspection Monitoring (Type 2)), used vehicle sales area is defined as an area or lot where any type of used motor vehicle or trailer is displayed for sale.
Utilities: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.3.11. (Utilities), utilities is defined as utility infrastructure as a primary use of land, necessary for the public provision of services such as water, sewer, power, or communications. For the purposes of this definition, utilities uses exclude the following off-site systems: transmission lines, pipes, or other systems for conveying and transmitting services within utility easements, as those systems are not regulated as a use of land by Article 5. (Use).
Utilities: Major: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.3.11.B. (Utilities: Major), utilities: major is defined as utility infrastructure that requires significant health, safety, and environmental precautions due to potential adverse impacts immediate surroundings, and requires on-site personnel. Utilities: major include non-solar power generation facilities, wastewater treatment, and water supply treatment.
Utilities: Minor: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.3.11.A. (Utilities: Minor), utilities: minor is defined as utility infrastructure that does not require significant health, safety, and environmental precautions, and do not require on-site personnel. Utilities: minor includes renewable energy generation, including wind turbines, geothermal systems, and solar photovoltaic systems serving no more than 10 different lots with supporting on-site storage, control and transmission equipment, storm water retention or detention ponds, aeration and septic systems, reservoirs, lift stations, water supply wells and water tanks or towers, telecommunications switching facilities, and electrical substations.
Utilities: Solar Energy Facility: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.3.11.C. (Utilities: Solar Energy Facility), utilities: solar energy facility is defined as utility infrastructure that generates energy for the general public using a solar photovoltaic system primarily for off-site use or sale serving 11 or more lots.
Utilities: Wireless Facility, Freestanding: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.3.11.D. (Utilities: Wireless Facility, Freestanding), utilities: wireless facility, freestanding is defined as a freestanding device or system including a monopole, tower, or antenna for the transmitting or receiving of electromagnetic signals, including, but not limited to, radio waves and microwaves, for cellular technology, personal communications services, mobile services, paging systems and related technologies. Facilities include antennas, microwave dishes, parabolic antennas and all other types of equipment used in the transmission and reception of such signals; structures for the support of such facilities, associated buildings or cabinets to house support equipment, and other accessory structures or development. A utilities: wireless facility, freestanding is a type of telecommunications facility.
Utilities: Wireless Facility, Rooftop: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.3.11.E. (Utilities: Wireless Facility, Rooftop), utilities: wireless facility, rooftop is defined as a device or system that is mounted on a building or structure rooftop for the transmitting or receiving of electromagnetic signals, including, but not limited to, radio waves and microwaves, for cellular technology, personal communications services, mobile services, private antennas, paging systems and related technologies. Facilities include antennas, microwave dishes, parabolic antennas and all other types of equipment used in the transmission and reception of such signals; structures for the support of such facilities, associated buildings or cabinets to house support equipment, and other accessory structures or development. A utilities: wireless facility, rooftop is a type of telecommunications facility.
Utility Area: Utility area is defined as any area containing mechanical equipment or utility equipment.
Utility Equipment: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.5.A.1.i. (Utility Equipment), utility equipment is defined as equipment related to publicly-operated or utility-operated systems, including their related wires, conduits and pipes. Examples of utility equipment include, but are not limited to: hydrants, transformers, utility cabinets, water utility devices, cable television boxes, Internet boxes, or phone boxes.
V
Vacant Lot: Vacant lot is defined as a lot on which no building, temporary or permanent, is erected; or which has no uses of the land.
Vanpool: Vanpool is defined as a vehicle carrying six or more persons to and from work on a regular schedule, and on a prepaid basis.
Variance: Pursuant to Sec. 13B.5.3. (Variance), variance is defined as granted relief from a standard or regulation in this Chapter or Chapter I. (General Provisions and Zoning) on the basis of hardship or difficulties.
Vegetation: For purposes of Sec. 14.1.5. (Encroachments) vegetation is defined as living organisms, absorbing water and organic substances through its roots and synthesizing nutrients. Examples of vegetation include, but are not limited to: trees, shrubs, flowers, herbs, vegetables, grasses, ferns, or moss.
Vehicle: Vehicle is defined as anything used to transport people or goods, including automobiles, vans, trucks, buses, and motorcycles, bicycles, or any other form of micro-mobility.
Vehicle Entry Restriction Device: Vehicle entry restriction device is defined as any device, such as mechanical gates or ticket dispensers, restricting ingress vehicle traffic during operating hours.
Vertical Band Articulation: Pursuant to Sec. 3D.6.4. (Vertical Band Articulation), vertical band articulation is a continuous band of material running vertically up a facade.
Vertical Circulation: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.5.B.1.d. (Vertical Circulation), vertical circulation is defined as enclosed and covered structures used for building circulation and rooftop access. Examples of vertical circulation may include, but are not limited to: elevator rooms and associated equipment, and stair accesses to a roof.
Vertical Encroachment: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.5.B. (Vertical Encroachments), vertical encroachment is defined as a structure or assembly that extends vertically into a space where structures are typically prohibited.
Very High Fire Hazard Severity Zone: The Very High Fire Hazard Severity Zone (VHFHSZ) are determined through the Local Hazard Mitigation Plan (LHMP) wildfire hazard assessment, based on boundaries established by the Los Angeles Fire Department in accordance with state law.
Very Low Income Household: A very low income household is a household whose annual income, adjusted for family size, does not exceed 50 percent of the area median income as designated for this category in California Health and Safety Code, Sec. 50105.
Vesting Preliminary Parcel Map: Vesting preliminary parcel map is defined as a preliminary parcel map for any land division that has printed conspicuously on its face the words "Vesting Preliminary Parcel Map" and is characterized by certain rights to proceed with development when filed and processed in accordance with Div. 13B.7. (Division of Land).
Vesting Tentative Tract Map: Vesting tentative tract map is defined as a tentative tract map for any land division that has printed conspicuously on its face the words “Vesting Tentative Tract Map” and is characterized by certain rights to proceed with development when filed and processed in accordance with Div. 13B.7. (Division of Land).
Vintage Original Art Mural: Vintage original art mural is defined as an original art mural that existed prior to October 12, 2013 (the operative date of Ord. No. 182,706). See Div. 4C.11. (Signs).
Visual Light Transmittance: Visual light transmittance is defined as the amount of light in the visible portion of the spectrum that passes through a glazing material as defined in manufacturer specifications.
Visual Obstruction: Visual obstruction is defined as any opaque object, assembly, or structure that obscures visibility through a transparent area, on the interior side of the transparent area of a building facade. See Sec. 3C.4.1. (Transparent Area).
W
Walking Distance: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.3.A.2. (Walking Distance), walking distance is defined as the distance measured as the most direct path of travel for a pedestrian.
Wall: Wall is defined as a constructed vertical barrier erected to enclose, screen, or separate areas. A wall differs from a fence in having a solid foundation along its whole length.
Wall Sign: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.11.6.C.12. (Wall Sign), wall sign is defined as a sign on the wall of a building or structure, with the exposed face of the sign in a plane approximately parallel to the plane of the wall, that has been attached to, painted on, or erected against the wall, projected onto the wall, or printed on any material which is supported and attached to the wall by an adhesive or other materials or methods.
Waste Enclosure: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.5.A.1.h. (Waste Enclosure), waste enclosure is defined as waste areas and their required screening structures. Examples of waste enclosures include, but are not limited to: trash compactors, garbage, recycling, or food waste.
Waste Facility: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.9.5. (Waste Facility), waste facility is defined as any heavy industrial use involving the receipt, storage, separation, conversion, combustion, processing of solid waste, transfer of waste directly from small to larger vehicles for transport, or operation as a landfill. This use includes facilities involved in the transfer, processing, and transformation of organic waste, construction and demolition debris, inert material, solid waste.
Waste Facility: Hazardous Waste: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.9.5.B. (Waste Facility: Hazardous Waste), waste facility: hazardous waste is defined as any waste facility use involving the storage, treatment, and disposal of hazardous waste, as defined in the California Health and Safety Code, Sec. 25117.1. (Definitions).
Waste Facility: Organic Waste: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.9.5.A. (Waste Facility: Organic Waste), waste facility: organic waste is defined as any waste facility use that receives any material that comes from a plant or animal and is biodegradable, for chipping and grinding, composting, curing, mulching or similar processing methods. This use does not include any chipping and grinding, composting, curing, or mulching conducted as part of the maintenance of landscaped areas associated with any public & institutional uses or open space & recreation uses.
Waste Facility: Solid Waste: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.9.5.C. (Waste Facility: Solid Waste), waste facility: solid waste is defined as any waste facility use that does not involve any storage, treatment, and disposal of hazardous waste, or that does not exclusively receive organic waste. For such uses, see Sec. 5D.9.5.B. (Waste facility: Hazardous Waste) and Sec. 5D.9.5.A. (Waste Facility: Organic Waste).
Water Supply: For the purposes of Div. 13B.7. (Division of Land), water supply is defined as the water system supply and distribution facilities necessary to provide a reliable and adequate water supply for private use and public fire protection purposes.
Weighted Solid Perimeter: Pursuant to Sec. 14.2.4.A.7. (Weighted Solid Perimeter), weighted solid perimeter is defined as the length of the perimeter plane weighted by the percent of the perimeter plane area that is composed of solid area, for each perimeter plane where perimeter planes consist of a mix of solid area and non-solid area.
Wetland: For the purposes of Sec. 13B.9.2. (Coastal Development Permit (Post-Certification)), wetland is defined as lands within the Coastal Zone, which may be covered periodically or permanently with shallow, water and include saltwater marshes, freshwater marshes, open or closed brackish water marshes, swamps, mudflats and fens.
Wholesale Trade & Warehousing: Pursuant to Sec. 5D.8.5. (Wholesale Trade & Warehousing), wholesale trade & warehousing is defined as any light industrial use facility primarily used for the high volume storage of goods for sale in large quantities primarily to businesses, or the storage of products intended for consolidation and distribution to manufacturers, wholesalers, retailers, or end users. This use includes seasonal inventory storage, distribution centers, fulfillment centers, cold storage facilities, and facilities housing goods for sale in bulk to businesses or institutions. This use does not include the sale of goods directly to consumers; for such uses see Sec. 5D.6.12. (Retail). This use does not include the transshipment of freight between different modes of transport, such as rail to trucking transport; for such uses see Sec. 5D.5.3. (Freight Transfer Facility).
Whorl: Whorl is defined as the arrangement of three or more buds, leaves, flowers, or twigs at the same node.
Window: Window is defined as an operable or inoperable opening constructed in a wall that admits light or air into an enclosure and is often framed and spanned with glass or other translucent material.
Window Assembly: Window assembly is defined as a manufactured assembly of a frame, sash, glazing, and necessary hardware, made to fit a window opening.
Window Display: Window display is defined as a display, behind a window, along the facade of a building exhibiting items or advertisements designed to attract the attention of passersby, including window signs.
Window Frame: Window frame is defined as the fixed frame of a window, consisting of two jambs, a head, and a sill.
Window Opening: Window opening is defined as an opening in the wall of a building for admitting light and air, usually fitted with a frame in which are set operable sashes containing panes of glass.
Window Recession: Pursuant to Sec. 3D.9.1.C.3. (Window Recession), window recession is defined as the depth that a window is set back from the surrounding facade.
Window Sash: Window sash is defined as the fixed or movable framework of a window or door in which panes of glass are set.
Window Sign: Pursuant to Sec. 4C.11.6.C.13. (Window Sign), window sign is defined as a sign, except for a supergraphic sign, that is attached to, affixed to, leaning against, or otherwise placed within six feet of a window or door in a manner so that the sign is visible from outside the building.
Wood Waste: Wood waste is defined as any discarded untreated or unpainted wood material, and includes pallets, plywood, and other construction-related scrap lumber, stumps, and tree trimmings.
X
Y
Yard: Yard is defined as all portions of a lot between exterior walls of a building and a property line. See Sec.14.2.16. (Yards).
Yard Sign: Pursuant to Sec. 4C. 11.6.C.14. (Yard Sign), yard sign is defined as a small sign placed in a yard or other amenity space.
Z
Zone String: Pursuant to Sec. 1.3.1. (Zone String), zone string is defined as the combination of zoning districts applied to a lot including, Form District (Part 2B.), Frontage District (Part 3B.), Development Standards District (Part 4B.), Use District (Part 5B.), and Density District (Part 6B.).
Zoning Administrator: Zoning Administrator is defined as the Chief Zoning Administrator or an Associate Zoning Administrator. The Director may appoint the Zoning Administrator to act as the Director’s designee or as a Hearing Officer for the Director. See Sec. 13A.1.7. (Zoning Administrator).
Zoning District: Zoning district is defined as all zoning districts that compose a zone string including Form Districts (Part 2B.), Frontage Districts (Part 3B.), Development Standards Districts (Part 4B.), Use Districts (Part 5B.), and Density Districts (Part 6B.). Pursuant to Sec. 1.3.1.B. (Zoning Districts), the term zoning district does not include Specific Plans, Supplemental Districts, or Special Zones.